Preparation method of CaSrNaA for adsorbing carbon dioxide under low pressure
A technology for adsorbing carbon dioxide and carbon dioxide, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problem of not explaining the influence of calcium ion content, and achieve the effect of increasing the adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
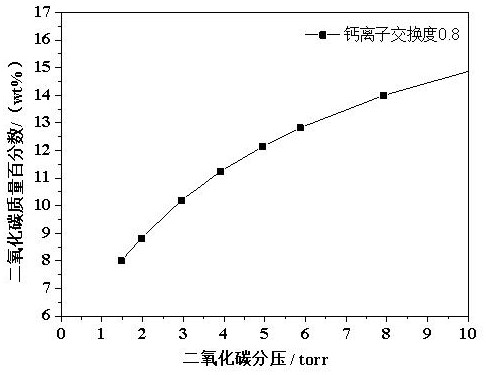
[0017] Example 1 Effect of Different Calcium Ion Exchange Degrees on Carbon Dioxide Adsorption by Molecular Sieves
[0018] Using 4A molecular sieve as raw material, calcium salt solution is used for ion exchange in aqueous solution. The adsorption capacity of carbon dioxide, the specific results are shown in Table 1.
[0019] Table 1 The effect of different calcium ion exchange degrees on the adsorption of carbon dioxide by molecular sieves under different pressures
[0020]
[0021] It can be seen from Table 1 that when the degree of calcium ion exchange is 0.7-0.9, the molecular sieve has the highest adsorption capacity for carbon dioxide under low pressure (2-6 torr). Excessively high calcium ion exchange degree will reduce the adsorption capacity of carbon dioxide.
Embodiment 2
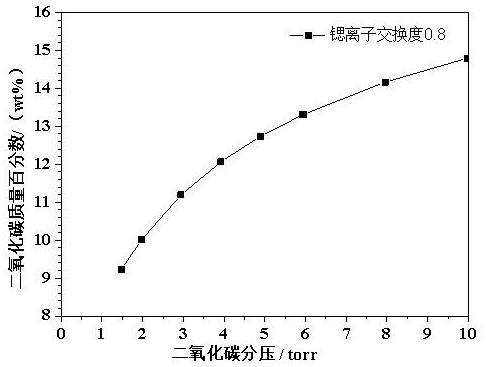
[0022] Example 2 Effects of different degrees of strontium ion exchange on the adsorption of carbon dioxide by molecular sieves
[0023] Using 4A molecular sieve as the raw material, the strontium salt solution is used for ion exchange in the aqueous solution. The adsorption capacity of carbon dioxide, the specific results are shown in Table 2.
[0024] Table 2 The effect of different strontium ion exchange degrees on the adsorption of carbon dioxide by molecular sieves under different pressures
[0025]
[0026] It can be seen from Table 2 that when the degree of strontium ion exchange is 0.7-0.8, the molecular sieve has the highest adsorption capacity for carbon dioxide under low pressure (2-6 torr). Excessively high strontium ion exchange degree will reduce the adsorption capacity of carbon dioxide.
Embodiment 3
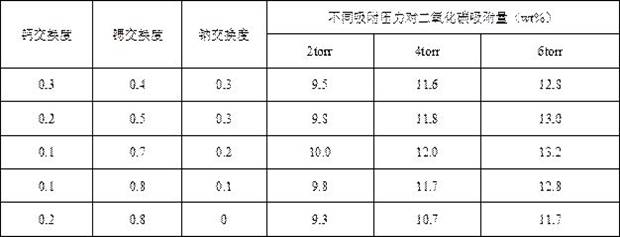
[0027] Example 3 Effects of different degrees of calcium and strontium ion exchange on the adsorption of carbon dioxide by molecular sieves
[0028] Using 4A molecular sieve as raw material, calcium salt and strontium salt solution are used for ion exchange in aqueous solution. The specific ion exchange degree is shown in Table 3. Then, an adsorption instrument is used to test the carbon dioxide adsorption capacity of the sample under low carbon dioxide pressure (2-6 torr). The specific results are shown in Table 3.
[0029] Table 3 Effects of different exchange degrees of calcium ions and strontium ions on the adsorption of carbon dioxide by molecular sieves under different pressures
[0030]
[0031] It can be seen from Table 3 that the adsorption capacity of molecular sieves for carbon dioxide under low pressure (2-6 torr) can be increased by using calcium ions and strontium ions to exchange molecular sieve samples. Higher calcium-strontium exchange degree and lower sod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com