Noninvasive ventilator
A ventilator and patient technology, applied in the medical field, can solve problems such as the destruction of normal physiological functions of patients, the loss of physiological functions of patients, and the increase of workload of medical staff.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
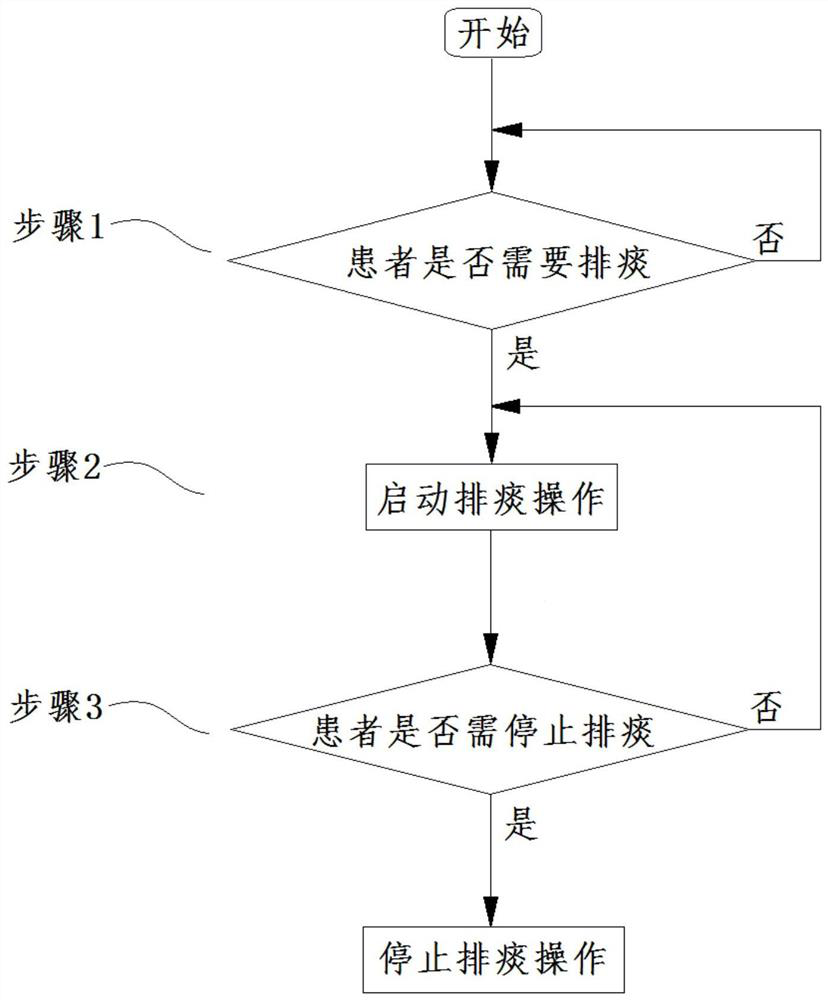
[0034] This embodiment provides an assisted expectoration method for a non-invasive ventilator, specifically, in the process of the non-invasive ventilator performing normal mechanical ventilation for the patient, after the non-invasive ventilator judges that the patient needs to expel Start the expectoration operation until it is judged that the patient needs to stop expectoration and stop the step of starting the above-mentioned expectoration operation in each respiratory cycle of the patient.
[0035] The assisted expectoration method for a non-invasive ventilator in this embodiment solves the problem of helping patients undergoing non-invasive ventilation to expel sputum. Especially when applied to a non-invasive ventilator, the solution to this problem can not only improve the success rate of non-invasive ventilation, reduce the number of invasive ventilation, but also improve the transition from invasive ventilation to non-invasive ventilation for patients who have been i...
Embodiment 2
[0057] refer to figure 2 In this embodiment, a non-invasive ventilator is provided, and the non-invasive ventilator can be used in the assisted expectoration method for the non-invasive ventilator provided in the first embodiment.
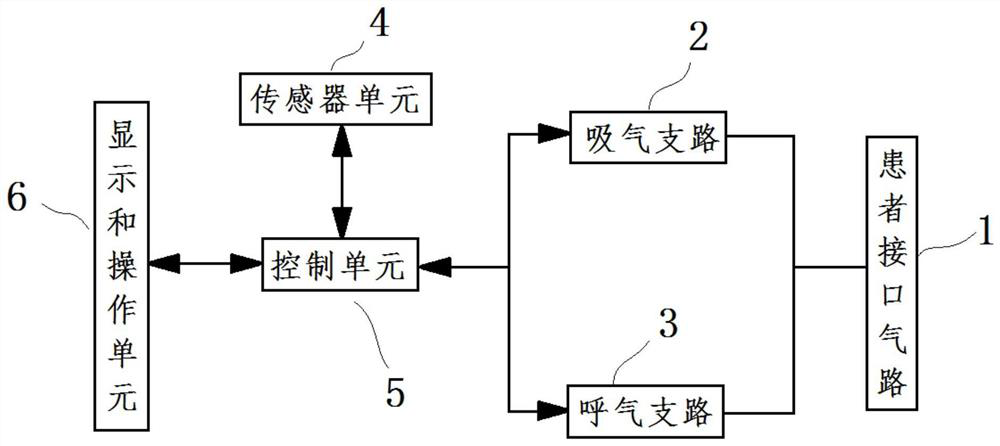
[0058] The non-invasive ventilator includes an inspiratory branch 2, an expiratory branch 3, a patient interface air circuit 1, a display and operation unit 6, a control unit 5, a sensor unit 4, a positive pressure air source (not shown in the figure) and a negative air source. Compressed air source (not shown in the figure).
[0059] Wherein, the positive pressure air source is arranged on the inspiratory branch 2 , and the negative pressure air source is arranged on the exhalation branch 3 .
[0060] Wherein, the sensor unit 4 can monitor the physiological data for judging whether the patient needs to expel sputum and whether to stop expectoration. In this embodiment, the sensor unit 4 includes a pressure sensor and a flow sensor arranged on t...
Embodiment 3
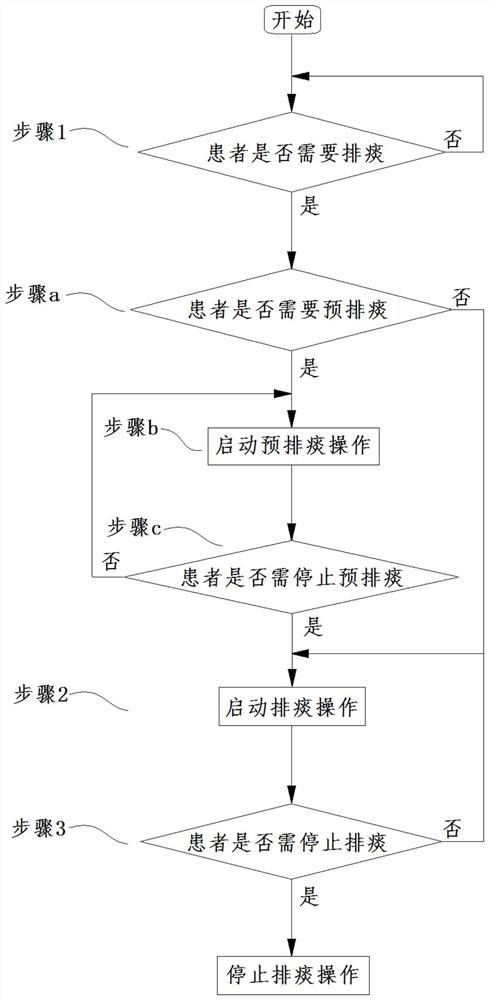
[0084] In this embodiment, on the basis of the first embodiment, the judgment and operation of pre-excretion are added. That is, after the non-invasive ventilator judges that the patient needs sputum removal, it judges whether the patient needs pre-sputum removal. Stop the pre-extraction operation and start the expectoration operation in each respiratory cycle of the patient; the non-invasive ventilator directly executes the expectoration operation in each respiratory cycle of the patient after judging that the patient does not need to perform pre-excretion.
[0085] Specifically, refer to image 3 , in this embodiment, the assisted expectoration method for the non-invasive ventilator is to perform the following steps during normal mechanical ventilation:
[0086] Step 1. The non-invasive ventilator judges whether the patient needs expectoration. If yes, perform step a. If not, repeat step 1. The judging method is the same as that in Embodiment 1 and will not be repeated her...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com