Linear array push-broom CCD image rapid automatic geometric correction method
A geometric correction and image technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as unable to meet actual needs, unable to achieve automatic correction, limitations, etc., to achieve the effect of fast automatic geometric correction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The derivation of the mathematical model formula of the linear array push-broom CCD image rapid automatic geometric correction method of the present invention
[0041] The basic principle of this calibration method
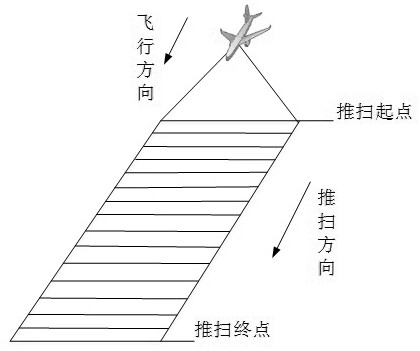
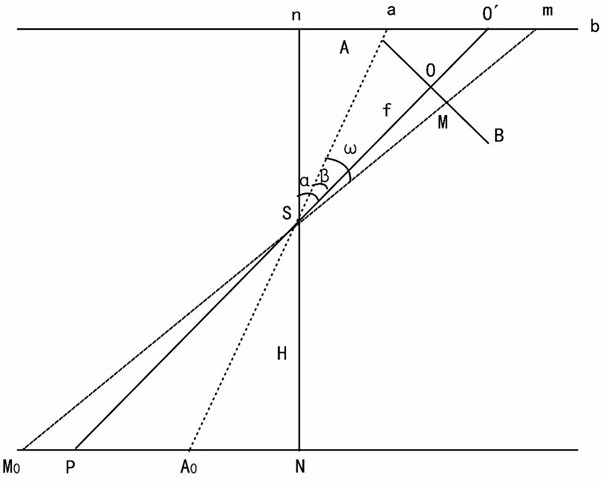
[0042] If the linear array push-broom CCD camera is installed obliquely, the scale of the oblique image along the oblique direction will not be uniform, resulting in deformation, which cannot reflect the positional relationship of the real ground objects. The linear array push-broom CCD camera images a line at every moment, which can be figure 1 Each line of the entire image from the push-broom start point to the push-broom end point is corrected separately to complete the correction of the entire image. The geometric relationship of the linear array push-broom CCD image at a certain moment of imaging is as follows: image 3 As shown, AB represents the linear array push-broom CCD image line at this moment, and ab represents the line in the corresponding o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com