MicroRNA biosensor for triggering 3-D double-leg DNA walker through exponential amplification reaction
A technology of biosensor and exponential amplification, applied in the direction of microbial measurement/inspection, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of limiting the walking efficiency of the total number of walkers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
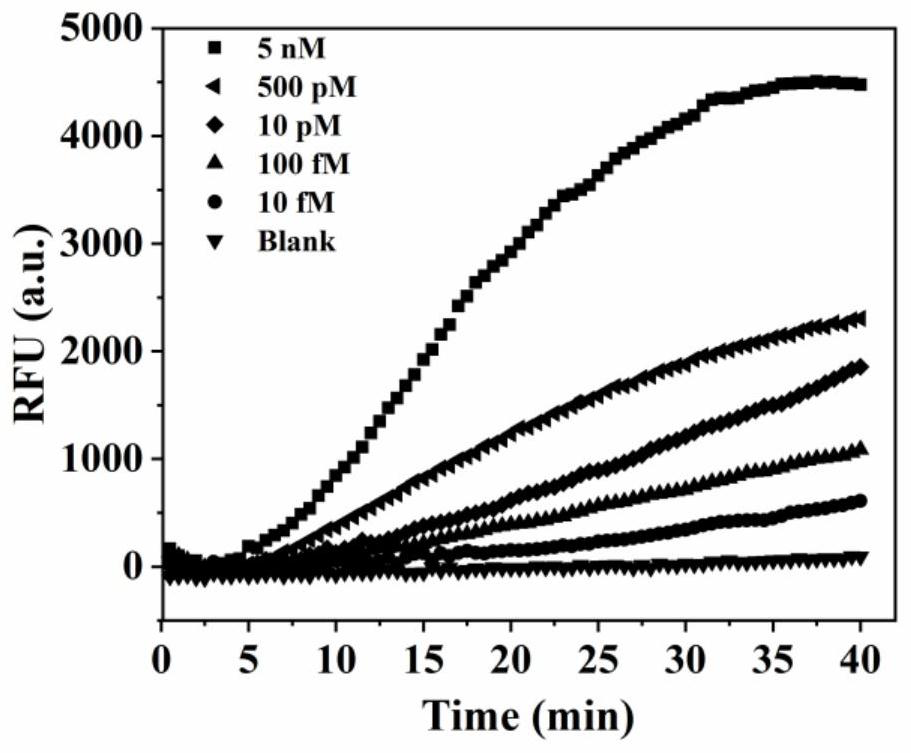
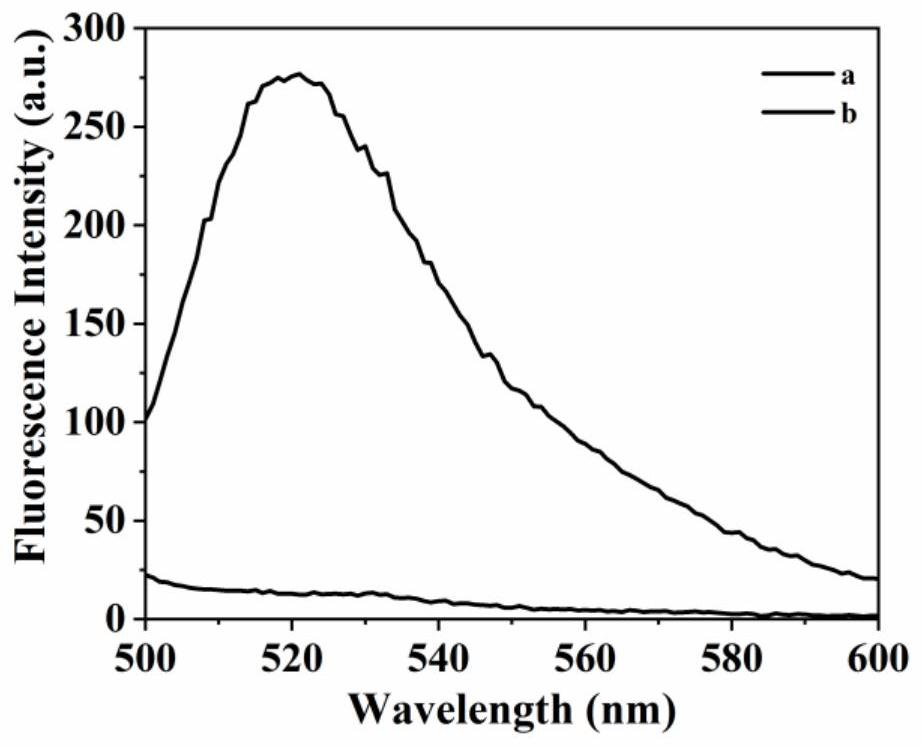
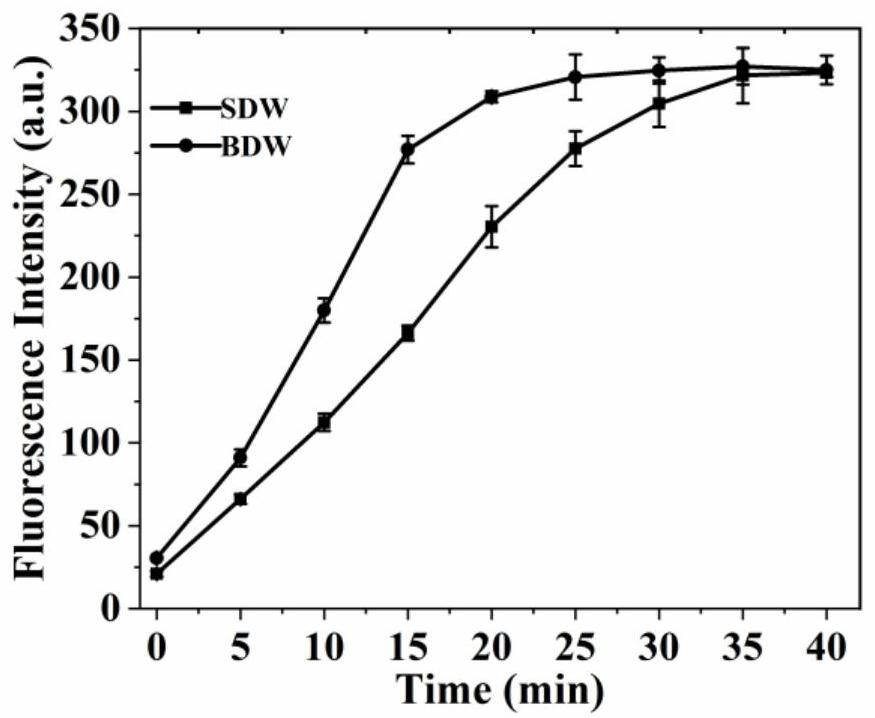
[0037] To prepare a biosensor based on a 3-D double-legged DNA walker triggered by an exponential amplification reaction, the steps are as follows:
[0038] (1) Isothermal Exponential Amplification Reaction (EXPAR) First, mix 100nM template, various concentrations of target microRNA, 1μL 10×CutSmart buffer and 1μL 10×NEBuffer 2, and heat in a water bath at 95°C for 5 minutes, then Slowly lower to room temperature. Then, 0.2 U of KF polymerase, 1 U of Ns.BsmAI, 250 μM dNTPs and DEPC-treated water were added to the mixture so that the final volume was 10 μL. Amplification reactions were performed at 37°C for 30 minutes. Finally, the reaction system was terminated by an enzyme inactivation treatment at 80° C. for 20 minutes. Store this solution at 4 °C for future use.
[0039] (2) Preparation of DNA walker probes 50 μL of streptavidin-coated microspheres were washed twice with 50 μL of binding buffer by centrifuging the microspheres at 12,000 rpm for 3 minutes, and then discar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com