Infrared imaging lens and imaging equipment
An infrared imaging and lens technology, applied in the field of imaging lenses, can solve the problems of small clear aperture, large temperature drift, small field of view, etc., and achieve the effect of compensating for focus shift, high-definition imaging performance, and high-definition resolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
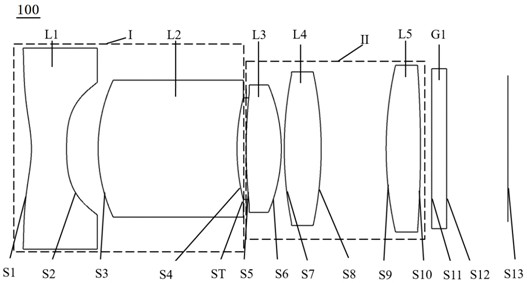
[0072] see figure 1 , which is a schematic structural view of the infrared imaging lens 100 provided in the first embodiment of the present invention, the infrared imaging lens 100 sequentially includes a first group I with a negative focal power, a light Stop ST, second group II with positive power, and filter G1.
[0073] The first group I comprises in turn from the object side to the imaging surface: a first lens L1 with negative refractive power, the object side S1 of the first lens is concave at the paraxial place, and the image side S2 of the first lens is concave; The second lens L2 with positive refractive power, the object side S3 of the second lens is a convex surface, and the image side S4 of the second lens is a concave surface;
[0074] The diaphragm ST is disposed between the second lens L2 and the third lens L3;
[0075] The second group II includes in order from the object side to the imaging surface: a third lens L3 with positive refractive power, the object...
no. 2 example
[0088] see Figure 5 , shows the structural diagram of the infrared imaging lens 200 provided in the second embodiment of the present invention, the structure of the infrared imaging lens 200 in this embodiment is roughly the same as that of the infrared imaging lens 100 in the first embodiment, the difference is that The curvature radius, thickness, and material selection of each lens of the optical imaging lens in this embodiment are different, and specific relevant parameters of each lens are shown in Table 3.
[0089] table 3
[0090]
[0091] The aspherical parameters of the infrared imaging lens 200 in this embodiment are shown in Table 4.
[0092] Table 4
[0093]
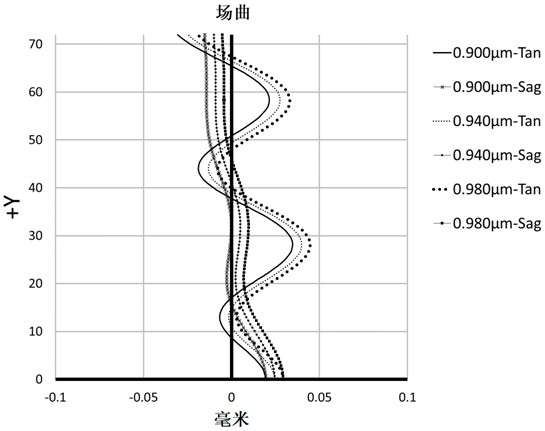
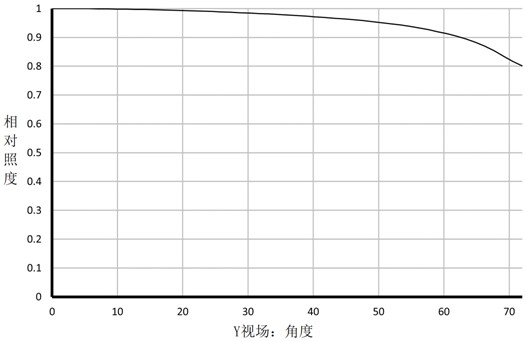
[0094] In this embodiment, the field curvature curve, the relative illuminance curve and the MTF curve in the working band of the infrared imaging lens 200 are respectively as follows Image 6 , Figure 7 and Figure 8 shown.
[0095] Depend on Image 6 It can be seen that the field curvature of...
no. 3 example
[0099] see Figure 9 , shows the structural diagram of the infrared imaging lens 300 provided in the third embodiment of the present invention, the structure of the infrared imaging lens 300 in this embodiment is roughly the same as that of the infrared imaging lens 100 in the first embodiment, the difference is that In this embodiment, the image side S10 of the fifth lens of the infrared imaging lens 300 is a concave surface, and the curvature radius, thickness, and material selection of each lens are also different. The relevant parameters of each lens are shown in Table 5.
[0100] table 5
[0101]
[0102] The aspherical parameters of the infrared imaging lens 300 in this embodiment are shown in Table 6.
[0103] Table 6
[0104]
[0105] In this embodiment, the field curvature curve, the relative illuminance curve and the MTF curve in the working band of the infrared imaging lens 300 are as follows Figure 10 , Figure 11 and Figure 12 shown.
[0106] Depend ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Optical length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com