Extraction method of bran coat cellulose and preparation method of bran coat fiber membrane
An extraction method and cellulose technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as complex components, difficult to recycle, and difficult to degrade, and achieve the effects of good light transmission, improved reaction ability, and good reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
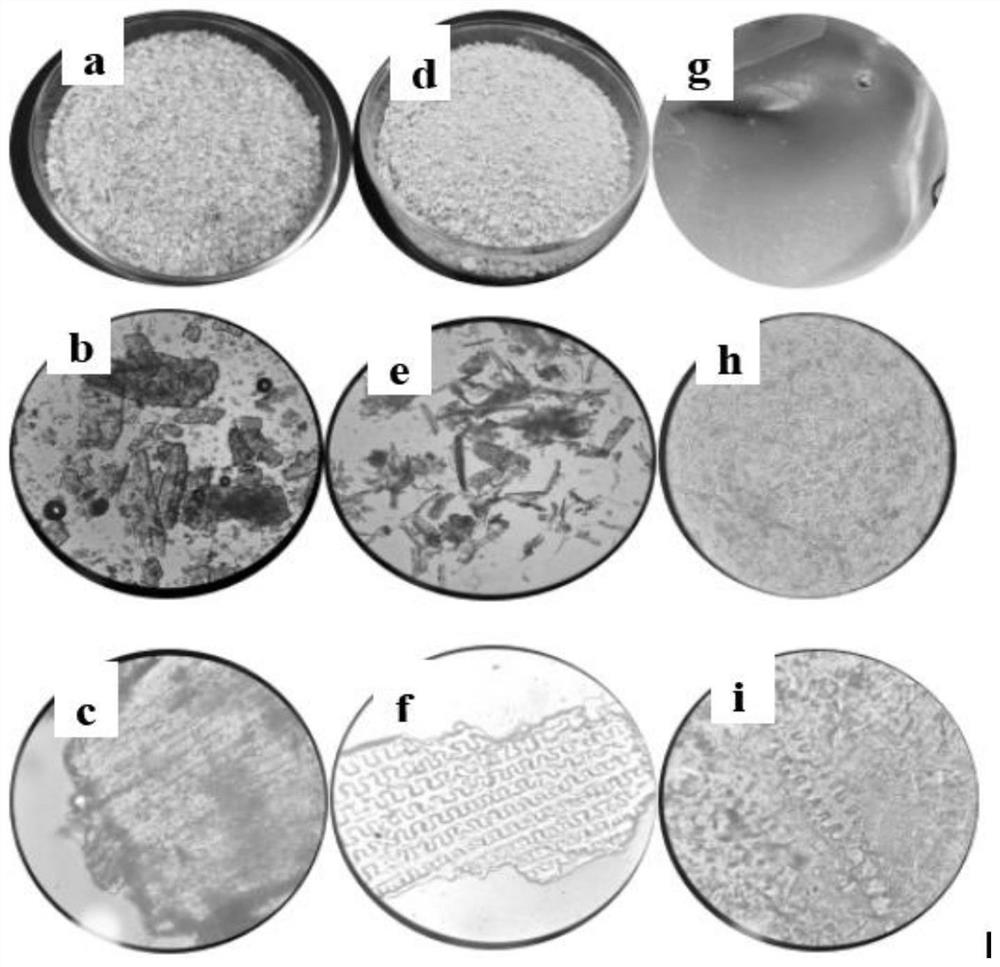
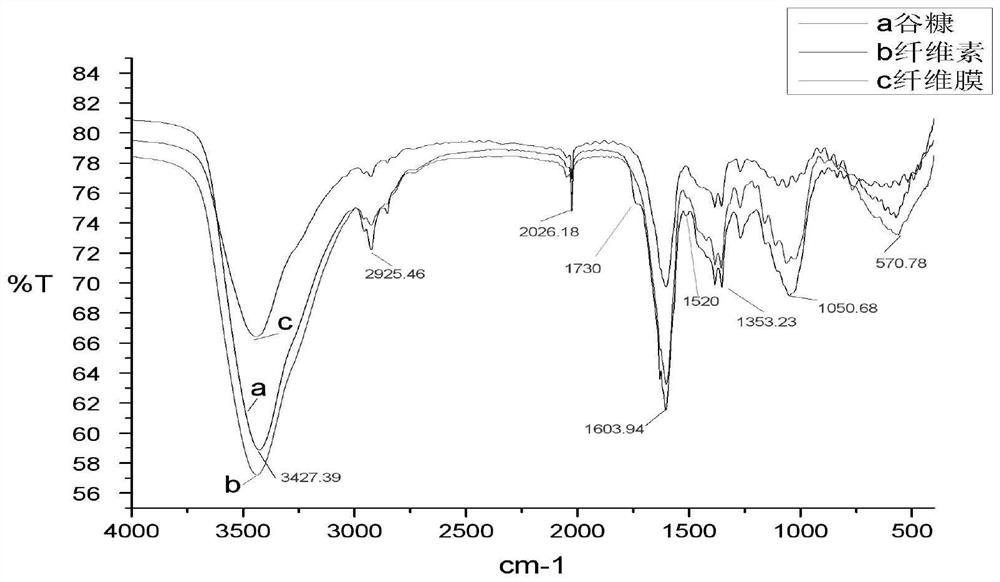
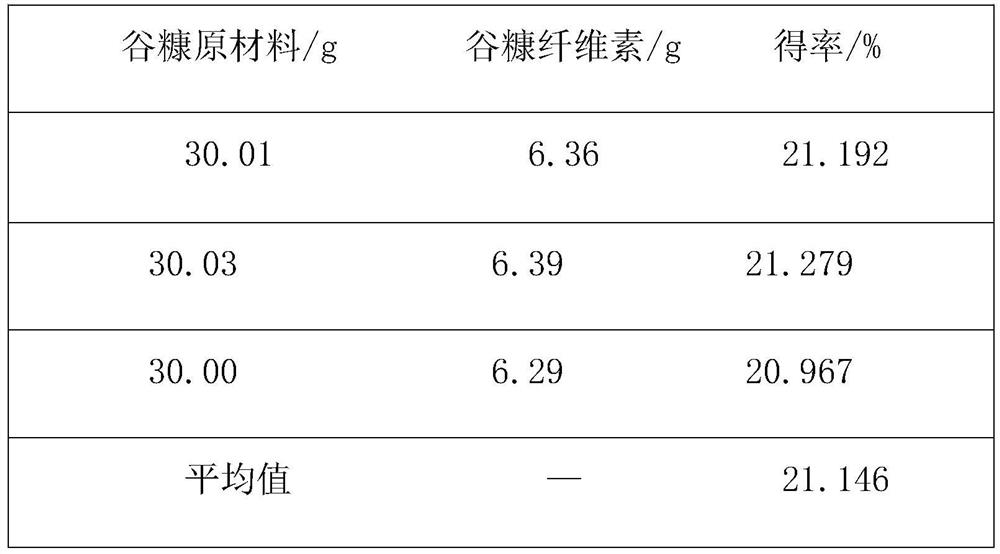
[0042]This embodiment relates to a method for extracting rice bran cellulose: fresh rice bran is cleaned after removing impurities, dried in an oven at 60° C., and passed through an 80-mesh sieve. Then take 30g of rice bran powder and treat it with 80wt% ethanol solution at 70°C for 4 hours, rinse the obtained residue with distilled water and dry it, and then wash it with 5wt% dilute H 2 SO 4 Treat at 120°C for 4 hours, wash the obtained residue with distilled water until it is neutral, and then dry it, then treat the residue with 9wt% NaOH solution at 100°C for 4 hours, and control the bath ratio to 1:20. Suction filtration after extraction is completed, wash with distilled water to neutrality and then dry, finally use 30wt% H 2 o 2 Place it at 90°C for 8 hours for decolorization treatment. After the reaction, wash the residue with distilled water, filter and dry to obtain relatively pure rice bran cellulose.
Embodiment 2
[0044] This embodiment relates to a method for extracting rice bran cellulose: fresh rice bran is cleaned after removing impurities, dried in an oven at 60° C., and passed through an 80-mesh sieve. Then take 30g of rice bran powder and treat it with 80wt% ethanol solution at 70°C for 4h, rinse the obtained residue with distilled water and dry it, and then wash it with 5wt% dilute H 2 SO 4 The solution was treated at 120°C for 4 hours, and the obtained residue was washed with distilled water until it was neutral, then dried, and then treated with 10 wt% NaOH solution at 100°C for 5 hours, and the bath ratio was controlled to be 1:30. Suction filtration after extraction is completed, wash with distilled water to neutrality and then dry, finally use 30wt% H 2 o 2 React at 90°C for 9 hours for decolorization. After the reaction, wash the residue with distilled water, filter and dry to obtain relatively pure bran cellulose.
Embodiment 3
[0046] This embodiment relates to a method for extracting rice bran cellulose: fresh rice bran is cleaned after removing impurities, dried in an oven at 60° C., and passed through an 80-mesh sieve. Then take 30g of rice bran powder and treat it with 80wt% ethanol solution at 70°C for 5h, rinse the obtained residue with distilled water and dry it, and then wash it with 5wt% dilute H 2 SO 4 The solution was treated at 120°C for 5 hours, and the obtained residue was washed with distilled water until neutral and then dried, and then treated with 11wt% NaOH solution at 100°C for 6 hours, and the bath ratio was controlled to be 1:40. Suction filtration after extraction is completed, wash with distilled water to neutrality and then dry, finally use 30wt% H 2 o 2 Place it at 90°C for 10 hours for decolorization. After the reaction, wash the residue with distilled water, filter and dry to obtain relatively pure bran cellulose. In Examples 1-3 of the present invention, the comparison...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com