Dynamic scene rendering acceleration method based on light path multiplexing
A technology of light paths and dynamic scenes, which is applied in the processing of 3D images, image data processing, instruments, etc., and can solve the problems that dynamic scenes are not very suitable.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
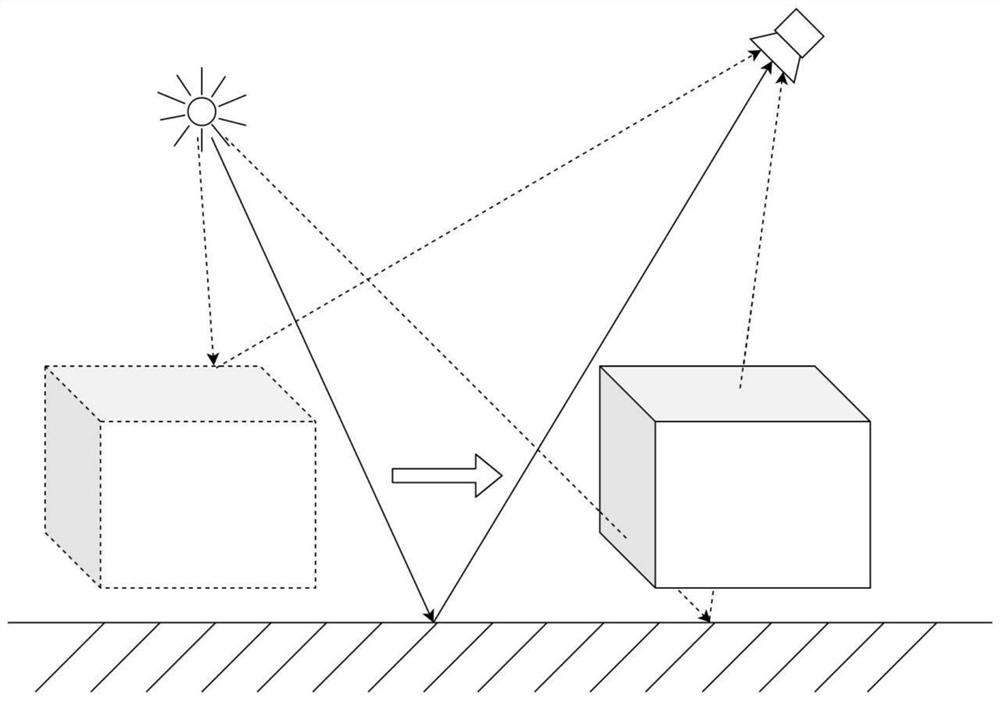
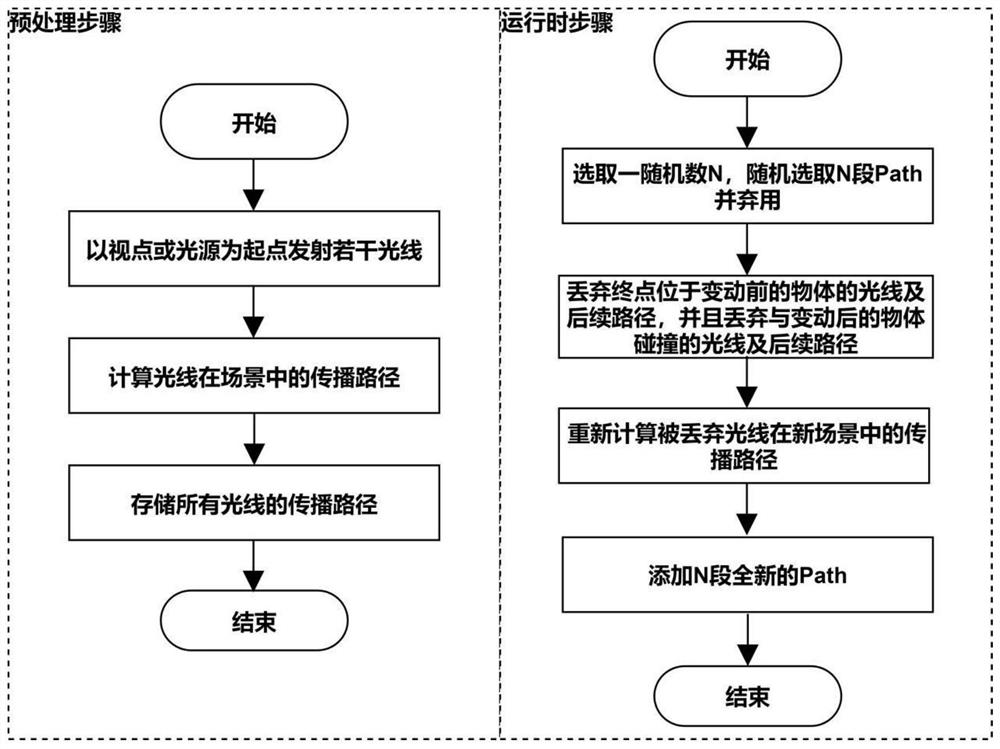
[0032] A dynamic scene rendering acceleration method based on ray path multiplexing, including a preprocessing step and a runtime step. When a number of rays are emitted to the scene and the corresponding scattered rays are traced to calculate an image, the preprocessing step is performed before running. If When the scene changes during the running process, the runtime steps are executed;
[0033] The preprocessing steps include the following steps:
[0034] S1. Emit a number of rays from a light source, or emit a number of rays traced back from a viewpoint;
[0035] S2. Calculate the propagation path of each light in the three-dimensional virtual scene, and calculate the collision point information between the light and the model in the scene;
[0036] S3. Set the complete propagation path corresponding to the light Light as: starting from a point in the scene, passing through the collision points scattered by each light, and ending the whole path, which is expressed as the ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , a dynamic scene rendering acceleration method based on ray path multiplexing, including a preprocessing step and a runtime step. When a number of rays are emitted to the scene and the corresponding scattered rays are traced to calculate an image, the preprocessing step is performed before running. If the scene changes during the running process, execute the runtime steps;
[0054] The preprocessing steps include the following steps:
[0055] S1. Emit a number of rays from a light source, or emit a number of rays traced back from a viewpoint;
[0056] S2. Calculate the propagation path of each light in the three-dimensional virtual scene, and calculate the collision point information between the light and the model in the scene;
[0057] S3. Set the complete propagation path corresponding to the light Light as: starting from a point in the scene, passing through the collision points scattered by each light, and ending the whole path, ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] 1. The film of the camera is divided into discrete grids (that is, pixels), and our goal is to determine the color value of each pixel;
[0075] 2. For each pixel, trace a ray from the camera position, pointing to the pixel;
[0076] 3. For this beam of light, judge whether it intersects with the object in the scene, if it intersects, go to step 4; otherwise, fill the background color into the current pixel, go back to step 2, and continue to process the next pixel;
[0077] 4. If the light intersects with the object, calculate the color value of the intersection point on the surface of the object, and the color value of the point is the color value of the pixel:
[0078] a. First check the contribution value of each light source at the intersection point. Tracing a new ray to the light source is used to determine whether the intersection is fully illuminated, partially illuminated, or not illuminated, and shadows are determined at the same time;
[0079] b. If the su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com