Special assessment method for pulse pressure variability corrected by respiratory mechanics
A technology of variability and pulse, applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of no significant improvement in the prediction efficiency of ΔPP, application limitations, and low area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
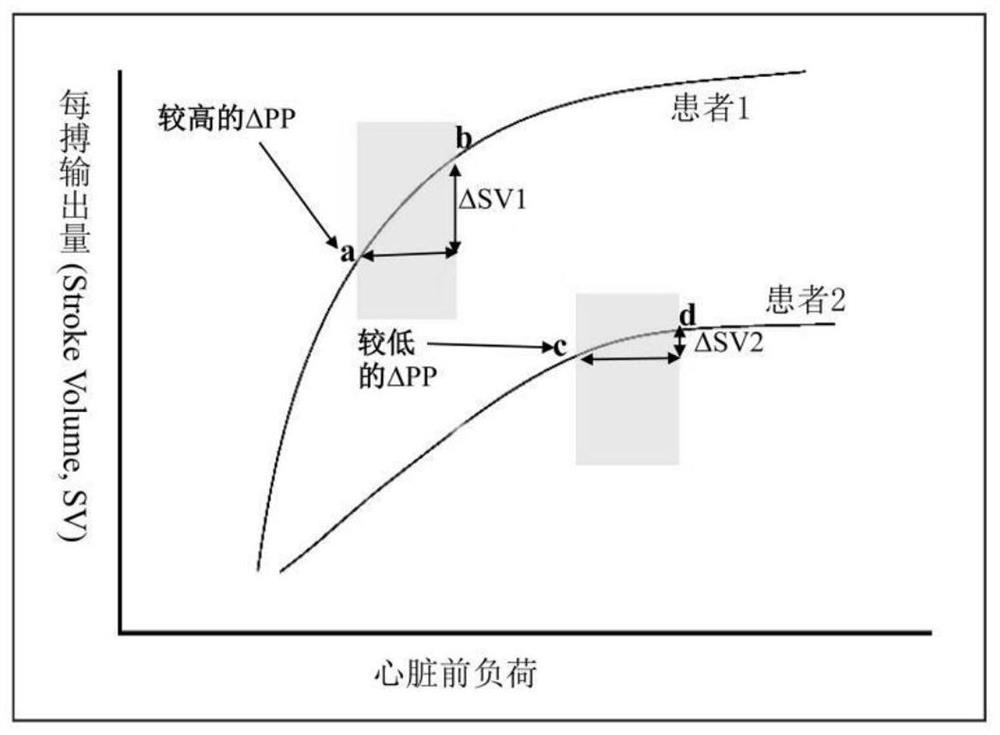
[0021] When the present invention is implemented, figure 1 : ΔPP in non-ARDS patients mainly reflects the slope of the Frank-Starling curve. Specifically, in the steep segment of the Frank-Starling curve (patient 1a-b), the change in SV after fluid therapy caused a change in preload was greater (ΔSV1, belonging to fluid responders), while the patient before fluid therapy (a ) is also larger in ΔPP; and when the patient’s heart works and the flat segment of the Frank-Starling curve (patient 2c-d) the change in SV after fluid therapy leads to a change in preload is smaller (ΔSV2, belonging to fluid non-responders), In this case the patient had a smaller ΔPP before fluid therapy (c).
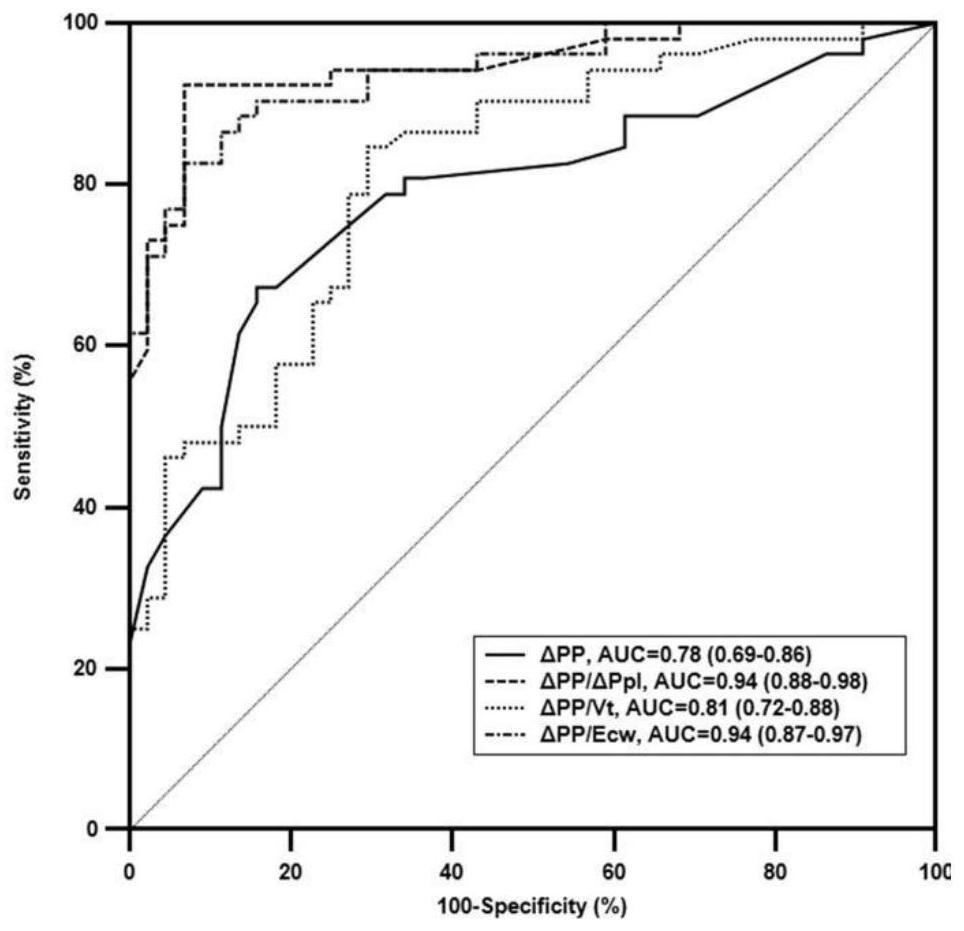
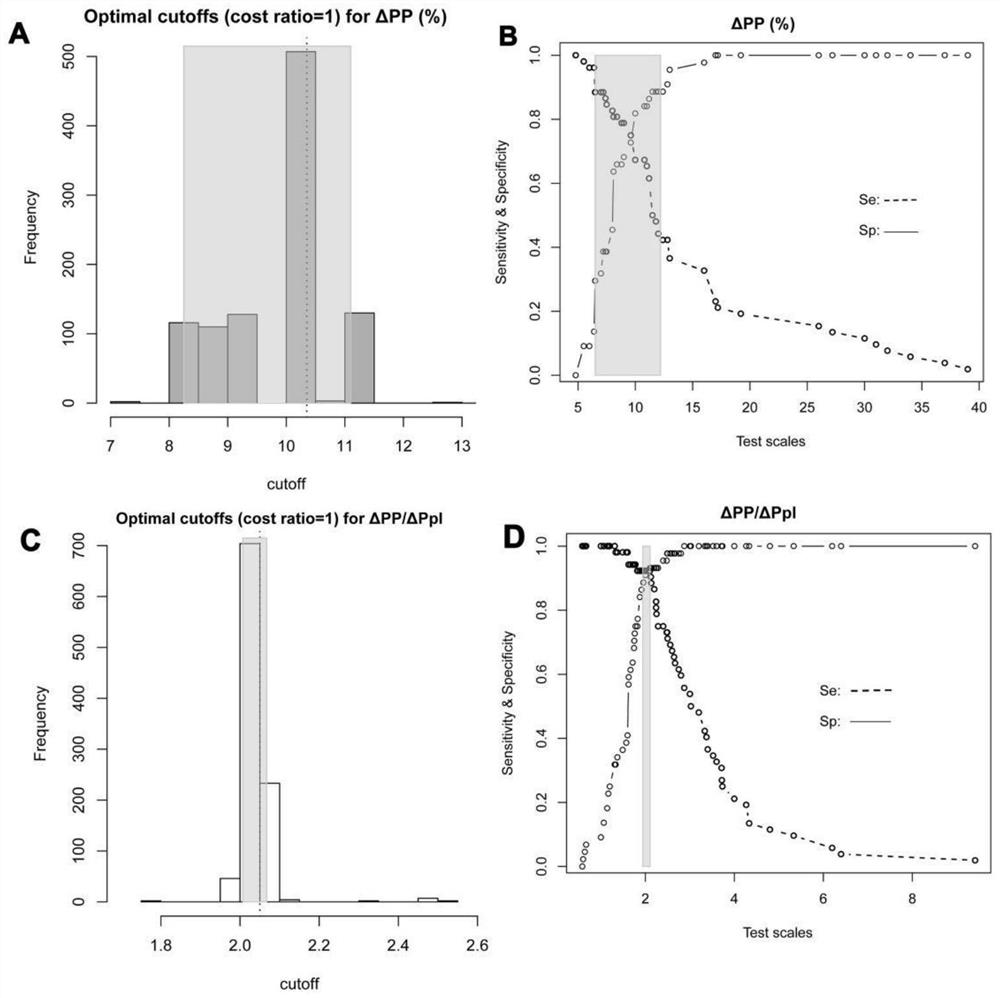
[0022] figure 2 : For the pulse pressure variability (ΔPP, %) corrected by intrathoracic pressure changes (ΔPpl, cmH2O), its AUC was significantly higher than the AUC value of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com