Space debris orbit rapid evolution method
A space debris and orbit technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as large computing costs, space debris orbit consumption, and a large number of debris, to ensure orbit accuracy, speed up orbit evolution, and reduce Computational Efficiency Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] A high-efficiency space debris orbit rapid evolution method, the orbit evolution of the method is divided into the following five steps:
[0051] Step 1. Use the space disintegration model of NASA to simulate the space disintegration of a certain spacecraft, and obtain a series of fragments of different sizes, as well as the corresponding area-to-mass ratio, mass and velocity increment (produced by disintegration).
[0052] The amount of debris produced by disintegrating the model is determined by formula (1):
[0053] N(L c ) = S6L c -1.6 (1)
[0054] Among them, L c is the characteristic length, S is a parameter, determined according to the disintegration model.
[0055] Then the surface-to-mass ratio of each fragment is determined by the binormal distribution (2):
[0056]
[0057] Among them, γAlg (η), η=A / M; θAlg (L c ); ε(θ) is the weight coefficient, which is determined by different disintegration types. mu i and σ i are the mean and variance of the...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Step 1, establishing the gravitational field model at the center of the earth and the dynamics model in the case of perturbation of space debris;
[0078] Step 2, constructing the computer algorithm and polynomial integral algorithm of Taylor polynomial automatic approximation;
[0079] Step 3, describe the initial velocity increment of the space debris in polynomial form, and perform Taylor polynomial approximation on the vector field of the ordinary differential equation describing the motion law of the space debris;
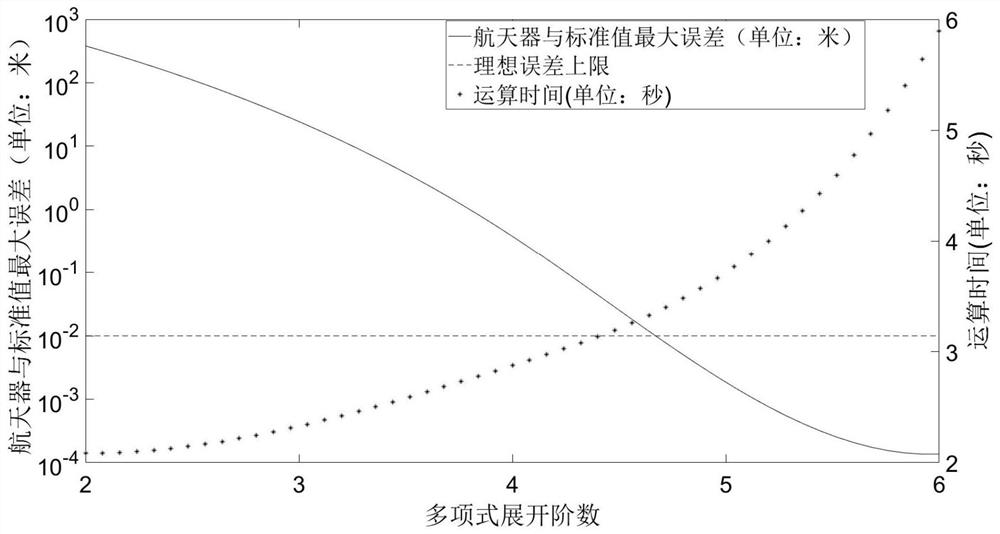
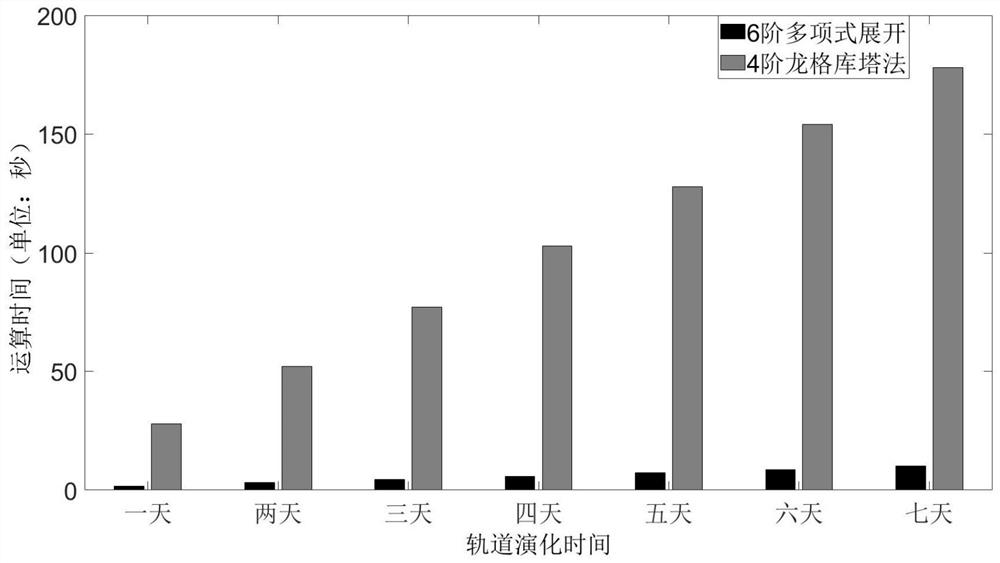
[0080] Step 4: Using the polynomial integration method, the polynomial differential equation obtained in step 3 is integrated along time to obtain a polynomial state solution at a certain moment. It is worth noting that the approximation error of this solution depends on the order of the Taylor expansion order, the size of the initial velocity increment and the time length of the orbital evolution;
[0081] Step 5. Substitute the velocity increments of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com