Method for computer-implemented simulation of LIDAR sensor in virtual environment
A virtual environment and sensor technology, applied in computing, 3D image processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high risk and high cost of accidents, and achieve the effect of simplifying evaluation and saving computing resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
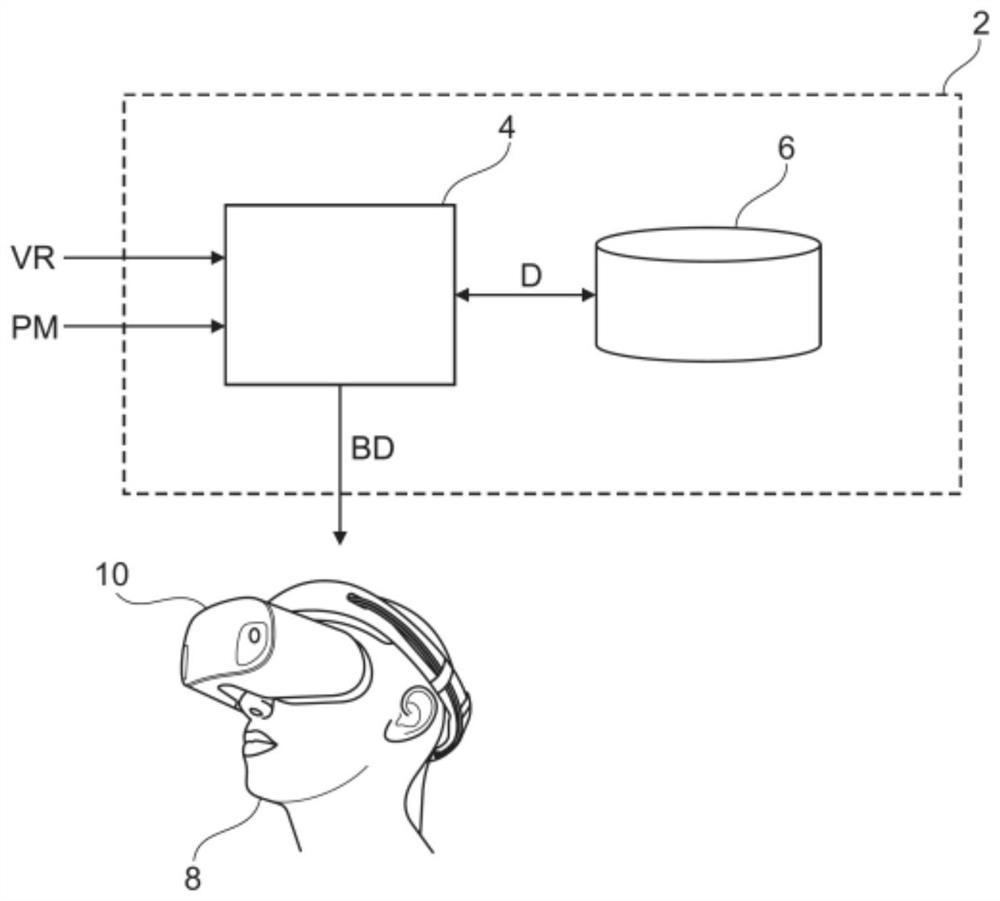
[0037] First refer to figure 1 .
[0038] It shows a system 2 for computer implementation of simulated LIDAR sensors in a virtual environment.
[0039] Virtual reality, or simply VR, denotes the representation and simultaneous perception of reality and its physical properties in an interactive virtual environment generated by a computer in real time.
[0040] To create a sense of immersion, specific output devices, such as virtual reality headsets, are used to represent the virtual environment. In order to give a spatial impression, two images are generated and represented from different angles (stereoscopic projection).
[0041] In order to interact with the virtual world, specific input devices (not shown), such as a 3D mouse, data glove or flight stick are required. The flying stick is used for navigation through an optical tracking system, where an infrared camera permanently informs the system 2 of the position in space by capturing a marker located on the flying stick...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com