Preparation method of cross-linked hyaluronic acid microspheres
A technology of cross-linked hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid, which is applied in medical science, bulk delivery, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of difficult preparation of microspheres, low mechanical properties of microspheres, and difficult operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] This example mainly studies the effect of the sodium hyaluronate content in the aqueous phase on the cross-linked sodium hyaluronate microspheres. The preparation method is as follows:
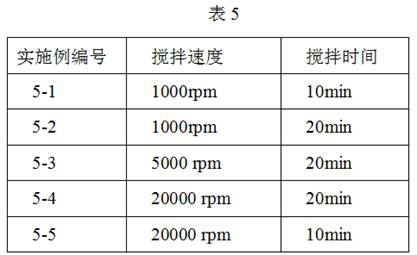
[0036] 1. Maintain a low temperature environment of 2-8°C, add 0.1g BDDE to 16mL water and mix well, then add sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight 2000KDa) of different quality, mix well to get gel 1, add 20 mL 1 to gel 1 Wt% NaOH solution was dispersed by a high-shear dispersing emulsification homogenizer at a speed of 5000 rpm for 10 min to obtain Gel 2, which is the aqueous phase.
[0037] 2. Add gel 2 to 400mL n-octane containing 2wt% Span80, emulsify with a high-shear dispersing emulsifying homogenizer at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and let stand to remove air bubbles after emulsification is uniform.
[0038] 3. After the emulsification is completed, the temperature of the emulsion is controlled at 30°C, and it is stirred for 12 hours to carry out cross-linking.
[0039] 4. After the...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This example mainly studies the effect of the amount of cross-linking agent in the water phase on the cross-linked sodium hyaluronate microspheres. The preparation method is as follows:
[0045] 1. Maintain a low temperature environment of 2-8°C, add BDDE of different qualities to 16mL water and mix well, then add 4 g sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight 2000KDa), mix well to obtain gel 1, add 20 mL 1 to gel 1 Wt% NaOH solution was dispersed by a high-shear dispersing emulsification homogenizer at a speed of 5000 rpm for 10 min to obtain Gel 2, which is the aqueous phase.
[0046] 2. Add gel 2 to 400mL cyclohexane containing 2wt% Span80, emulsify with a high-shear dispersing emulsifying homogenizer at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and let stand to remove air bubbles after emulsification is uniform.
[0047] 3, with embodiment 1.
[0048] 4, with embodiment 1.
[0049] 5. Same as embodiment 1.
[0050] The amount of crosslinking agent is shown in Table 2 below.
[0051]...
Embodiment 3
[0053] This example mainly studies the influence of crosslinking temperature and crosslinking time on crosslinked sodium hyaluronate microspheres. The preparation method is as follows:
[0054] 1. Maintain a low temperature environment of 2-8°C, add 0.1g BDDE to 16mL water and mix well, then add 4 g sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight 2000KDa), mix well to obtain gel 1, add 20 mL 1 wt% to gel 1 For NaOH solution, a high-shear dispersing emulsification homogenizer was used to break up the gel at a speed of 5000 rpm for 10 min to obtain gel 2, which is the aqueous phase.
[0055] 2, with embodiment 1.
[0056] 3. After the emulsification is completed, the temperature and time of the emulsion are controlled to carry out cross-linking.
[0057] 4, with embodiment 1.
[0058] 5. Same as embodiment 1.
[0059] The crosslinking temperature and crosslinking time are shown in Table 3 below.
[0060]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com