Boundary condition setting method for processing irregular frequency in ship hydrodynamic calculation
A boundary condition and hydrodynamic technology, applied in computer-aided design, calculation, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as irregular frequency and no obvious improvement in calculation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0073] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
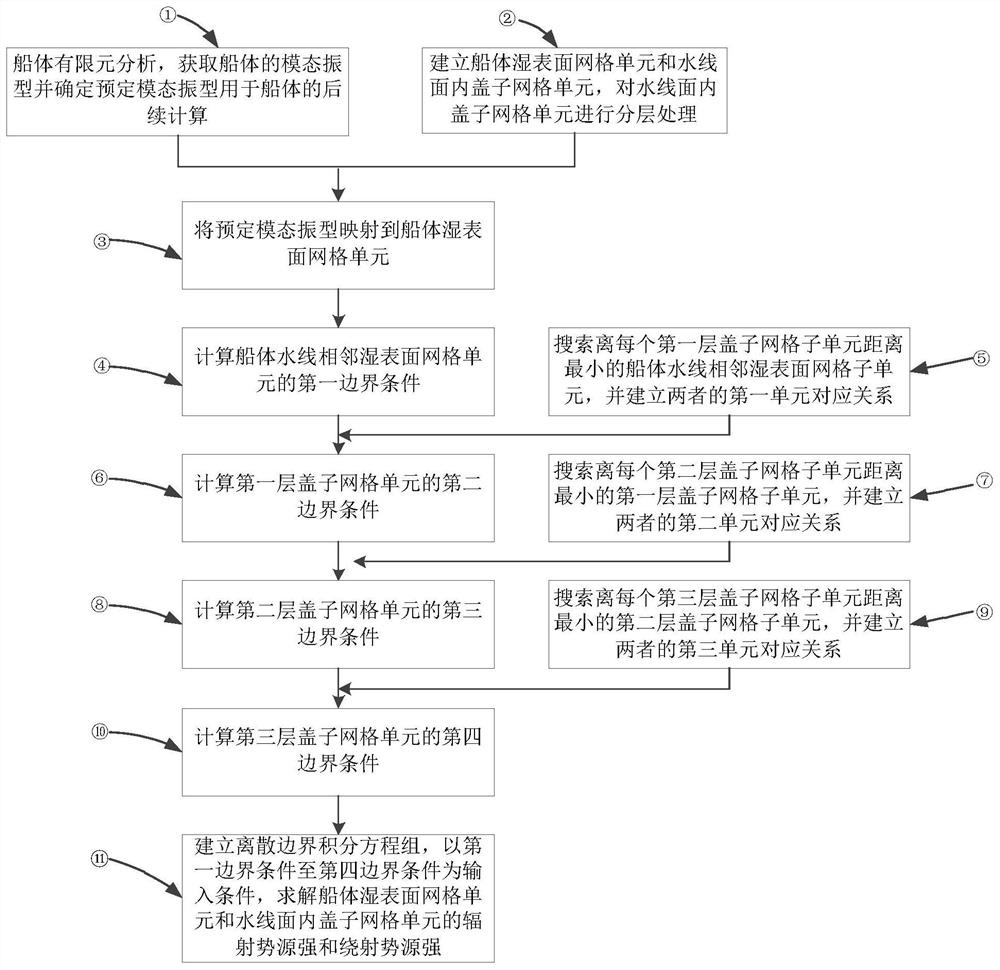
[0074] This application discloses a method for setting boundary conditions for dealing with irregular frequencies in ship hydrodynamic calculations. The flow chart of the method is as follows figure 1 As shown, this method is suitable for the hydroelastic calculation of straight-walled ships, including the following steps:
[0075] Step 1: Establish a three-dimensional finite element model of the hull, solve its mode shape and determine the predetermined mode shape.
[0076] According to the dynamic overall equation of the hull structure, the mode shape of the three-dimensional finite element model of the hull is solved, and the expression of the dynamic overall equation is:
[0077]
[0078] Among them, [M] is the total mass matrix, [C] is the total damping matrix, [K] is the total stiffness matrix, {U} is the motion response of the tot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com