Target re-identification method and system based on non-supervised pyramid similarity learning
A re-identification and similarity technology, applied in the field of target re-identification, can solve the problems of inaccurate target model, poor performance, performance degradation, etc., and achieve the effect of simple and general feature block and good performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
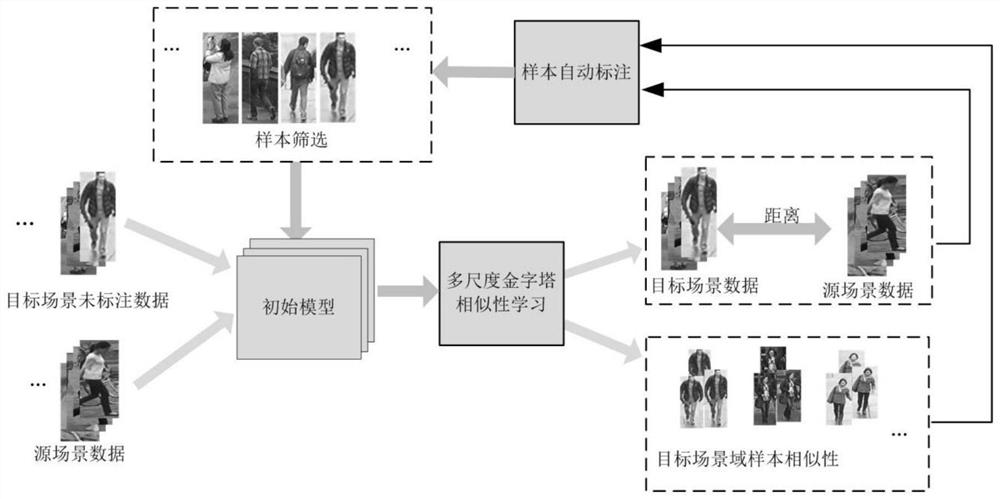
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the target re-identification method based on non-supervised pyramid similarity learning of this embodiment includes:
[0043] Step 1: Obtain the sample image to be queried and the image of the target scene domain;
[0044] Step 2: Output the target image in the target scene domain that matches the sample image to be queried through the target re-identification model;
[0045] Among them, the training and updating process of the target re-identification model is:
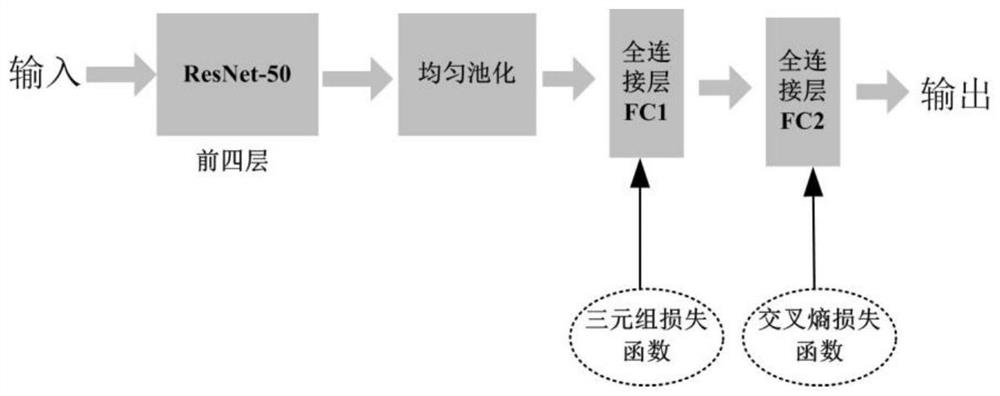
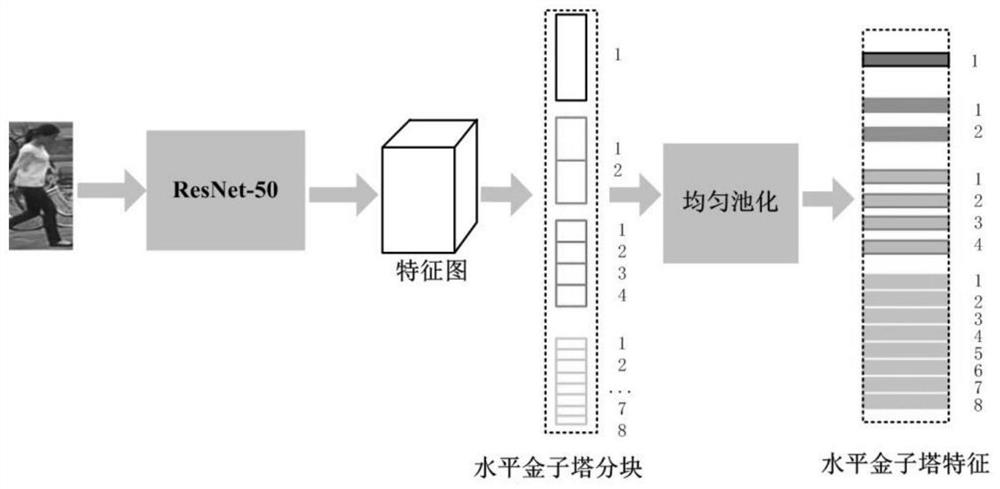
[0046] Unsupervised multi-scale horizontal pyramid similarity learning for source and target scene domain images;
[0047] According to the similarity, the sample images of the target scene domain are automatically marked and the training samples are selected to train and update the initial model to obtain the target re-identification model.
[0048] The labeled and filtered samples are used to continue training the model. After several iterations of training, the updated model wi...
Embodiment 2
[0095]The target re-identification system based on non-supervised pyramid similarity learning of the present embodiment includes:
[0096] An image acquisition module, which is used to acquire sample images to be queried and target scene domain images;
[0097] A target re-identification module, which is used to output a target image matching the sample image to be queried in the target scene domain through the target re-identification model;
[0098] Among them, the training and updating process of the target re-identification model is:
[0099] Unsupervised multi-scale horizontal pyramid similarity learning for source and target scene domain images;
[0100] According to the similarity, the sample images of the target scene domain are automatically marked and the training samples are selected to train and update the initial model to obtain the target re-identification model.
[0101] Each module of the target re-identification system based on non-supervised pyramid similar...
Embodiment 3
[0103] This embodiment provides a computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored. When the program is executed by a processor, the target re-identification method based on non-supervised pyramid similarity learning as described in the first embodiment above is implemented. step.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com