Large shallow lake deep and shallow bottom layer landform reconstruction and benign stable ecological system
A technology for ecosystems and lakes, applied in the treatment of polluted waterways/lakes/ponds/rivers, water pollutants, water conservancy projects, etc. Blurred boundaries, shallow lakes without temperature stratification, etc., achieve the effect of improving water environment quality, improving water transparency, improving retention environment and living space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
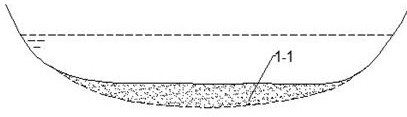
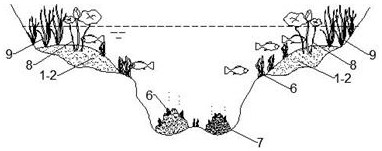
[0023] Specific as figure 1 , 2 , 3, and 4, in a lake with an average water depth of 3.0m, a shallow lake deep-water area 5 is formed by excavating the sediment a1-1. The excavation depth is 1m, and the excavated sediment a1-1 is buried in In other areas of the lake, the sediment b1-2 formed after the sediment a1-1 is transported is further accumulated to form a shallow water area 4, which reconstructs the bottom landform of a shallow-water lake.
[0024] In the lakeside zone 3, where the average water depth is less than or equal to 0.5m, a windbreak zone of emergent plants 9 shall be established to reduce wind disturbance to the lake water, improve the retention environment and living space of microorganisms and aquatic organisms in the lakeside zone 3, and effectively improve the water environment quality of coastal waters.
[0025] In the shallow water area 4, the bottom of the lake is selected to be flat, and the submerged plants 6 are transplanted in the water area with ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Specific as figure 1 , 2 As shown in , 3 and 4, in a lake with an average water depth of 2.0m, the deep-water area 5 of a shallow lake is formed by excavating the sediment a1-1. The excavation depth is 5m, and the sediment a1-1 obtained from the excavation is buried in In other areas of the lake, the sediment b1-2 formed after the sediment a1-1 is transported is further accumulated to form a shallow water area 4, which reconstructs the bottom landform of a shallow-water lake.
[0033]In the lakeside zone 3, where the average water depth is less than or equal to 0.5m, a windbreak zone of emergent plants 9 shall be established to reduce wind disturbance to the lake water, improve the retention environment and living space of microorganisms and aquatic organisms in the lakeside zone 3, and effectively improve the water environment quality of coastal waters.
[0034] In the shallow water area 4, the bottom of the lake is flat, and the submerged plants 6 are transplanted in...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Specific as figure 1 , 2 , 3, and 4, in a lake with an average water depth of 1.5m, a shallow lake deep-water area 5 is formed by excavating the sediment a1-1. The excavation depth is 10m, and the excavated sediment a1-1 is buried in In other areas of the lake, the sediment b1-2 formed after the sediment a1-1 is transported is further accumulated to form a shallow water area 4, which reconstructs the bottom landform of a shallow-water lake.
[0042] In the lakeside zone 3, where the average water depth is less than or equal to 0.5m, a windbreak zone of emergent plants 9 shall be established to reduce wind disturbance to the lake water, improve the retention environment and living space of microorganisms and aquatic organisms in the lakeside zone 3, and effectively improve the water environment quality of coastal waters.
[0043] In the shallow water area 4, the bottom of the lake is selected to be flat, and the submerged plants 6 are transplanted in the water area with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com