Toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8)-specific antagonists and methods of making and uses thereof
An individual and dependent technology, applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve harmful autoimmune diseases and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0184] Example 1: Identification of potent and selective TLR8 inhibitors
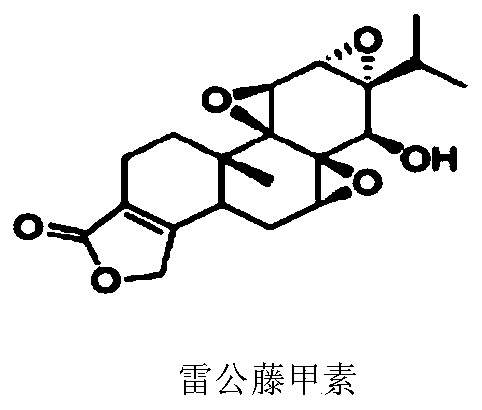
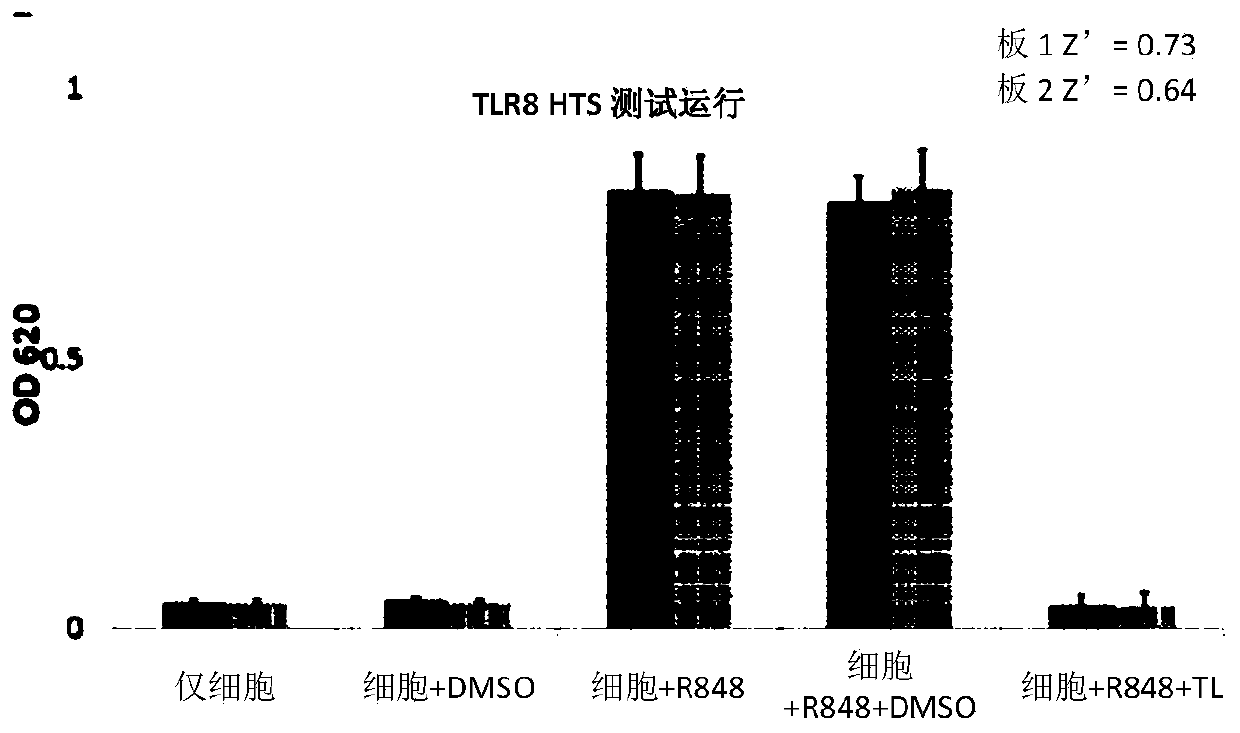
[0185] To establish a robust high-throughput assay for TLR8 inhibitors, the inventors first engineered cell lines that stably overexpress human TLR8, the activation of which can be reported by a secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) assay. TLR8 overexpressed HEK-Blue cells were prepared by lentiviral infection of HEK-Blue Null cells with basal expression of empty or low endogenous TLR genes. Overexpression and endosomal localization of human TLR8 were confirmed using confocal microscopy. TLR8-mediated NF-kB activation can be assessed by measuring SEAP activity. Using the previously established NF-kB inhibitor, triptolide (Figure 1), as a positive control, the measured Z' factor was 0.68 ( figure 2 ), demonstrating that the assay is reliable for high-throughput screening (HTS).
[0186] Next, the inventors screened a commercial library with 14,400 members (Maybridge HitFinder VI 1) containing...
Embodiment 2
[0195] Example 2: CU-CPT8m inhibits TLR8-mediated production of inflammatory cytokines
[0196] R848-induced activation of TLR8 leads to increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8. Next, the inventors investigated the inhibitory effect of CU-CPT8m in various cell lines. First, the inhibitory effect of CU-CPT8m on the mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines was investigated by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-PCR). Such as Figure 4D As shown, treatment with 1 μM CU-CPT8m completely abolished the R848-induced increase in TNF-α and IL-8 mRNA levels. In contrast, the inhibitory effect of the inactive analogue 4a was negligible.
[0197] The inventors then showed that CU-CPT8m significantly suppressed the protein levels of various cytokines. R848 treatment resulted in a marked increase in TNF-[alpha] production, reaching approximately 10-fold the maximum after 24 hours. Figure 4E demonstrated that CU-CPT8m inhibited R848-induced TNF-α produ...
Embodiment 3
[0199] Example 3: High resolution crystal structure of the CU-CPT8m-TLR8 complex
[0200] Previously, two ligand-binding sites have been identified for TLR7 and TLR8. In TLR8, site 1 is the binding site for RNA-degrading uridine and tricyclic imidazoquinoline ligands (such as R848 and CL097), while site 2 is bound by the dinucleotide UG (Cheng, K. , et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133:3764-67 (2011); Hennessy, E.J., et al., Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9:293-307 (2010)). The inventors determined a high-resolution X-ray crystal structure of the TLR8 / CU-CPT8m complex. Interestingly, the crystal structure indicates that CU-CPT8m is sandwiched between two promoters (TLR8 and TLR8*, throughout this disclosure an asterisk is used to indicate the second TLR8 and its residues) and is housed in the TLR8 and in the hydrophobic pocket of the protein-protein interface of TLR8*. This pocket is only formed in the preformed dimer at rest and is partially filled by several water molecules in the unliga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com