Electromagnetic induction structure for locally heating tin source in superconducting cavity
A technology of electromagnetic induction and local heating, applied in ion implantation plating, coating, metal material coating process, etc., can solve the problem that superconducting cavity cannot be used in superconducting cavity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The experimental methods used in the following examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified.
[0037] The materials and reagents used in the following examples can be obtained from commercial sources unless otherwise specified.
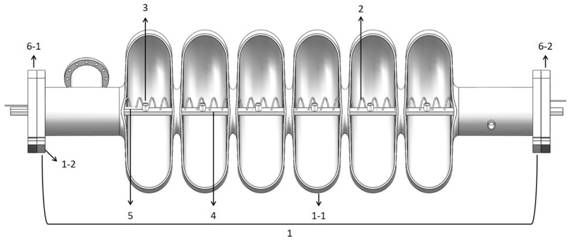
[0038] The structure diagram of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, an electromagnetic induction structure for locally heating the tin source inside the superconducting cavity will be described in detail below.
[0039] The superconducting cavity 1 in this illustration is a 650MHz ellipsoidal superconducting cavity with 6 accelerating units. The main body of the cavity is made of high-purity metal niobium with residual resistivity > 300, and the flange of the beam channel is made of niobium-titanium alloy. into, wherein the mass percentage of niobium is 45%.
[0040] The center diameter of the electromagnetic induction heating coil 2 is 40mm, the pitch is 30mm, and the number of turns is 40; the electromagnetic indu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com