Double-field cooperative driving omni-directional motion robot and driving method thereof
A robot and field synergy technology, applied in the field of flexible robots, can solve the problems of poor active obstacle avoidance, insufficient omnidirectional movement, and reduced controllability of the robot's movement direction, and achieve the effect of increasing the degree of freedom of manipulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
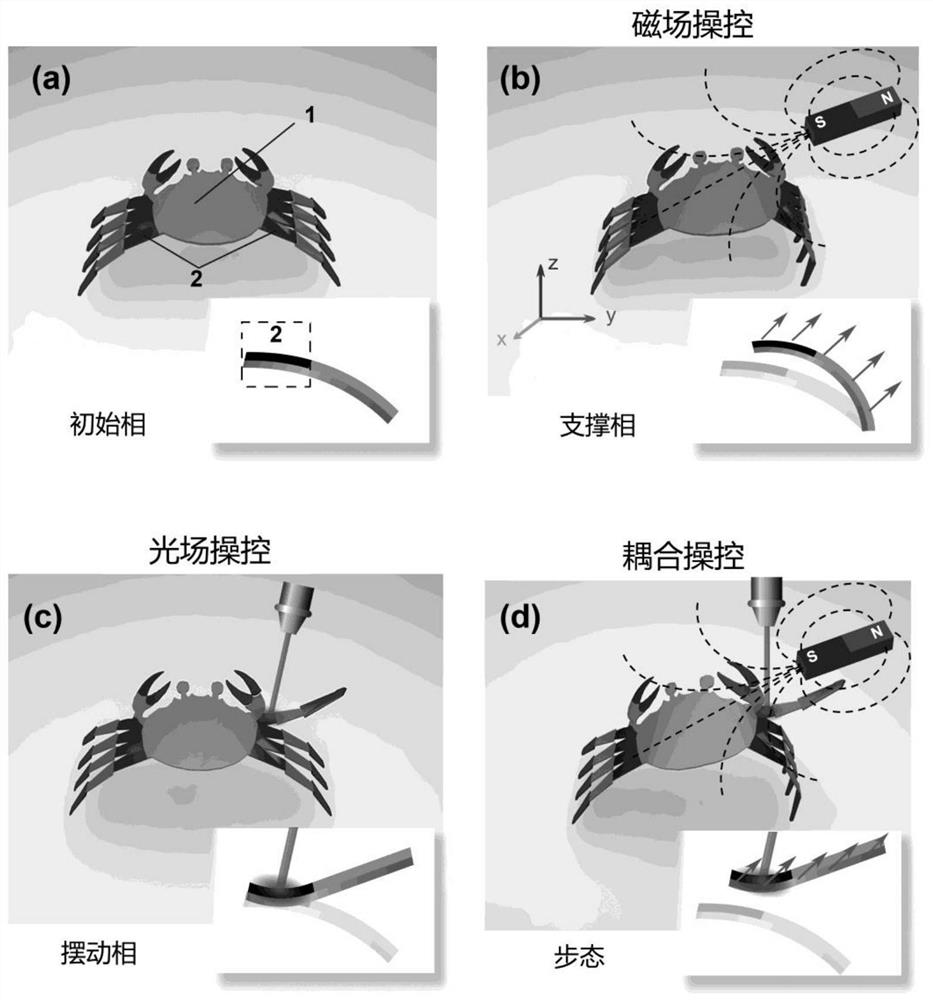
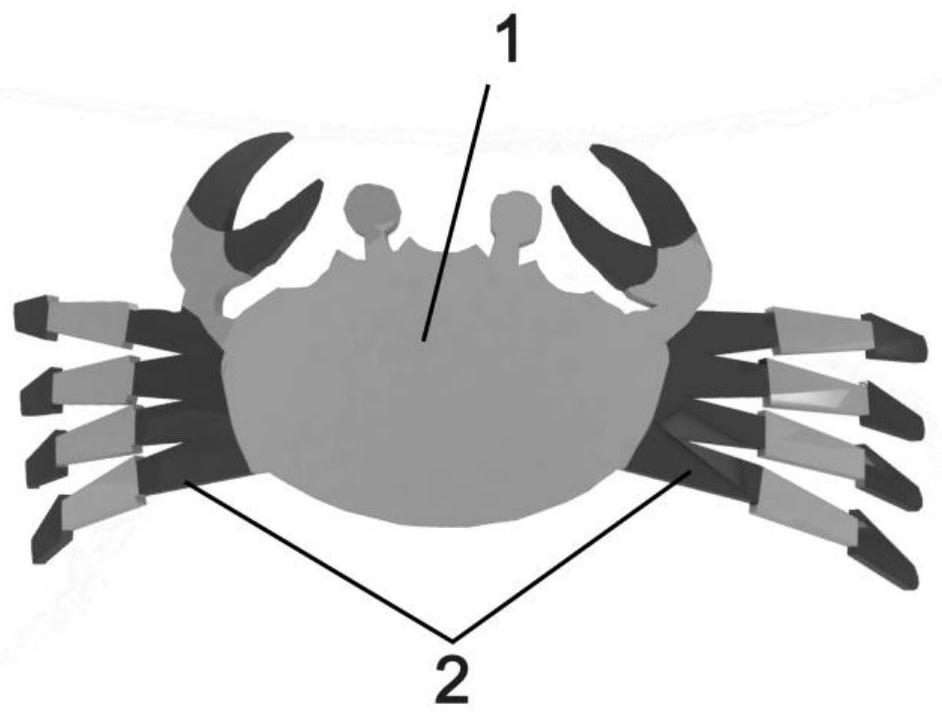
[0028] A dual-field cooperatively driven omnidirectional motion robot, such as figure 1 -(a), consisting of a main structure 1 with magnetic response and a secondary structure 2 with light response, the main structure 1 is a double-layer film with multiple foot structures on the edge, wherein the upper layer of the double-layer film is magnetic Responsive material, the lower layer is a flexible material; the main structure 1 will produce macroscopic deformation under the action of an external magnetic field, and the internal stress will accumulate directionally, thus determining the overall movement direction of the robot, such as figure 1 -(b); the secondary structure 2 is a plurality of double-layer drivers arranged on the foot structure, the upper layer of the double-layer driver is a material with both optical response and magnetic response, and the lower layer is a flexible material; the secondary structure 2 is in Driven by the external light field, it will bend to reali...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This embodiment provides a dual-field cooperatively driven omnidirectional motion robot, the preparation method of which is as follows:
[0031] Step 1: material preparation;
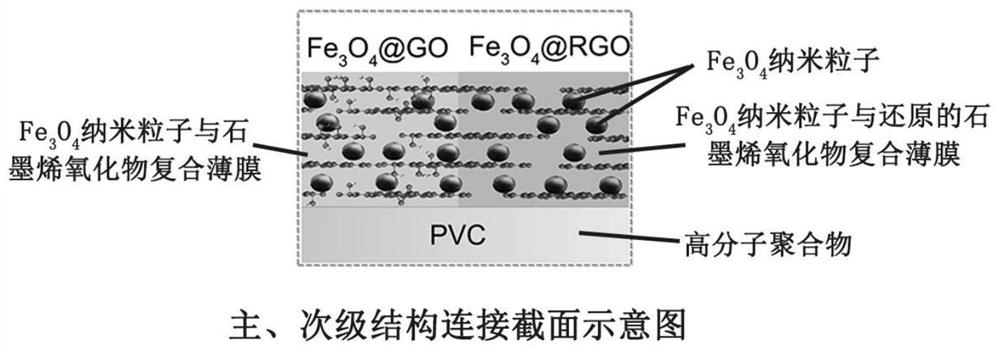
[0032] The preparation process of the magnetic response material in the upper layer of the main structure 1 includes ferric oxide nanoparticles prepared by the chemical co-precipitation method, which have superparamagnetic properties (concentration is 50 mg / mL). Graphene oxide (concentration is 10mg / mL) prepared in batches by Hummers method. The two materials are compounded and stirred, and the composite volume ratio is 1:50. This composite material has both superparamagnetic properties and certain light-to-heat conversion capabilities;
[0033] The composite material is directly attached to the polymer film by spin coating and evaporation. The thickness range of the composite material film after spin coating and evaporation is 5 μm. The flexible polymer can choose commercial film with a thickne...
Embodiment 3
[0049] A driving method for an omnidirectional mobile robot driven by double-field coordination. Specifically, the main structure will undergo macroscopic deformation under the action of an external magnetic field, and the internal stress of the main structure will accumulate directionally, thereby determining the overall movement direction of the robot; Under the coordinated drive of the field, the robot realizes the process of shifting the center of gravity and moving at the same time, so that the secondary structure of the robot walks along the stress direction of the main structure.
[0050] Such as Figure 4 As shown in Fig. 1 , it is an example of a robot walking to the right, and the force analysis in the process of cooperative driving of the magnetic field and the light field. In the initial state, the robot has a symmetrical macrostructure with a single bending arc due to the symmetrical structure. When a rightward magnetic field is applied to the robot, the entire c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com