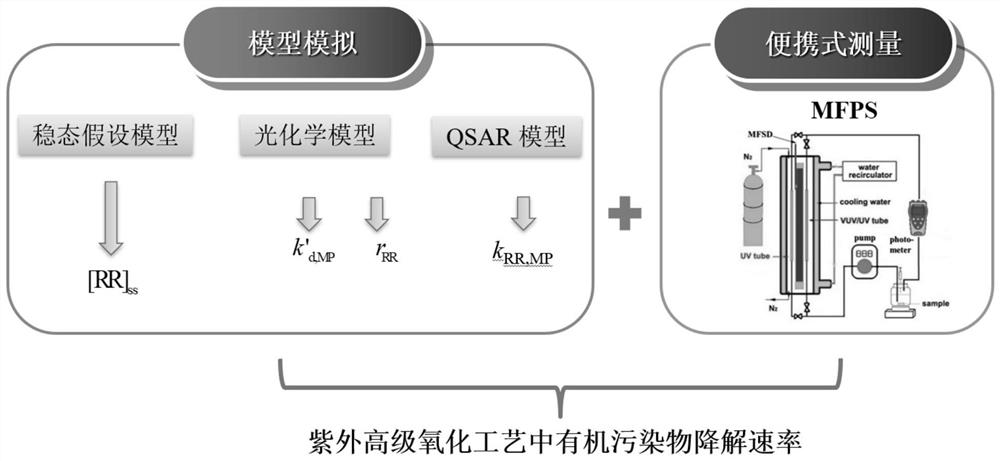
A prediction method for the degradation rate of organic pollutants in the actual water UV advanced oxidation process
An advanced oxidation and degradation rate technology, applied in the direction of testing organic pollutants in water, water pollutants, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of heavy workload, long time and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
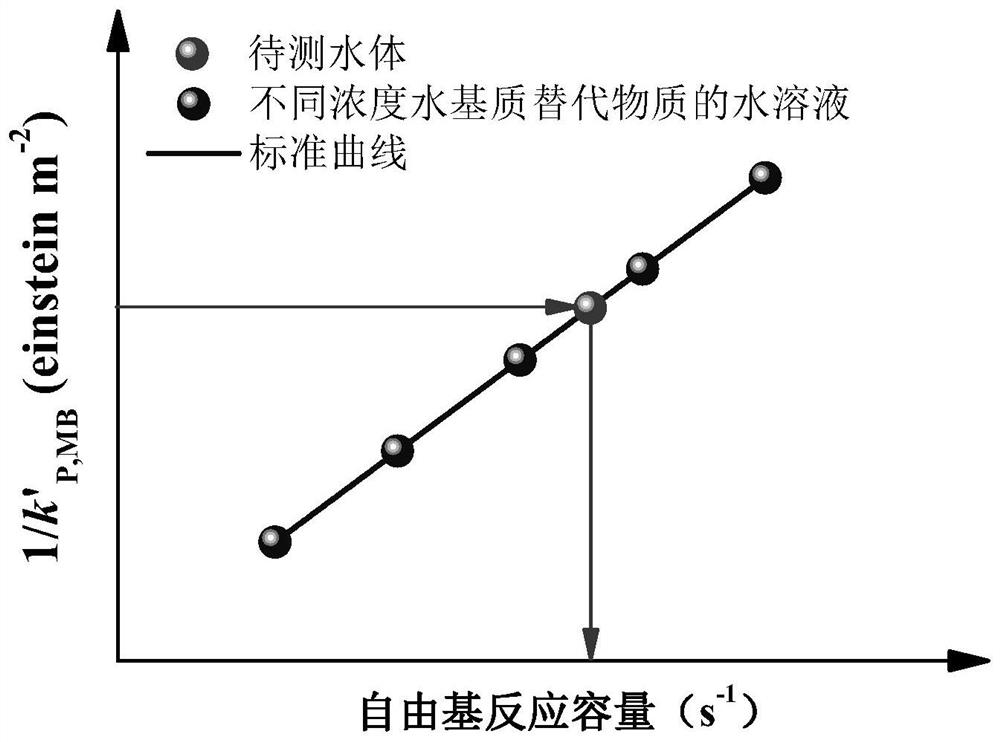
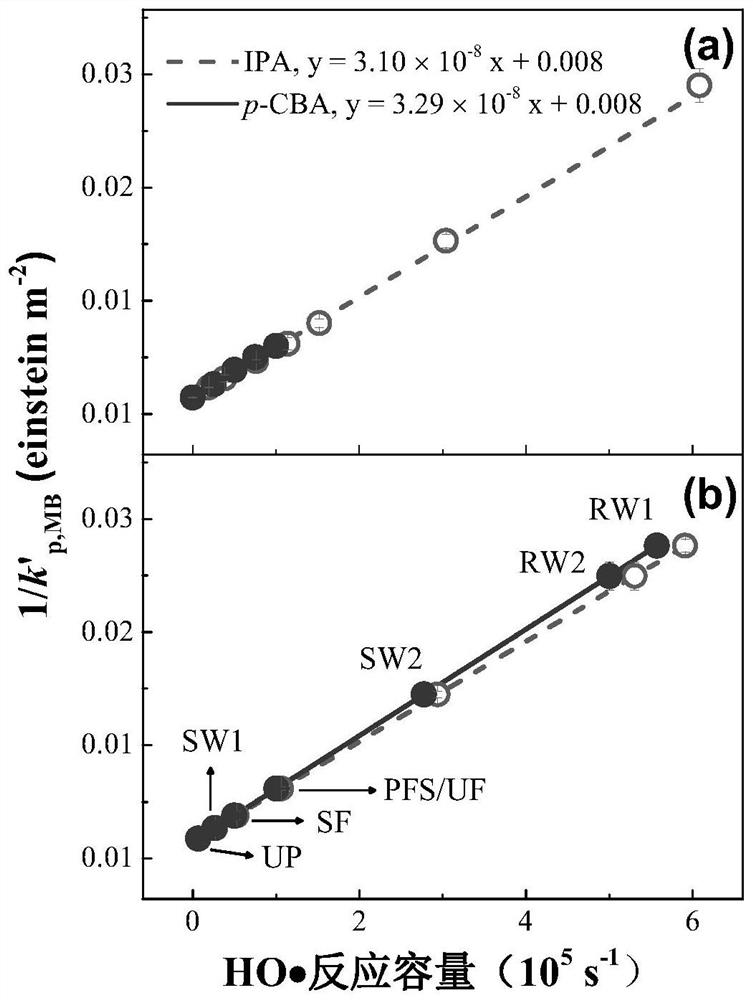
[0160] Example 1. Measure the free radical reaction capacity of different actual water bodies and the UV / H of actual water bodies 2 O 2 Prediction and experimental verification of degradation rate of organic pollutants in process treatment
[0161] (1) Use the water matrix substitute substance IPA or p-CBA to simulate the background water composition, and add the probe MB to the [IPA] 0 = 0, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 160, 320 μM or [p-CBA] 0 =0, 5.0, 10, 15, 20 μM in aqueous solutions of different concentrations of water-based substitutes, probes [MB] 0 =5mgL -1 , obtain the initial system of simulated water body; use UV / H 2 O 2 (MFPS as photoreactor, [H 2 O 2 ] 0 = 25mg L -1 , the UV intensity is 3.98×10 -4 einstein m -2 s -1 , the water circulation temperature is 25 °C) process to degrade the initial system of the simulated water body, and the concentration of MB in the solution of different concentrations of the water matrix substitute substance during the degradation...
Embodiment 2
[0172] Embodiment 2, actual water body UV / Cl 2 The organic pollutant degradation rate prediction and experimental verification in the process treatment are tested according to the method in Example 1, and the test conditions and results are as follows:
[0173] (1) Use the water matrix substitute substance BA to simulate the background water composition, and add the probe MB to the [BA] 0 = 0, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 μM in aqueous solutions of different concentrations of water-based substitutes, 0.5 mM nitrobenzene was added to mask HO · , probe [MB] 0 =5μmol L -1 , obtain the initial system of simulated water body; use UV / Cl 2 (MFPS as photoreactor, [Cl 2 ] 0 =5mgL -1 , the UV intensity is 3.98×10 -4 einstein m -2 s -1 , the water circulation temperature is 25 °C) process to degrade the initial system of the simulated water body, and the concentration of MB in the solution of different concentrations of the water matrix substitute substance during the degradation process ...
Embodiment 3
[0184] Example 3. Actual water UV / S 2 O 8 2- Prediction and experimental verification of degradation rate of organic pollutants in process treatment
[0185] Test according to the method in Example 1, and the test conditions and results are as follows:
[0186] (1) Use the water matrix substitute substance BA to simulate the background water composition, and add the probe MB to the [BA] 0 = 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40 μM in aqueous solutions of various concentrations of water-based substitutes, with 0.5 mM nitrobenzene added to mask HO · , probe [MB] 0 =5μmol L -1 , obtain the initial system of simulated water body; use UV / S 2 O 8 2- (MFPS as photoreactor, [S 2 O 8 2- ] 0 = 200mg L -1 , the UV intensity is 3.98×10 -4 einstein m -2 s -1 , the water circulation temperature is 25 °C) process to degrade the initial system of the simulated water body, and the concentration of MB in the solution of different concentrations of the water matrix substitute substance during the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com