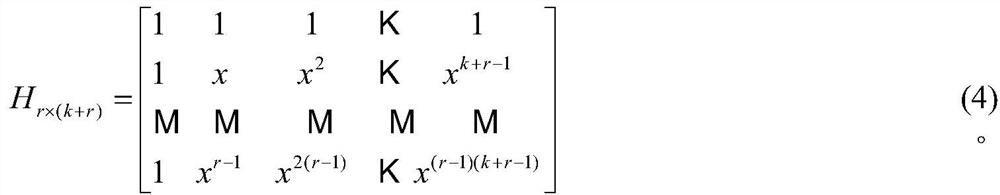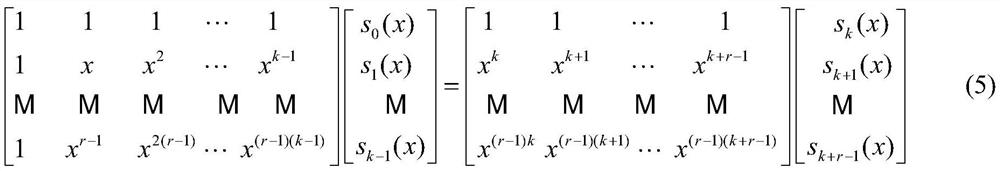Universal EBR encoding method and decoding method thereof
A technology of encoding method and decoding method, which is applied in the field of EBR encoding method and its decoding method, can solve the problems of high computational complexity of decoding method, low decoding efficiency, limited selection of EBR encoding parameters, etc., and achieve low decoding complexity and high decoding efficiency. The effect of high efficiency and low complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0059] Specific embodiment one: a kind of general EBR encoding method that this embodiment provides, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0060] Step 1, for the original k(p-1)τ information bits, define a pτ×(k+r) matrix, where τ is a positive integer, p is a prime number, k=p-r; 1≤ri,j Represents the elements of the i-th row and j-th column of the pτ×(k+r) matrix, i=0,1,...,pτ-1; j=0,1,...,k+r- 1; Given k(p-1)τ information bits s i,j , that is, the original k(p-1)τ information bits are sequentially used by s i,j To represent, take i=0,1,...,(p-1)τ-1 at this time; j=0,1,...,k-1;
[0061] Step 2, calculate the τ parity bits s in column j according to formula (2) (p-1)τ,j ,s (p-1)τ+1,j ,K,s pτ-1,j :
[0062]
[0063] where μ=0,1,...,τ-1; l=0,1,...,p-2;
[0064] Step 3. In order to determine other parity digits, set pτ in column j to s 0,j ,s 1,j ,K,s pτ-1,j Expressed as a quotient ring GF(2)[x]mod(1+x pτ ) in a polynomial s j (x)=s 0,j +s 1,j x+s 2,j x2...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0117] Specific embodiment two: a kind of universal EBR coded decoding method that this embodiment provides, described decoding method is in ring R pτ Based on the LU decomposition algorithm to solve the Vandermonde linear equation (LU decomposition is essentially an expression of the Gaussian elimination method, which essentially transforms the matrix into an upper triangular matrix through elementary row transformation), it can effectively solve the equations such as Formula (6), specifically includes the following process:
[0118] A. In the ring R pτ on 1+x b The division calculation of
[0119] Theorem 4: b is a positive integer, 1≤bb )g(x)=f(x)mod(1+x pτ The coefficient g of g(x) in ) j for:
[0120]
[0121] where j=0,1,...,n-1;
[0122] Other coefficients can be obtained iteratively: g bl+j = f bl+j +g b(l-1)+j ,in
[0123] Proof: (1+x b )g(x)=f(x), wherein, 1≤b
[0124] Solve for g(x), i.e. find 1+x b In the ring GF(2)[x] / 1+x pτ the ...
Embodiment 1
[0142] When r=3, a 3×3 Vandermonde matrix;
[0143] phalanx
[0144]
[0145] Calculate the complexity as follows:
[0146] Solving Linear Equations uL r (1) L r (2) …L r (r-1) u r (r-1) u r (r-2) …U r (1) =v can be carried out by the following steps: input: positive integer r, prime number p, integer a 1 ,a 2 ,...,a r ;v=(v 1 (x),...,v r (x))∈C pτ ;Output: u=(u 1 (x),...,u r (x))∈C pτ , and satisfy uV r×r (a)=vmod(1+x pτ );
[0147] Requirement: for all 1≤i 1 ≤ i 2 ≤r, with M pτ (x) is mutually prime in GF(2)[x];
[0148]
[0149]
[0150] Steps 2-4 require r(r-1) / 2 additions and r(r-1) / 2 multiplications, steps 5-9 require r(r-1) / 2 additions and r(r-1) / 2 divisions (factor ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com