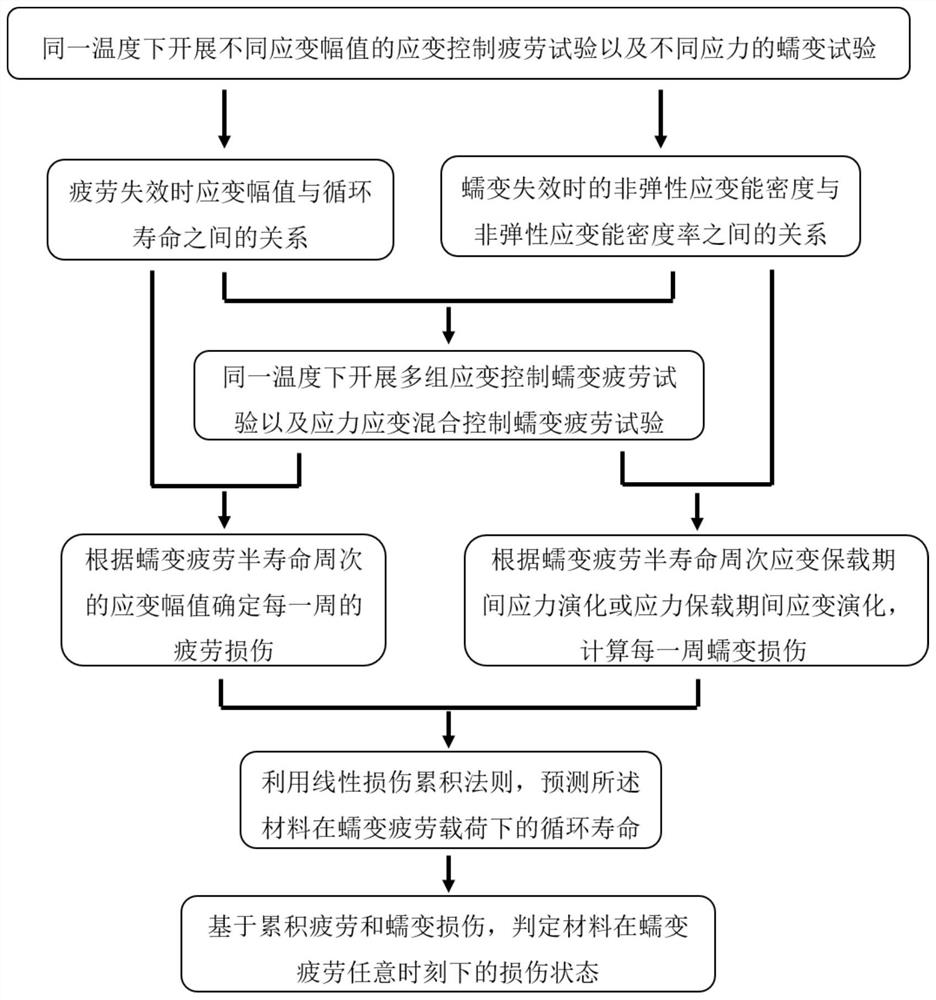
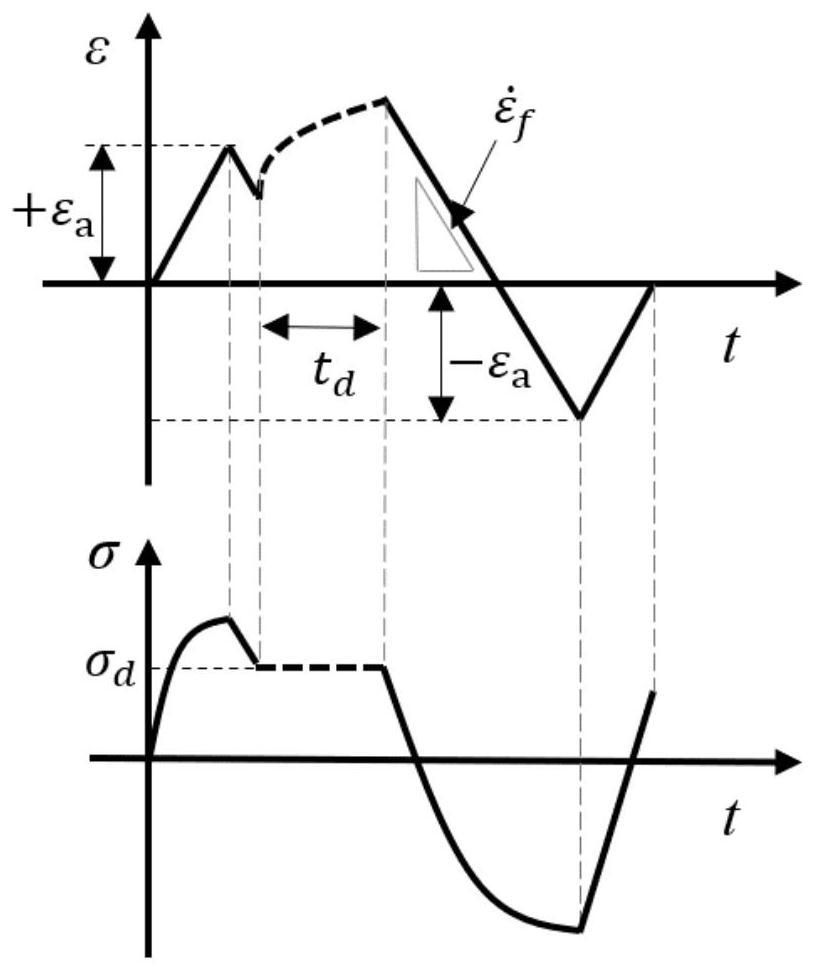
Universal method suitable for judging stress-strain hybrid creep-controlled fatigue damage state
A fatigue damage, stress-strain technology, applied in the direction of applying repetitive force/pulse force to test the strength of materials, instruments, measuring devices, etc., to achieve the effect of wide applicability, convenient calculation and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Example 1 The cycle life of different temperatures and materials under strain control and stress-strain mixed creep control fatigue loads is predicted by using the general method of the present invention suitable for judging the damage state of stress-strain mixed creep controlled fatigue.
[0082]The selected data is the stress-strain mixed control creep fatigue test of 15 groups of P92 steel at 625°C. The holding time is 300s, 600s, 1800s, and the holding stress is 140MPa-180MPa. The test method is as described in the specification. 4 sets of strain-controlled creep fatigue tests of P92 steel at 650°C, and 5 sets of strain-controlled creep fatigue tests of P92 steel at 600°C, the test methods are as described in the specification. The fatigue test of P92 steel under different temperatures and strain amplitudes uses the data of published papers [Wang X, Zhang W, Zhang T, et al. A New Empirical Life Prediction Model for 9–12% Cr Steels under Low Cycle Fatigue and Creep F...
Embodiment 2
[0085] Embodiment 2 adopts the general method of the present invention suitable for judging the damage state of stress-strain mixed creep-controlled fatigue to determine the damage state of the material under strain-controlled and stress-strain mixed creep-controlled fatigue loads at any moment.
[0086] The linear damage accumulation does not consider the effect of creep-fatigue interaction, and often underestimates the creep-fatigue damage. Therefore, in the current creep fatigue design, the bilinear design criterion is introduced. For 9Cr-1Mo material, ASME III-NH (Code for Design of Boilers and Pressure Vessels) defines that both cumulative creep damage and cumulative fatigue damage reach 0.3 as the interactive turning point in the bilinear criterion, such as Figure 4 shown. The selected data in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 1. Based on the creep and fatigue damage expressions proposed by the present invention, this embodiment determines the damage st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com