Semi-quantitative post-stack seismic fracture prediction method
A crack prediction, semi-quantitative technology, applied in seismology, seismic signal processing, measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as seldom azimuth processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for predicting semi-quantitative post-stack seismic fractures, comprising the following steps: S1 acquiring initial seismic data, performing structure-guided filtering on the initial seismic data to obtain first seismic data S 1 ; S2 to the first seismic data S 1 Perform power exponent operation to obtain the second seismic data S 2 , to increase the participation of weak reflections in the first seismic data, namely where x is the weak reflection enhancement index; S3 uses the third-generation coherent algorithm to analyze the second seismic data S 2 Carry out coherence analysis and dip scanning to obtain the maximum similarity coefficient C of each sample point in the seismic data and the corresponding dip and direction of the maximum similarity coefficient C, and the maximum similarity coefficient C of all sample points is set as the similarity number body; S4 squares the maximum similarity coefficient C of each sample point in the similarity coefficient ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The present embodiment is further limited on the basis of embodiment 1:
[0037] The value range of the weak reflection enhancement index x is 0.1-0.5, if the strong and weak reflection difference of the first seismic data is large, then the value of x is less than or equal to 0.3; if the strong and weak reflection difference of the first seismic data is small, then x The value is greater than 0.3. The determination of the degree of difference between strong and weak reflections of seismic data is selected according to the actual situation of seismic data. For example, if the difference between strong and weak reflections of seismic data is greater than 5 times or more, it is defined as a large difference between strong and weak reflections of seismic data.
[0038] The specific steps to obtain the maximum similarity coefficient C of each sample point in the seismic data and the dip angle and direction corresponding to the maximum similarity coefficient C are as follows...
Embodiment 3
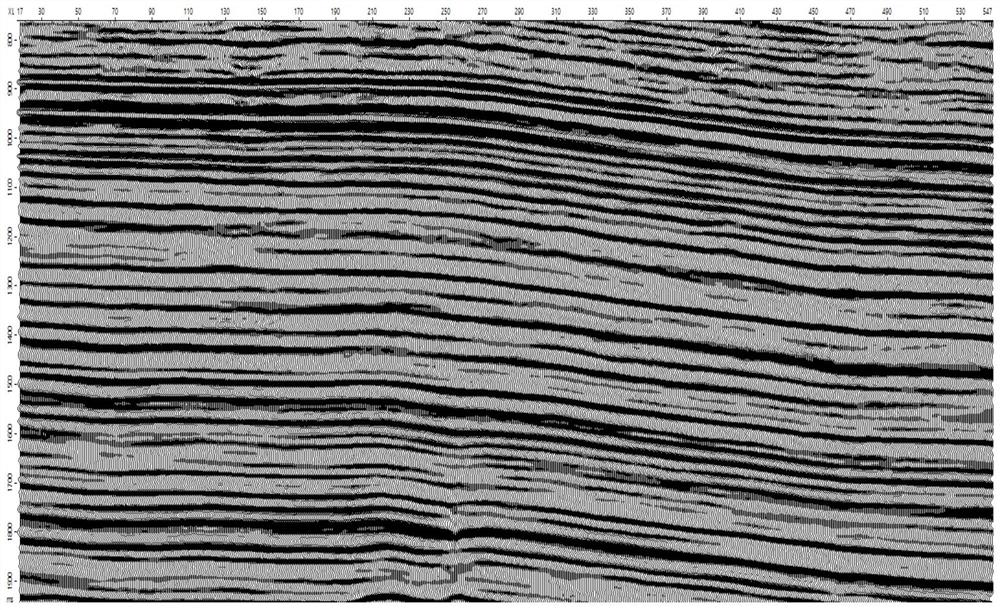
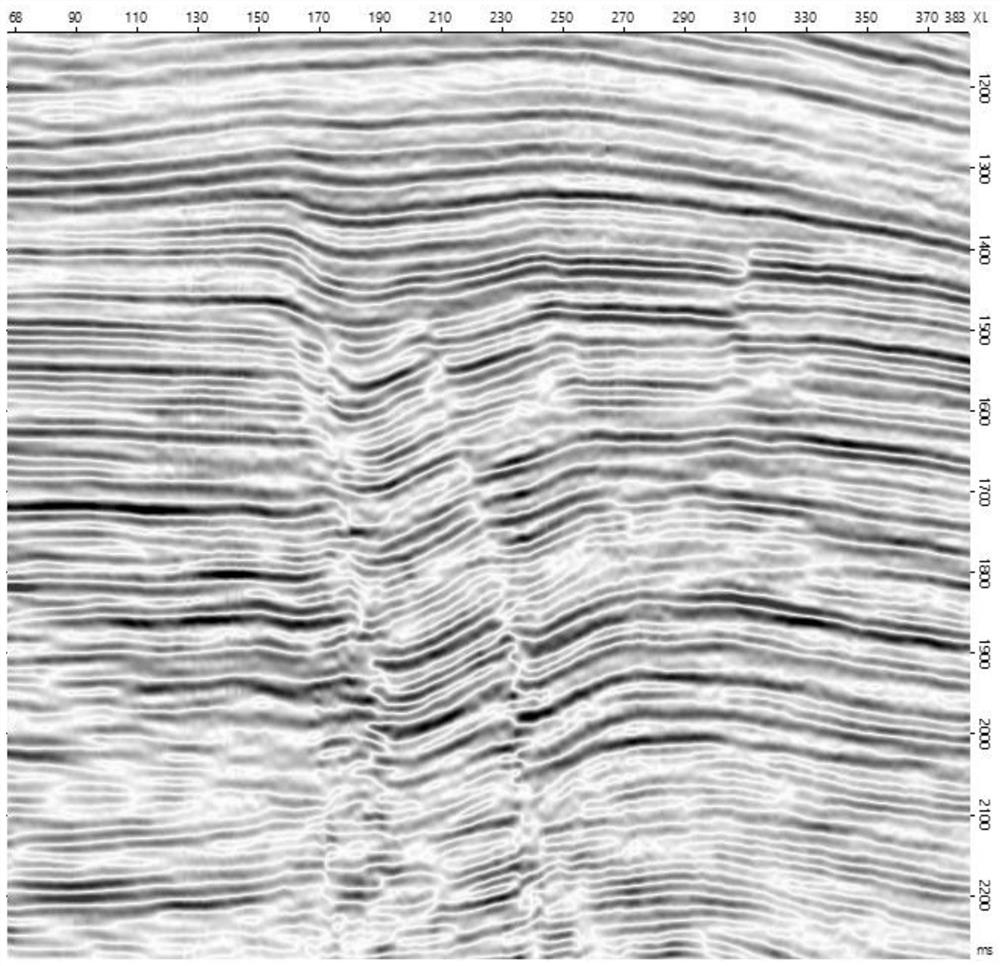
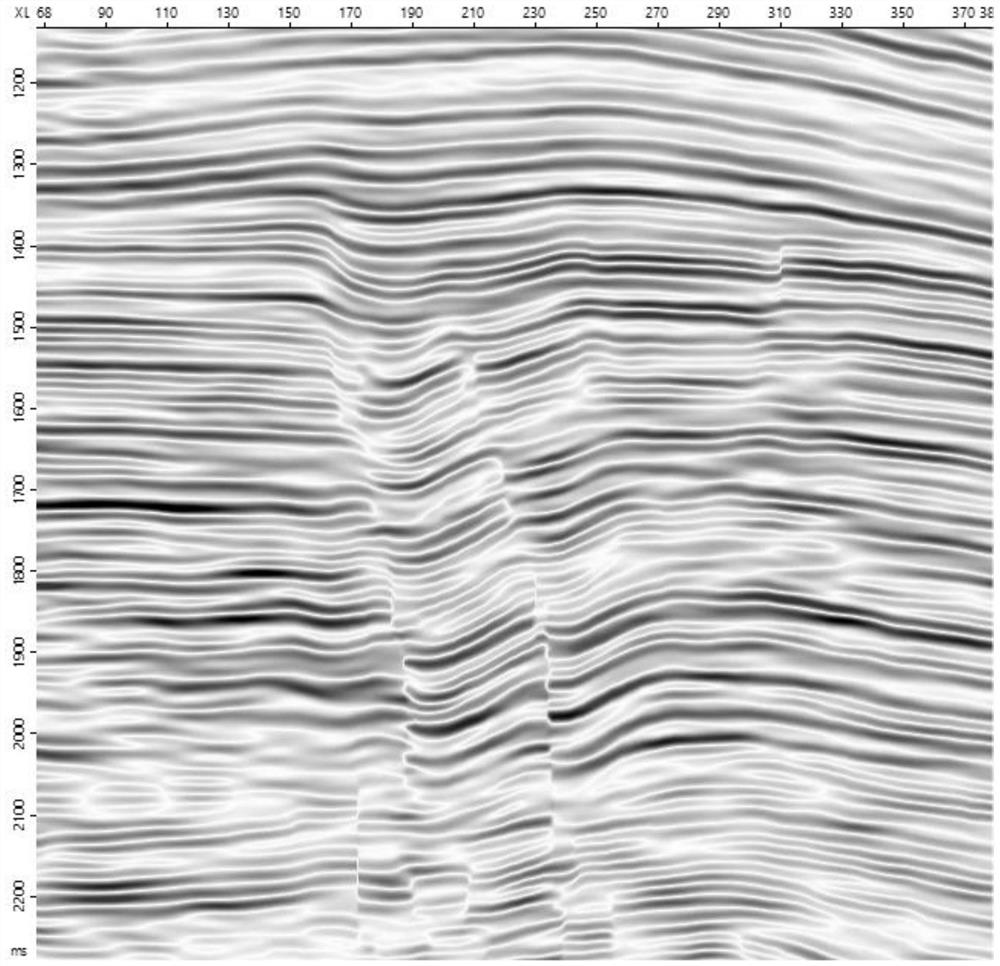
[0045] Such as Figure 1-Figure 12 , taking the seismic data of an oilfield in the Middle East as an example, in order to carry out fracture prediction, according to a semi-quantitative post-stack seismic fracture prediction method provided by the present invention, the following steps are implemented:
[0046] S1 performs structure-oriented filtering on seismic data to reduce the influence of seismic reflection discontinuity caused by noise in acquisition and processing, static correction and other factors, and highlight the discontinuity characteristics caused by faults and cracks. as attached figure 1 As shown, the original seismic section is relatively not smooth, with figure 2 For the structurally guided seismic section, the continuity of the seismic reflection event is greatly enhanced at the non-fault fractures, and the breakpoints are clearer.
[0047] S2 performs power exponential function calculation S on the seismic data obtained in S1 x , S is the seismic signa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com