Lignin particle based hydrogel and method for preparation of lignin colloidal particles by solvent evaporation process
A technology of lignin and hydrogel, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, dissolution, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problems of not reflecting the one-pot method of spherical lignin nanoparticles, and not disclosing the application of colloidal lignin particles, etc. Achieved to facilitate easy printing and improve structure retention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0060] In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of:
[0061] - providing a solution of unmodified lignin in a mixture of a volatile organic solvent for lignin and a non-solvent for lignin; and
[0062] - Evaporation of the volatile organic solvents of the lignin, especially under reduced pressure, to produce an aqueous dispersion of colloidal lignin particles.
[0063] In one embodiment, more non-solvent is added to the solution prior to evaporation.
[0064] In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of:
[0065] - providing a solution of unmodified lignin in a mixture of a volatile organic solvent for lignin and a non-solvent for lignin; and
[0066] -Adding more non-solvent to produce an aqueous dispersion of colloidal lignin particles.
[0067] In one embodiment, the solvent mixture used to prepare the colloidal lignin particles by diluting the organic solvent with a lignin non-solvent, such as water, corresponds to the solvent mixture used in the embodi...
Embodiment 1
[0104] Example 1. Preparation and Characterization of Colloidal Lignin Particles
[0105] This example describes the preparation of CLP by adding lignin solution to water. BIOPIVA 100, UPM softwood kraft lignin (7.5 g, dry basis) was dissolved in 150 g of acetone-water 3:1 w / w solvent mixture. After stirring for three hours at 22°C, the solution was filtered through a glass microfiber filter (Whatman, GF / F grade) and immersed in vigorously stirred deionized water (450 g) at 22°C. The colloid formed was diluted ~20-fold and analyzed by particle dynamic light scattering.
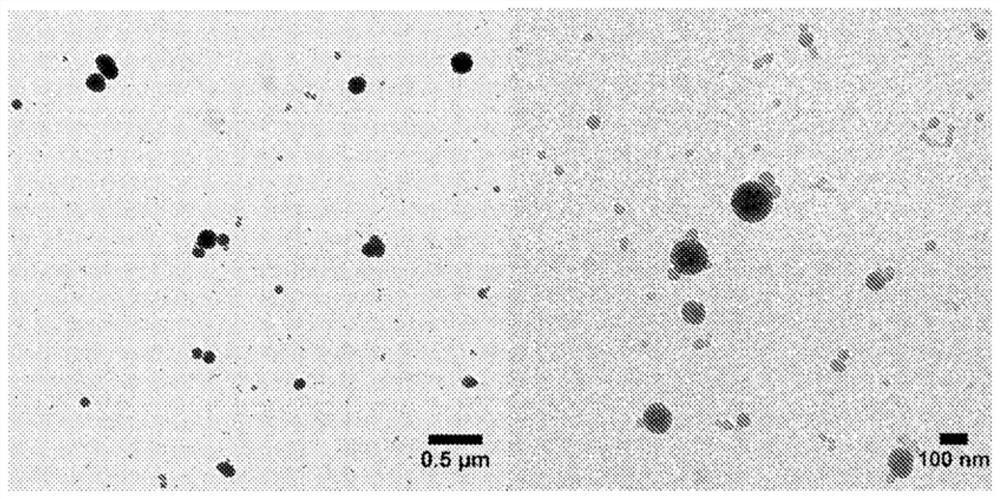
[0106] figure 1 TEM micrographs of colloidal lignin particles produced by adding lignin solution in acetone-water 3:1 w / w to deionized water are shown. TEM images were acquired in brightfield mode on a FEevaI-FEevaI Tecnai 12 operated at 120kV.
[0107] It is evident that by the described method colloidal lignin particles are obtained with a Z-average particle size of 170±3 nm and a PdI of 0.15±0.02 (N=3)....
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2: Effect of pH on particle properties of colloidal lignin particles
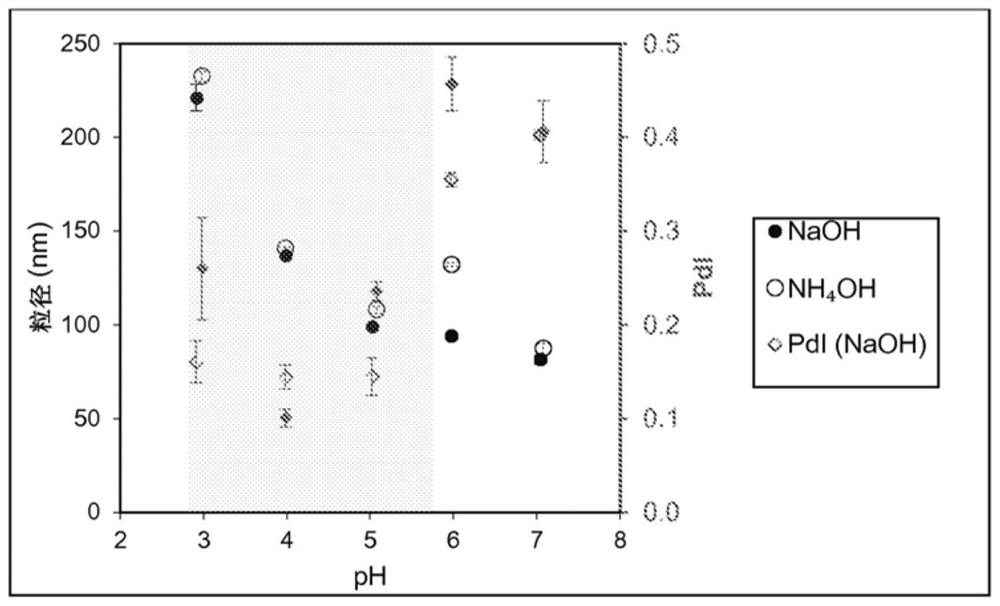
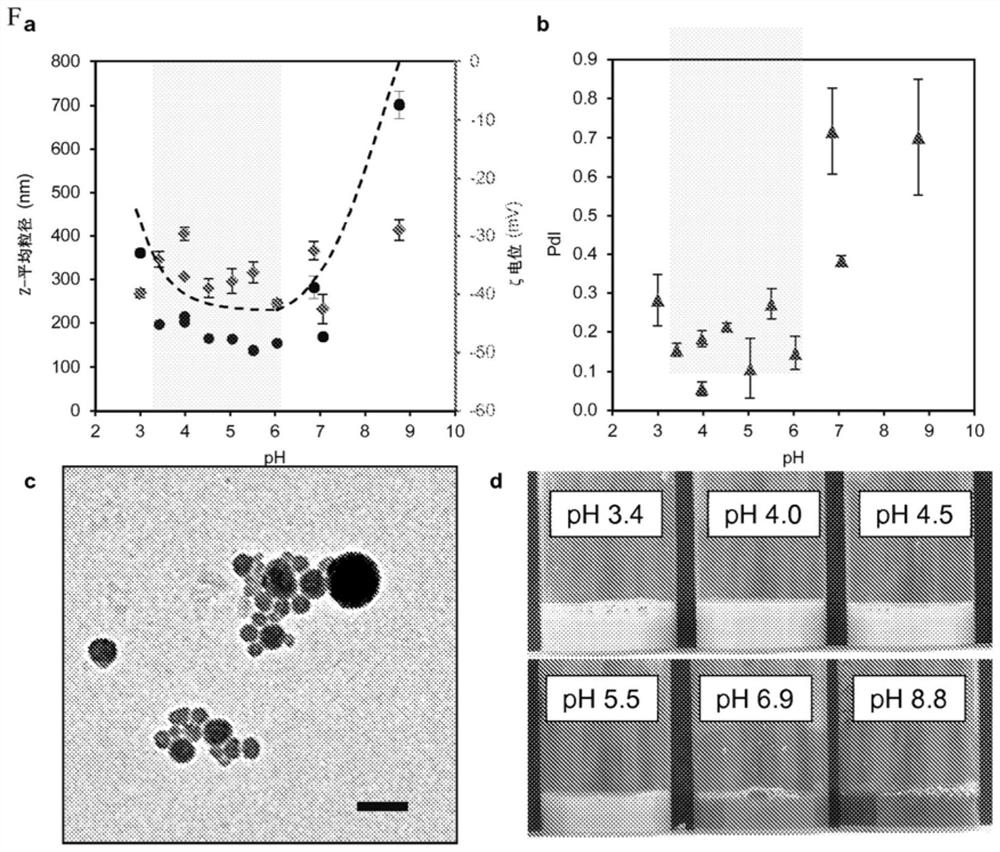
[0109] The purpose of this example is to show the effect of pH on the particle size of colloidal lignin particles. A 1 wt% concentration lignin solution in acetone-water 3:1 w / w solvent mixture was adjusted to a predetermined pH value by adding a small amount of aqueous hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide or ammonium hydroxide. These lignin solutions were used to prepare colloidal lignin particles by quickly pouring deionized water as a non-solvent into the lignin solutions.
[0110] figure 2 The effect of pH on the particle size of lignin colloids is shown. More specifically, figure 2 CLP formation by direct precipitation is shown. pH vs. Z-average particle size of colloidal lignin particles prepared by adding deionized water (120 g) to 40 g of a 1 wt % lignin solution in acetone-water 3:1 w / w solvent mixture (○ ) and the polydispersity index Impact. Adjustment of pH was performed ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com