Method and system for monitoring hidden faults of power supply equipment
A technology for hidden faults and power supply equipment, which is applied in fault location, information technology support system, fault detection according to conductor type, etc. It can solve the problems of unsuitable traveling wave analysis method, difficult real-time application of ultrasonic monitoring method, and unpredictable fault point, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
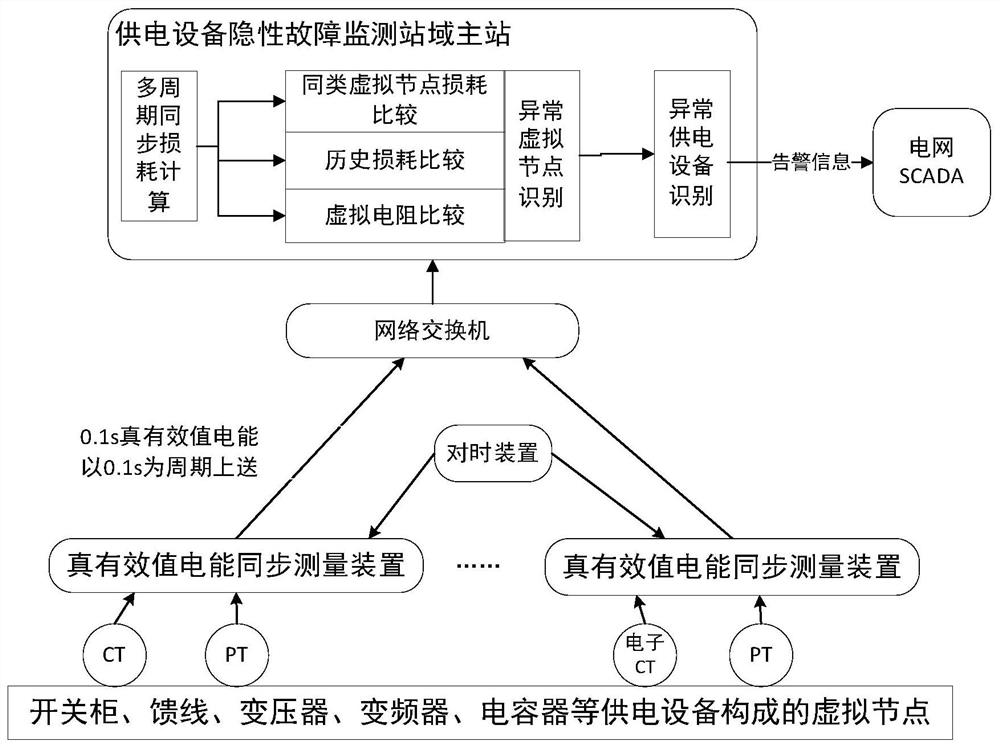
[0072] attached Figure 4 It is an example of a one-line diagram of a part of a 6kV / 0.4kV substation. In the figure, 401, 402, 403, and 404 are the numbers of the corresponding branch switch cabinets. The figure also exemplarily draws a remote power supply through cables. motor load. The operator hopes to timely discover the faults such as poor contact, discharge, insulation breakdown and other faults in the power supply equipment such as the switch cabinets, switches, and the cable joints of the power supply cables to the load. Timely detection and early warning of internal or external faults of power supply equipment such as transformers and capacitors. Embodiments using the methods and systems disclosed in this patent are as follows:
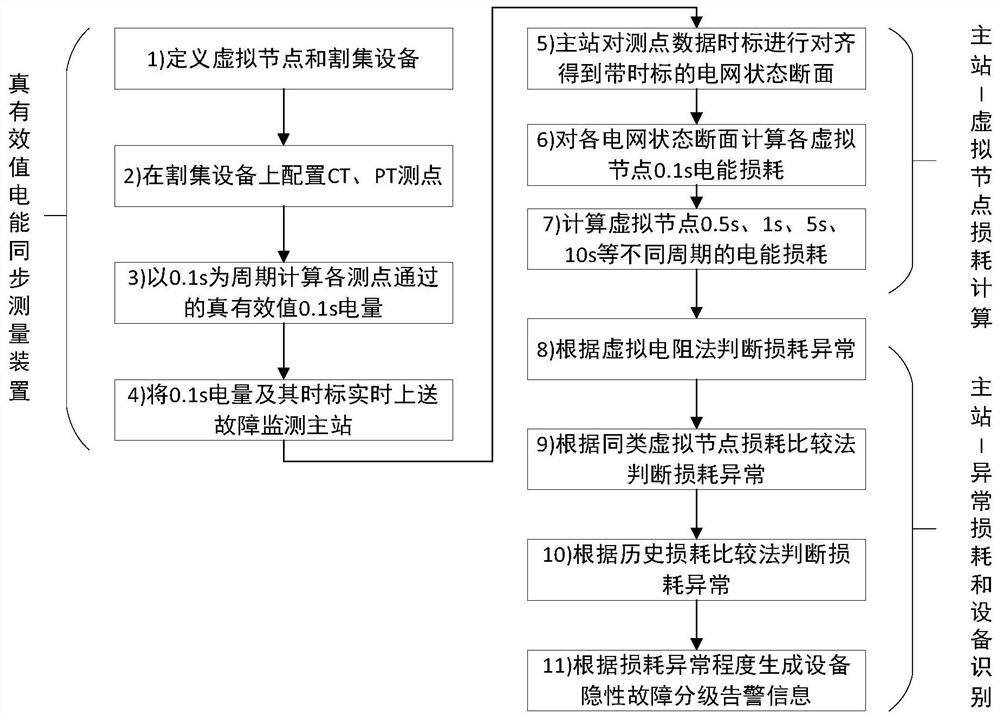
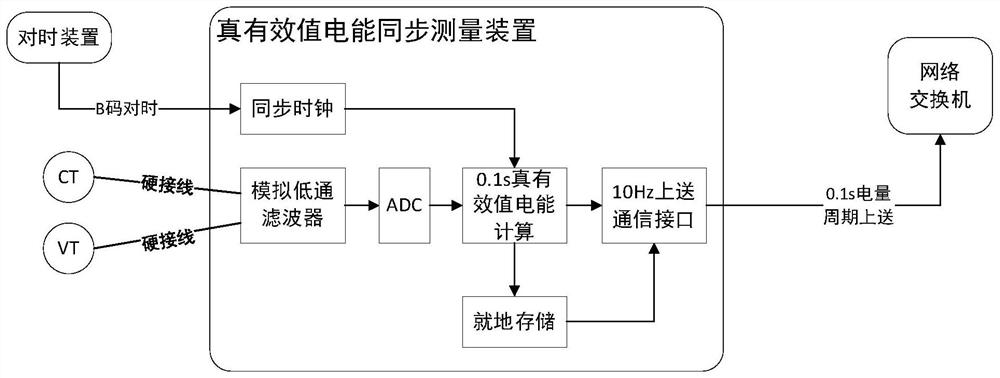
[0073] attached figure 1 Shown is a schematic flowchart of a method for monitoring a hidden fault of a power supply device based on the true RMS measurement of power loss disclosed in the present invention, and the method for monitoring a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com