Monolithic integrated edge-emitting laser and manufacturing method
An edge-emitting laser and monolithic integration technology, which is applied to lasers, laser components, semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve the problems of low system stability and bulky laser radar system, and achieve reduced power density, improved reliability, and high output The effect of power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] In this embodiment, the working wavelength of the monolithically integrated edge-emitting laser is 940 nm and is based on gallium arsenide (GaAs) material.
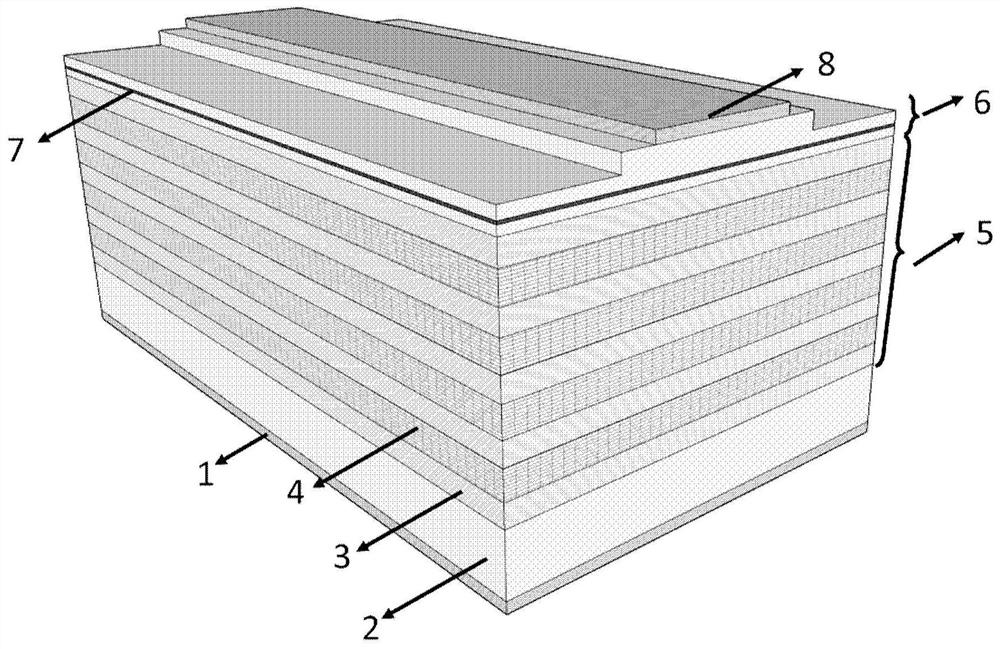
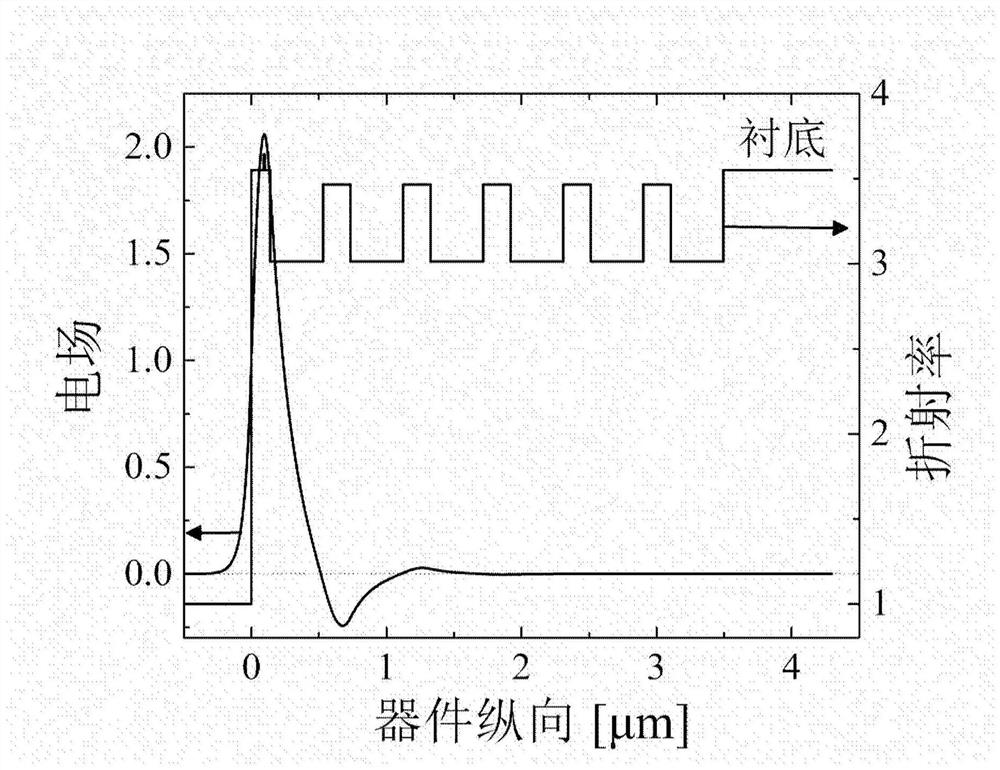
[0059] The structure of a monolithically integrated edge-emitting laser is as follows figure 1 As shown: the first electrode 1 is a negative electrode, and the material is AuGeNiAu; the second electrode 8 is a positive electrode, and the material is TiPtAu; the substrate 2 is made of n-type GaAs; the low-refractive index material layer 3 is n-type Al 0.9 Ga 0.1 As layer, the thickness is 334nm, the first high refractive index material layer 4 is n-type Al 0.12 Ga 0.88 The As layer has a thickness of 157 nm. The low-refractive-index material layer 3 and the first high-refractive-index material layer 4 grow 5.5 groups periodically and alternately in the material epitaxy to form a multilayer structure 5 similar to the Bragg mirror structure. The multilayer structure 5 is formed on the substrate, and many The layer...
Embodiment 2
[0064] In this embodiment, the working wavelength of the monolithically integrated edge-emitting laser is 940 nm and is based on gallium arsenide (GaAs) material.
[0065] The structure of a monolithically integrated edge-emitting laser is as follows Figure 5 As shown: the first electrode 1 is a negative electrode, and the material is AuGeNiAu; the second electrode 8 is a positive electrode, and the material is TiAu; the substrate 2 is made of n-type GaAs; the low-refractive index material layer 3 is n-type Al 0.9 Ga 0.1 As layer, the thickness is 334nm, the first high refractive index material layer 4 is n-type Al 0.12 Ga 0.88 The As layer has a thickness of 157 nm. The low-refractive-index material layer 3 and the first high-refractive-index material layer 4 grow 5.5 groups periodically and alternately in the material epitaxy to form a multilayer structure 5 similar to the Bragg mirror structure. The multilayer structure 5 is formed on the substrate, and many The layer ...
Embodiment 3
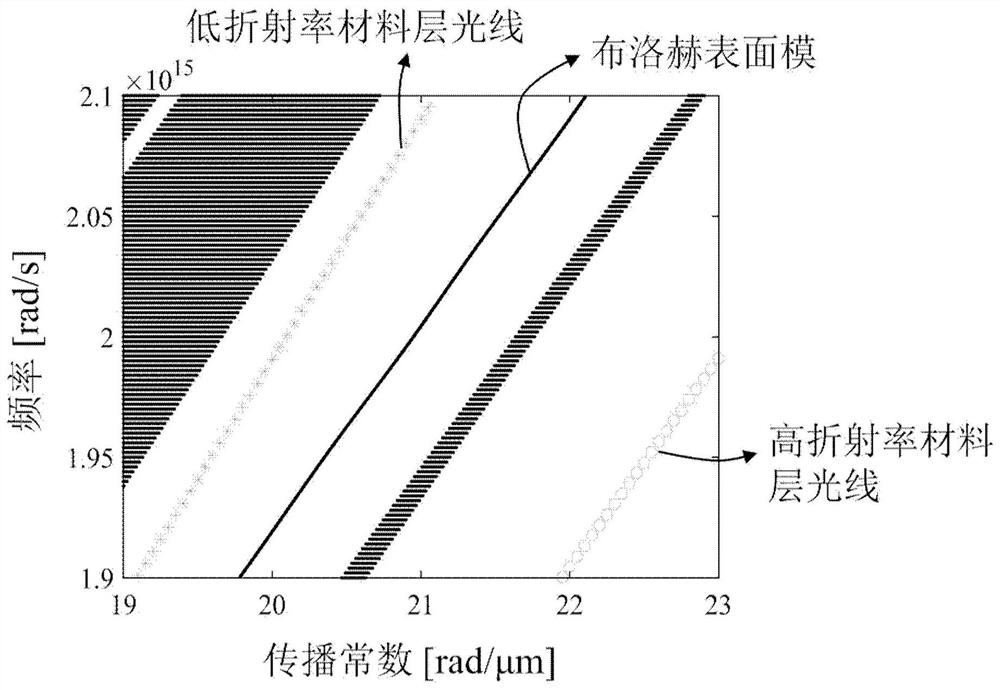
[0067] In this embodiment, the working wavelength of the monolithically integrated edge-emitting laser is 940 nm and is based on gallium arsenide (GaAs) material. The structure is similar to that of Embodiment 2, except that a one-dimensional periodic surface micro-nano structure, ie a one-dimensional surface grating, is introduced into the ridge waveguide 9, which is fabricated by electron beam exposure and dry etching to achieve longitudinal mode selection. Image 6 A schematic top view of a one-dimensional surface grating is shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com