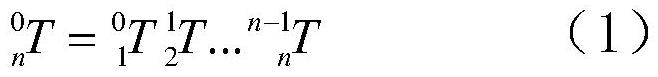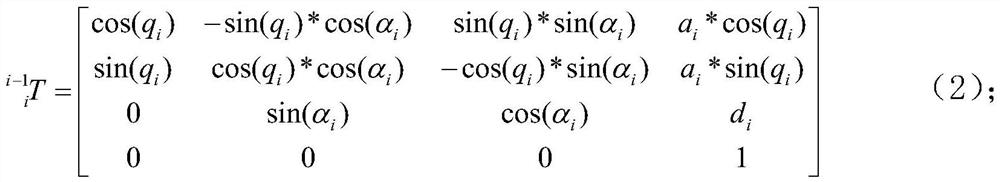Robot track synchronous control method and computer readable storage medium
A synchronous control and robot technology, applied in the direction of program control of manipulators, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as poor synchronization of joints, approximately the same command response, and not exactly the same command follow, so as to ensure synchronization and improve trajectory accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] A robot trajectory synchronization control method, in this embodiment, specifically consists of two parts, an inner control loop and an outer control loop, specifically, including the following steps:
[0075] Step 1. Use the second-order system of the mass spring damping model to perform closed-loop control on the position and attitude of the robot end, and obtain the linear acceleration in Cartesian space and angular acceleration
[0076] Specifically include:
[0077] Step 1.1: If figure 1 As shown, according to the feedback angle q of each joint of the robot, the robot’s forward motion formula KIN(q) is used to calculate the feedback pose X of the robot end, as follows:
[0078] The kinematics model of the robot is established by the standard D-H method, and the D-H parameters of the robot are obtained: d, a, α. According to the coordinate transformation method, the homogeneous transformation matrix of the robot end coordinate system {n} in the robot polar coo...
Embodiment 2
[0125] This embodiment discloses a computer device, which may be a server, and the computer device includes a processor, a memory, a network interface, and a database connected through a system bus. Wherein, the processor of the computer device is used to provide calculation and control capabilities. The memory of the computer device includes a non-volatile storage medium and an internal memory. The non-volatile storage medium stores an operating system, computer programs and databases. The internal memory provides an environment for the operation of the operating system and computer programs in the non-volatile storage medium. The database of the computer equipment is used to store the data involved in the robot trajectory synchronous control method. The network interface of the computer device is used to communicate with an external terminal via a network connection. When the computer program is executed by the processor, the robot trajectory synchronous control method is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com