Gynecological Exam
A technology for gynecological examination and inspection team, applied in the field of gynecological examiners, can solve the problems of low screening efficiency, long inspection duration, low one-time diagnosis efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of high screening efficiency and short duration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
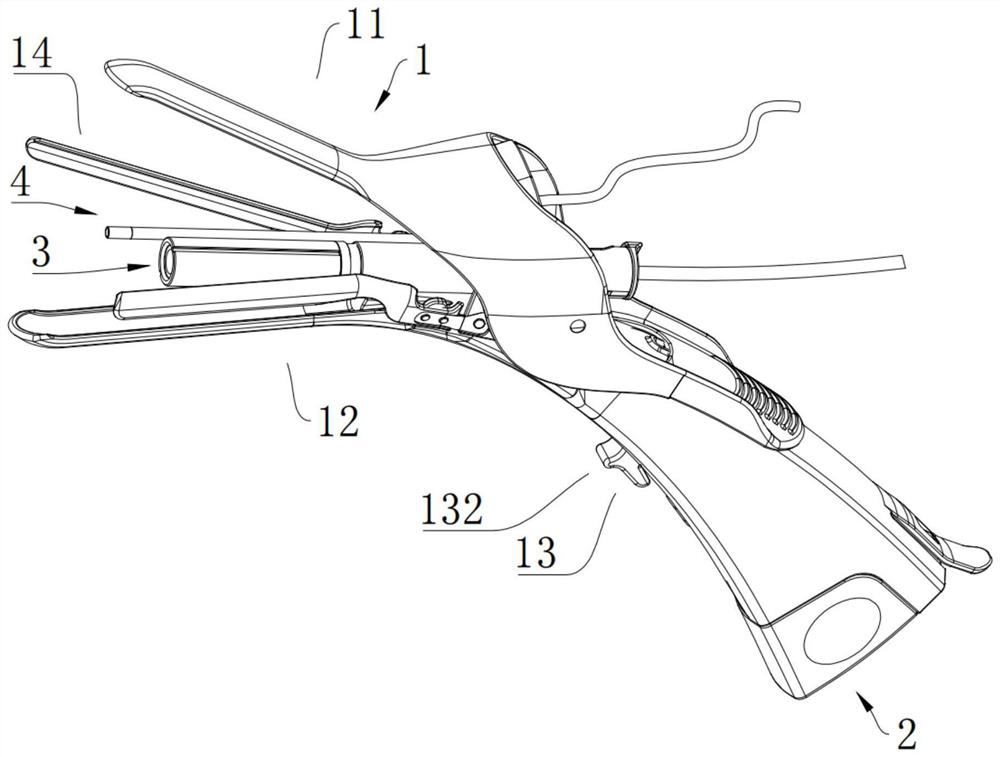
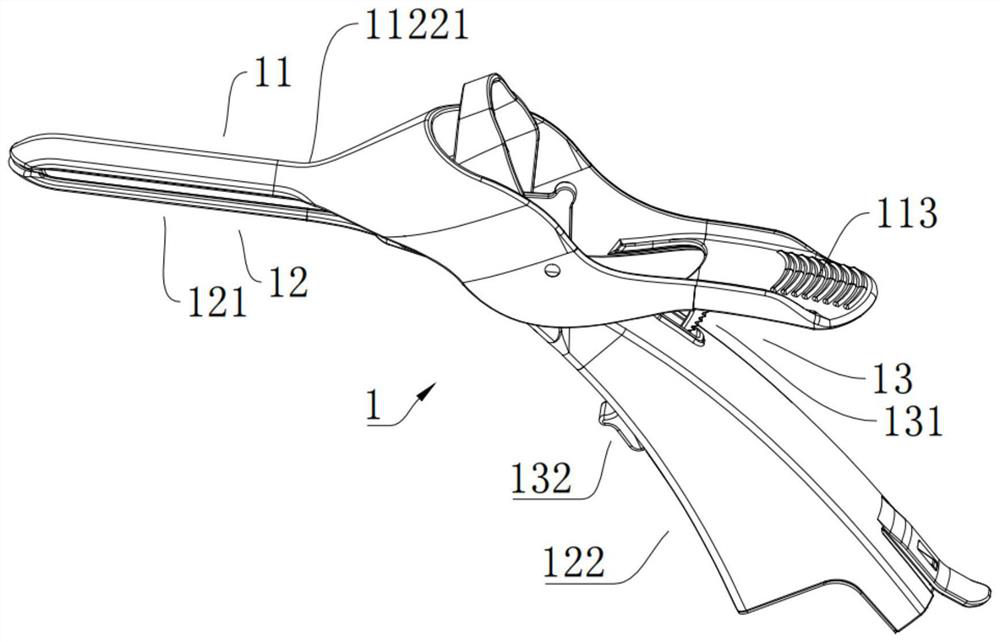
[0052] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , figure 1 For the structural representation of the gynecological examiner in the embodiment, figure 2 It is a schematic structural diagram of the expansion mechanism in the closed state in the embodiment. The gynecological examiner in this embodiment includes an expansion mechanism 1 , a visualization mechanism 2 and an inspection mechanism 3 . The expansion mechanism 1 includes an upper expansion component 11, a lower expansion component 12 and a locking component 13. The upper expansion component 11 is connected to the lower expansion component 12 and can be rotated relative to each other. During the relative rotation, the two are switched between an open state and a substantially closed state. , when in the open state, an inspection channel is formed between the two. The locking component 13 includes a locking member 131 and a locking member 132. The locking member 131 and the locking member 132 can be disconnected. When the lock...
Embodiment 2
[0075] continue to refer to figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 as well as Figure 13 , Figure 13 in the example Figure 4A magnified view of part A. The difference between the gynecological examiner in this embodiment and the gynecological examiner in Embodiment 1 is that the expansion mechanism 1 further includes a side expansion assembly 14 , and the side expansion assembly 14 includes a lateral expansion linkage 141 and two lateral expansion members 142 , the side expansion link member 141 is rotatably connected to the lower expansion member 12, and is connected with the upper expansion member 11. The lower expansion member 12 has a side expansion member 124, one end of the two side expansion members 142 is connected with the side expansion link member 141, and the two The other end of each side expansion member 142 extends away from the side expansion link member 141 and passes through the side expansion member 124. During the relative expansio...
Embodiment 3
[0082] continue to refer to Figure 16 to Figure 19 , Figure 16 is another cross-sectional view of the inspection mechanism in the embodiment, Figure 17 For another exploded view of the inspection mechanism in the embodiment, Figure 18 in the example Figure 16 The enlarged view of part B, Figure 19 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the inspection component in the embodiment. The difference between the gynecological examiner in this embodiment and the gynecological examiner in the first embodiment is that the see-through member 311 includes a concave lens portion 3112 , one end of the concave lens portion 3112 is set at one end of the first protective member 312 , and the concave lens portion The other end of the 3112 extends toward the inspection assembly 32 and is abutted with the inspection end of the inspection assembly 32 .
[0083] The arrangement of the concave lens portion 3112 facilitates the maintenance of the state of being in contact with the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com