Method and system for measuring topological charges and positive and negative values of partially coherent vortex beams
A vortex beam and measurement part technology, applied in the field of optical measurement, can solve the problems of cumbersome, harsh conditions, difficult operation, etc., to achieve the effect of improving the success rate, reducing the harsh requirements, and simplifying the measurement process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and specific embodiments, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the present invention and implement it, but the examples given are not as limitations of the present invention.
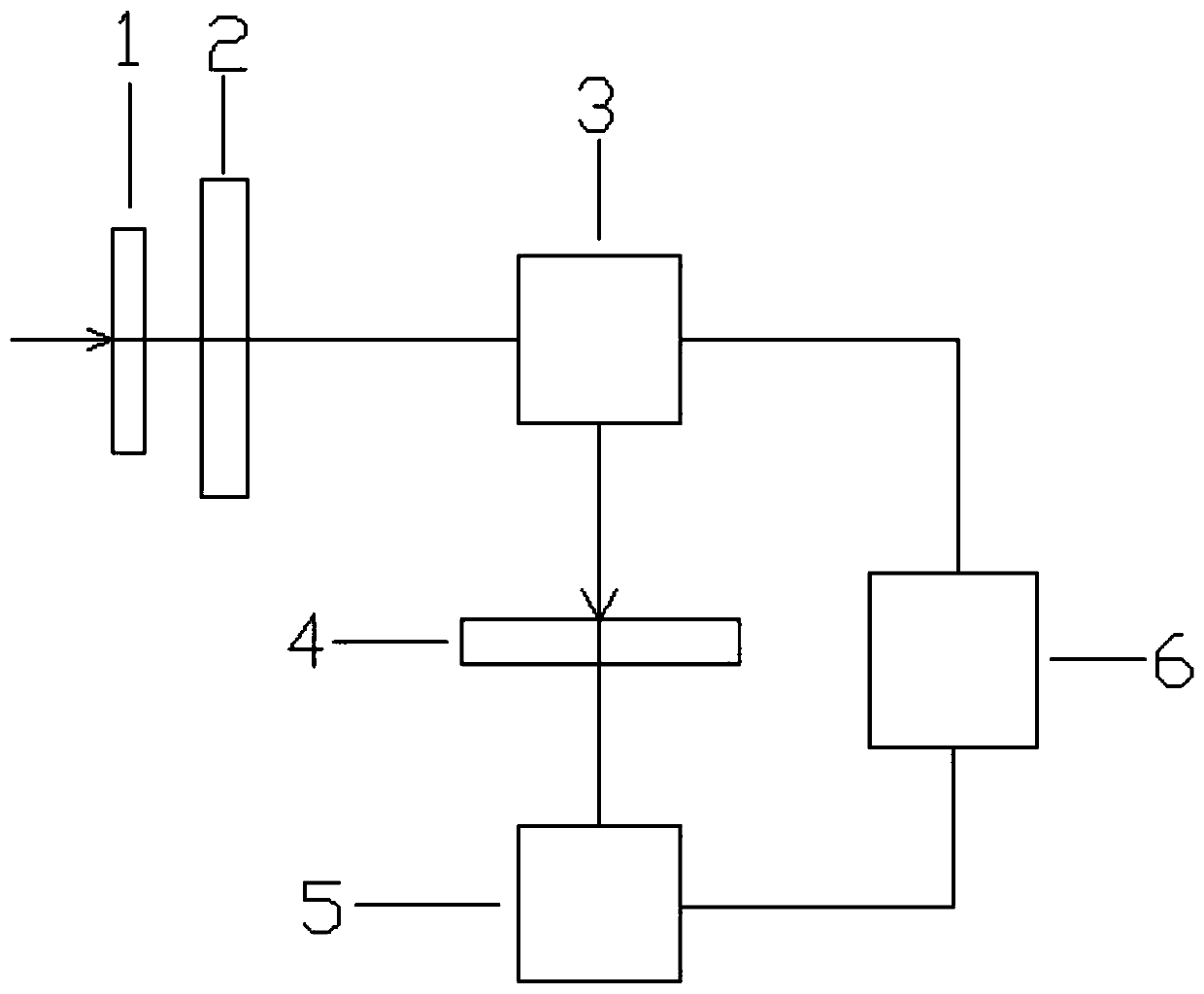
[0060] like figure 1 As shown, it is a method for measuring the topological charge of a partially coherent vortex beam according to an embodiment of the present invention, and the method includes the following steps:
[0061] Step S110, inject the partially coherent vortex beam into the double slit and interfere.
[0062] In one embodiment, the partially coherent vortex beam is generated by irradiating the partially coherent beam on a phase-only spatial light modulator loaded with a vortex phase.
[0063] Among them, the partially coherent vortex beam is incident on the double slit, and its cross spectral density expression is:
[0064]
[0065] where the double slit is next to the source pla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com