Light parallel intersection method based on many-core processor and optical path tracking system
A technology of many-core processors and rays, which is applied in the field of ray parallel intersecting method and optical path tracing system, can solve the problems of consuming calculation time and reducing the efficiency of optical path tracing algorithm, so as to improve computing efficiency, shorten optical path tracing time, and ensure rendering quality effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
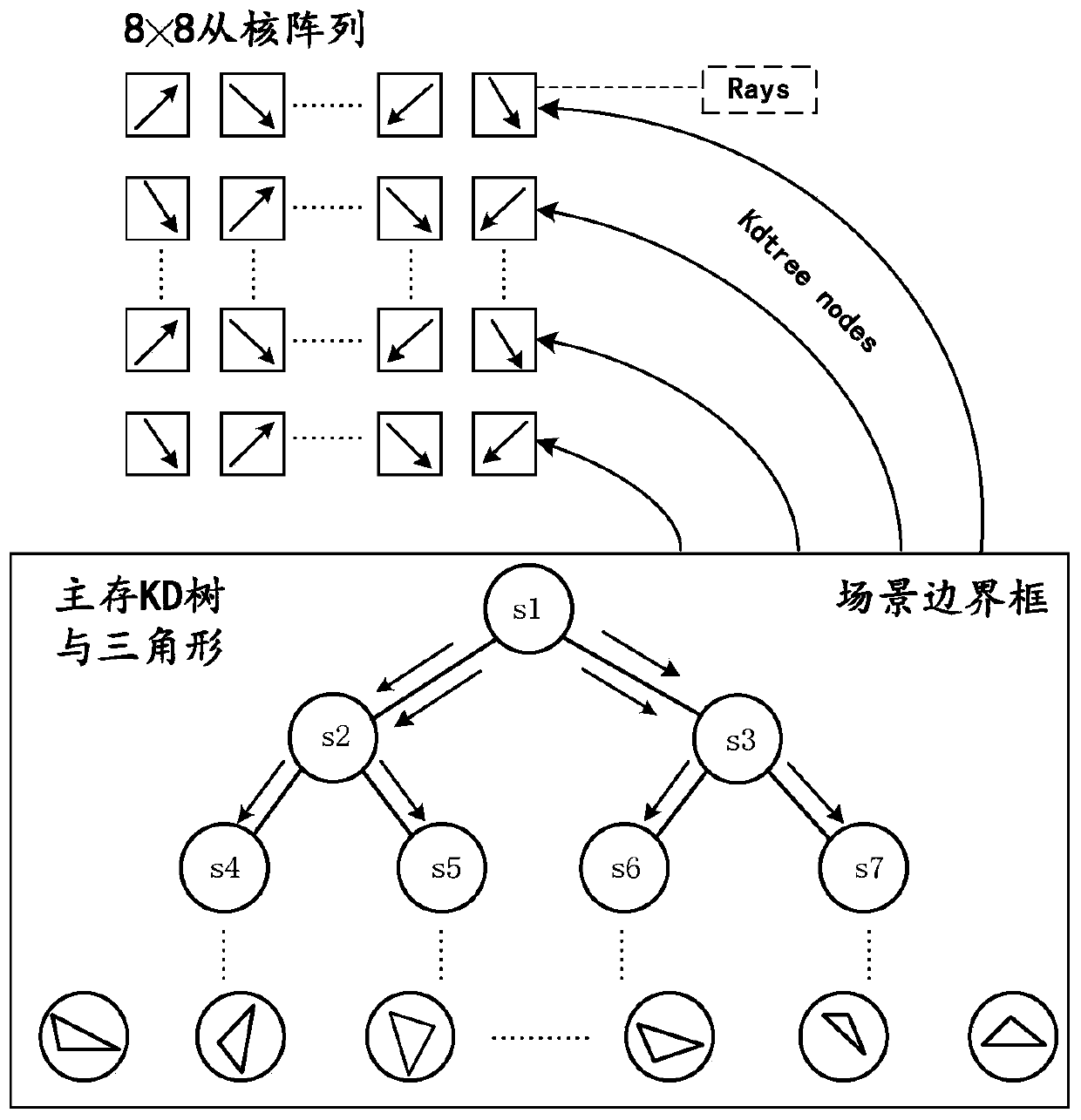
[0034] The light path tracing algorithm process is to launch a ray from the camera or observer’s point of view, and trace the ray in reverse according to the reversible optical principle of light. The ray first intersects with the scene, and then performs the coloring operation at the intersection point to generate reflected or refracted rays, namely The next ray (secondary ray) is traced until the ray intersects the light source. This is a complete optical path of a ray, and the integration is performed on this optical path to calculate the contribution value of this ray to the light radiance of a pixel.
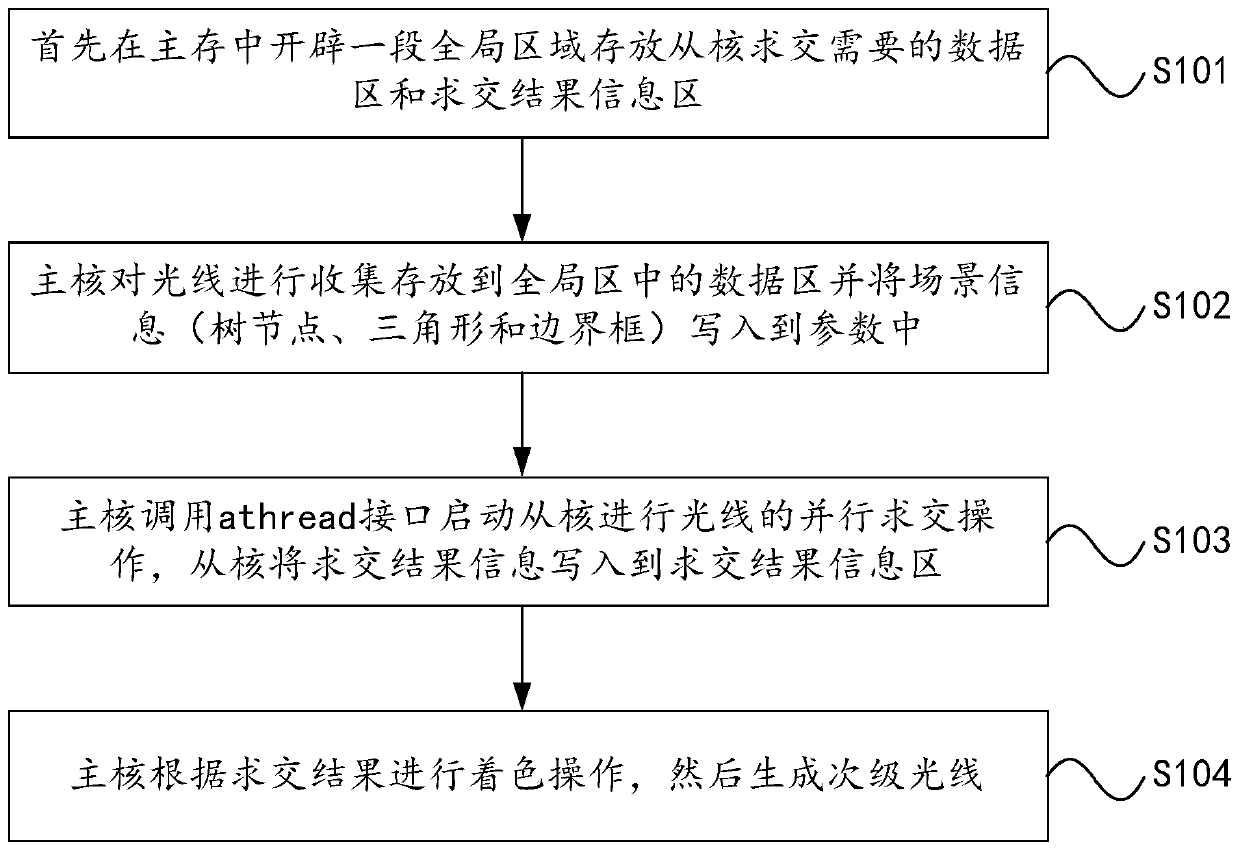
[0035] In this embodiment, a method for intersecting rays in parallel based on many-core processors is provided, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0036] Open up a global data area for storing sampling rays in the main core, perform ray intersection of the sampling rays in parallel from the checker, and store the intersection result in the global data area, and the main...
Embodiment 2
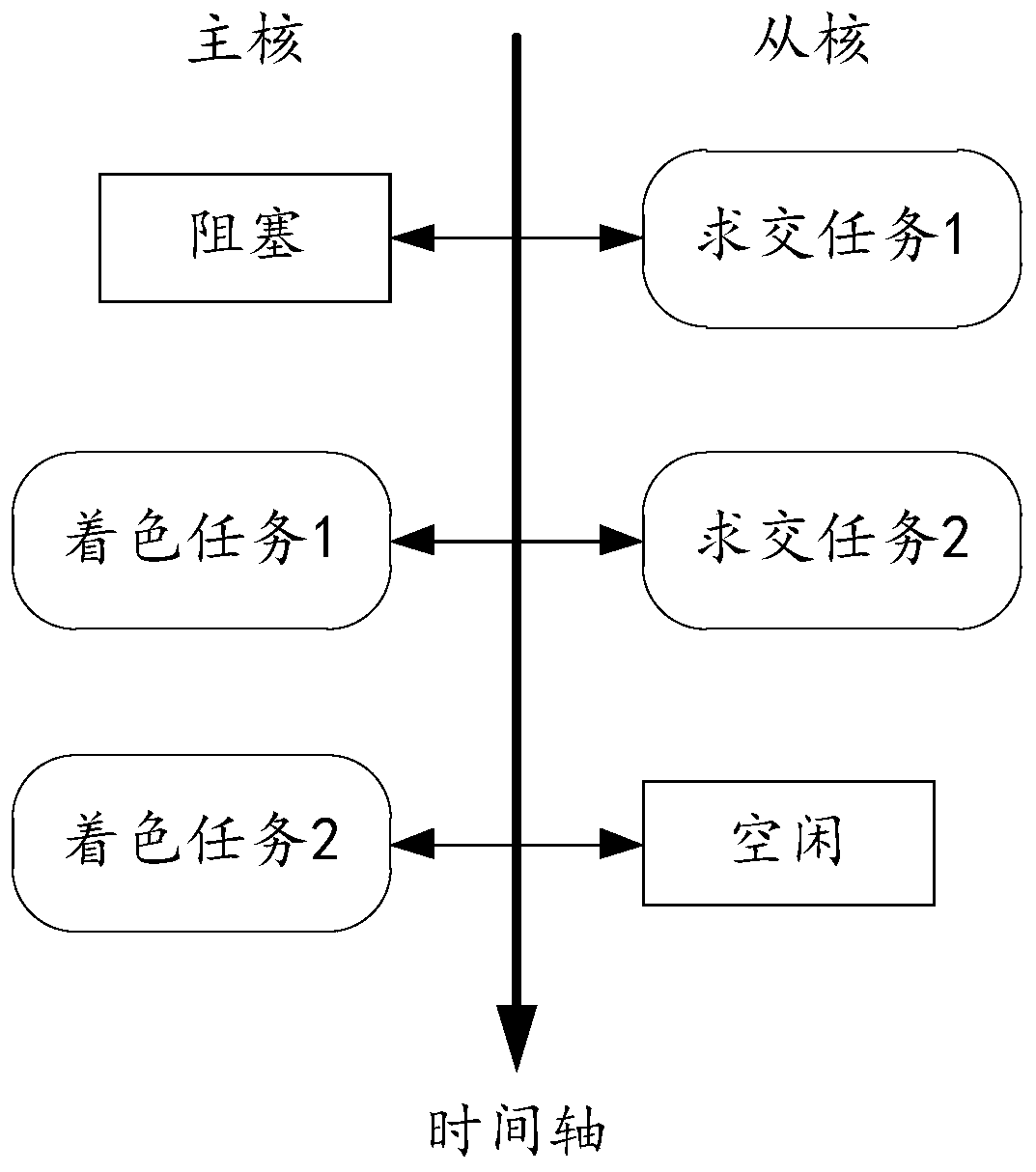
[0069] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment provides a parallel intersection method for ray occlusion judgment based on many-core processors, which executes the occlusion judgment after the intersection point samples the light source in parallel during the shading process, reduces the time consumed in the shading process, and effectively shortens the optical path. Tracked computation time, including:
[0070] Opening up a global data area for storing sampling rays in the main core, performing parallel intersecting of the sampling rays from the checker, and storing the intersecting results in the global data area; the main core performs coloring operations according to the intersecting results;
[0071] In the coloring operation, the light source is sampled according to the intersection point to obtain the shadow sampling light, and the shadow sampling light is checked in parallel to determine whether the shadow sampling light is blocked, and the main core updates the in...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this embodiment provides an optical path tracing system based on many-core processors, including several core groups, the core groups include master cores and slave cores, and the optical path tracing is divided in the master core of any core group , assign the divided light path tracing subtasks to other core groups;
[0092] The core group completes the steps described in the parallel intersecting method of rays based on many-core processors or the parallel intersecting method of ray occlusion judgment based on many-core processors.
[0093] The process of calling other core groups in the full-chip sharing mode is: initialize the runtime parameters of each core group, and distinguish the memory layout in each shared area to prevent concurrent reads and writes between core groups and the occurrence of dirty data. question;
[0094] Use the pthread library to initialize other core groups before running, and then hand over the executed work ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com