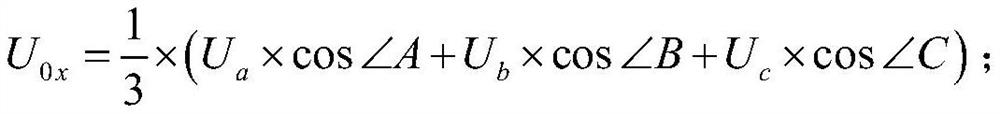Generator stator ground fault positioning method
A generator stator, ground fault technology, applied in motor generator test, phase angle between voltage and current, measurement of electrical variables and other directions, can solve the problems of generator closed bus damp, generator damage, long downtime , to avoid inaccurate calculation, simple calculation process and wide range of units
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0060] According to the article "Comparative Analysis of Multiple Stator Grounding Protection Accidents of the Same Unit" (Huang Xiaopeng et al.), the generator grounding accident case provided is used as an embodiment of the present invention.
[0061] The relevant parameters of the unit are as follows: the generator capacity is 630MW, each phase-to-ground capacitance is 0.27uF, the ground-to-ground capacitance of the generator outlet circuit breaker system (GCB) on the generator side is 0.14uF, the system-side GCB to-ground capacitance is 0.26uF, and the outlet rated The voltage is 20kV, the TV transformation ratio is 20kV / 100V, the neutral point resistance cabinet transformation ratio is 20kV / 500V, and the grounding resistance tap is selected as 0.295Ω (the total resistance value is 0.852Ω).
[0062] Accident 1: The voltage of phase A of the generator is 54.3V∠51.7°, the voltage of phase B is 57.7V∠-78.5°, and the voltage of phase C is 64.6V∠169.6°.
[0063] Accident 1 is a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com