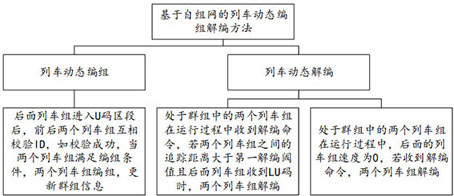
Train dynamic marshalling and un-marshalling method and system based on ad-hoc network
A train group and self-organizing network technology, applied in the field of transportation, to avoid high costs and improve departure efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0088] Dynamic marshalling example 1: The dynamic marshalling of a single vehicle tracking train group.
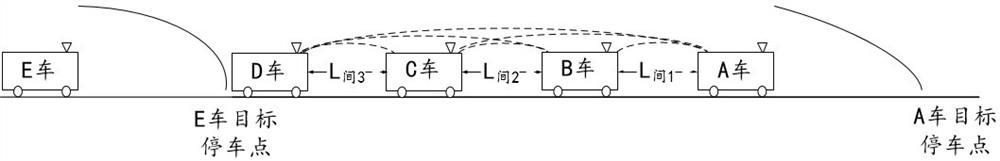
[0089] like figure 2 As shown, the train group Q{A,B,C,D} composed of train A, train B, train C and train D is running, and train E is normally tracking after the train group Q. Car A, car B, car C and car D communicate with each other through the ad hoc network established among them. Car E joins the ad hoc network and communicates with car A, which is not shown in the figure. The distance between car A, car B, car C and car D is L 间1 , L 间2 , L 间3 ; L 间1 Indicates the distance between the first train and the second train in the group network, L 间2 Indicates the distance between the second train and the third train in the group network, L 间3 Indicates the distance between the third train and the fourth train in the group network. Since A train, B train, C train and D train form a train group Q{A,B,C,D} to run, the train group Q controls A train, B train, C train ...
example 2
[0091] Dynamic grouping example 2: train group tracking dynamic grouping of bicycles.
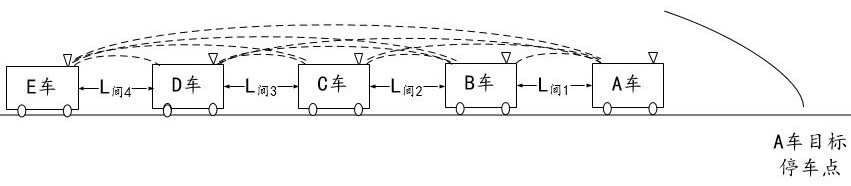
[0092] The train group Q{A,B,C,D} composed of A train, B train, C train and D train is tracking the normal operation of the previous train F, such as Figure 4 shown. If the current marshalling plan is train group Q{A,B,C,D} and train F train marshalling as train group Q'{F,A,B,C,D}, then train A will be shortened according to the plan and the preceding car F The distance between trains, when train A enters the U code section, train A and train F will verify IDs with each other. After the verification is successful, train A continues to run until the marshalling condition is met, and train group Q is marshalled with train F to form a new train group Q'{F,A,B,C,D}, such as Figure 5 shown. In the train group Q, the distances between trains A, B, C and D are L respectively 间1 , L 间2 , L 间3 . After forming a new train group Q', the distance between train F and train A is L 间1 , the dis...
example 3
[0093] Example 3 of dynamic grouping: train group tracking dynamic grouping of train groups.
[0094] A train group Q consisting of cars C and D 后 {C,D} is tracking the train group Q consisting of car B and car A ahead 前 {A,B} works normally, such as Image 6 shown. If the current marshalling plan is train group Q 后 {C,D} and Q 前 {A,B} is grouped into train group Q 合 {A,B,C,D}, then train C shortens the distance with the preceding car B according to the plan, when train C enters the U code section, car C and car A check each other’s ID. After the verification is successful, the C car continues to run until the marshalling condition is met, and the Q car 后 {C,D} and Q 前 {A,B} marshalling, forming a new train group Q 合 {A,B,C,D}, such as Figure 7 shown.
[0095] Specifically, the dynamic unmarshalling includes: a first demarring and a second demarring; the dynamic train demarring also includes: receiving a dismantling plan, and setting a dismantling command according ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com