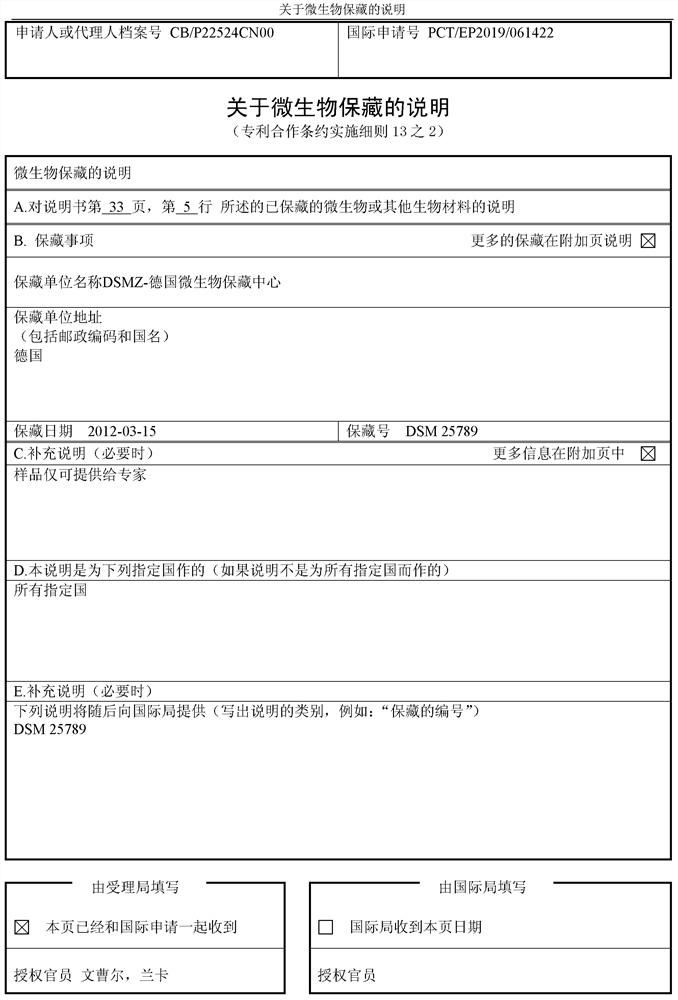
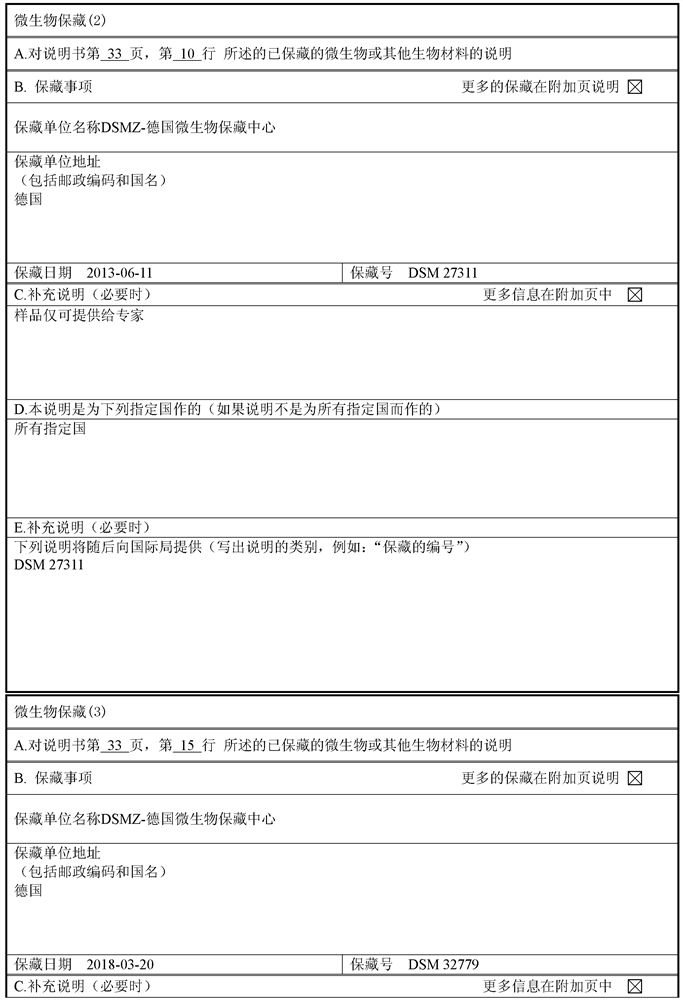
Improved recovery of nitrate reductase activity
A technology of reductase and nitrate, applied in the field of nitrate reductase activity, can solve the problems of loss of nitrate reductase activity, no disclosure of stabilization, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0225] Preparation of Staphylococcus carnosus
[0226] Formulation 1:
[0227]
[0228] Formulation 2:
[0229] Sodium ascorbate: 27.8%
[0230] Inositol : 15.6%
[0231] Water: 56.6%
[0232] The formulation was boiled at 100°C for 20 minutes. The doses of the preparations were 100 g of S. carnus concentrate mixed with 8 g of Preparation 1, and 100 g of S. carnus concentrate mixed with 12.4 g of Preparation 2, and 100 g of S. carnus concentrate was used as a negative control (no addition of any Protective agent). After mixing, samples were kept at -50°C, then freeze-dried and ground.
[0233] Nitrate reductase activity (NRA) was measured before and after lyophilization.
[0234] The conversion rate of nitrate to nitrite (nitrate reductase activity) of the Staphylococcus species in question was determined by measuring the concentration of nitrite to a given time, for example as in the example herein In the kinetic setup of the Griess test described in (Reference: Co...
Embodiment 2
[0239] Preparation of Staphylococcus calf
[0240] Formulation 1:
[0241]
[0242]
[0243] Formulation 2:
[0244] Sodium ascorbate: 27.8%
[0245] Inositol : 15.6%
[0246] Water: 56.6%
[0247] Formulations 1 and 2 were boiled at 100°C for 20 minutes.
[0248] The doses of the formulations were 100 g of S. bovis concentrate mixed with 8 g of formulation 1, and 100 g of S. bovis concentrate mixed with 12.4 g of formulation 2, and 100 g of S. carnus concentrate used as a negative control (without Add any preservatives). After mixing, samples were kept at -50°C, then freeze-dried and ground. Nitrate conversion, or NRA, was measured before and after freeze-drying. The conversion rate of nitrate to nitrite (nitrate reductase activity) of the Staphylococcus species in question was determined by measuring the concentration of nitrite to a given time, for example as in the example herein (Reference: Colorimetry and Spectrophotometry" Vogel's Textbook of Quantitative ...
Embodiment 3
[0253] Effect of Different Formulations Containing Inositol and Citrate on Nitrate Conversion Ratio (NRA) of Staphylococcus carnosus
[0254] Different formulations containing inositol were prepared according to Table 3 below. In the formulation, trisodium citrate monohydrate or sodium ascorbate is used in combination with inositol.
[0255] The formulation was boiled, mixed with S. carnus concentrate, frozen and lyophilized as described in Example 1. Nitrate reductase activity was measured as described above.
[0256] Table 3: Different formulations of inositol and citrate
[0257]
[0258] As shown in Table 4 below, freeze-dried products were obtained.
[0259] Table 4: Comparison of NRAs of inositol formulations
[0260]
[0261] As can be seen from the table above, the use of an AI formulation comprising ascorbic acid and inositol was compared to a CI formulation comprising citric acid and inositol, as measured by the nitrate conversion ratio (NRA) of Staphyl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com