An Improved Load Redistribution Method Based on the Maximum Residual Capacity of Nodes
A technology of remaining capacity and load distribution, applied in digital transmission systems, safety communication devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as overload, high network cost, and cascading fault spread.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
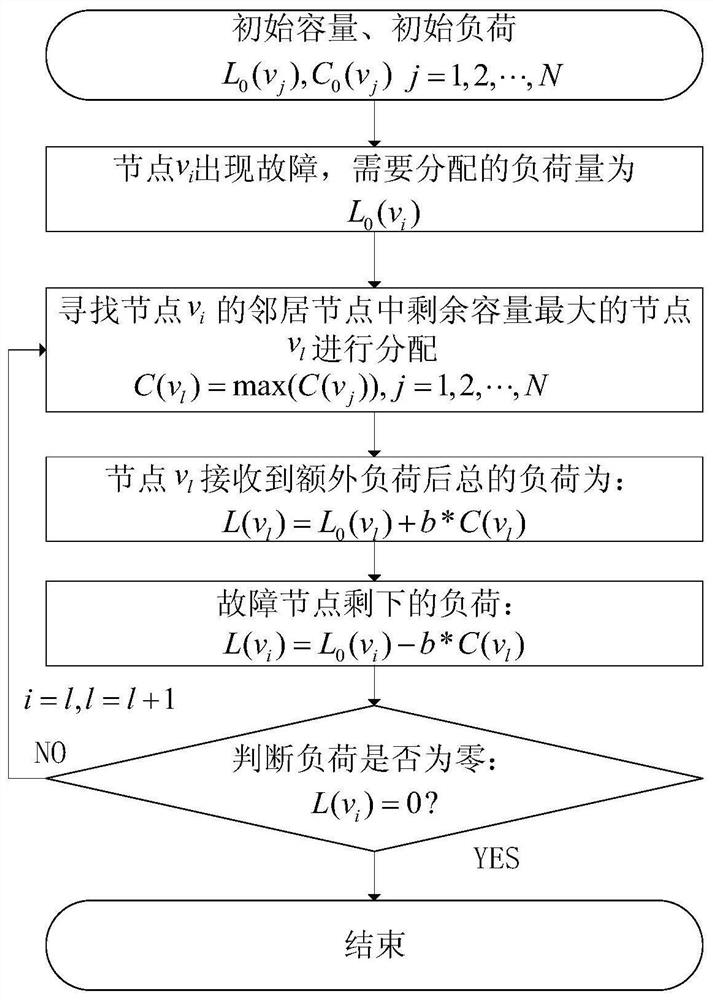
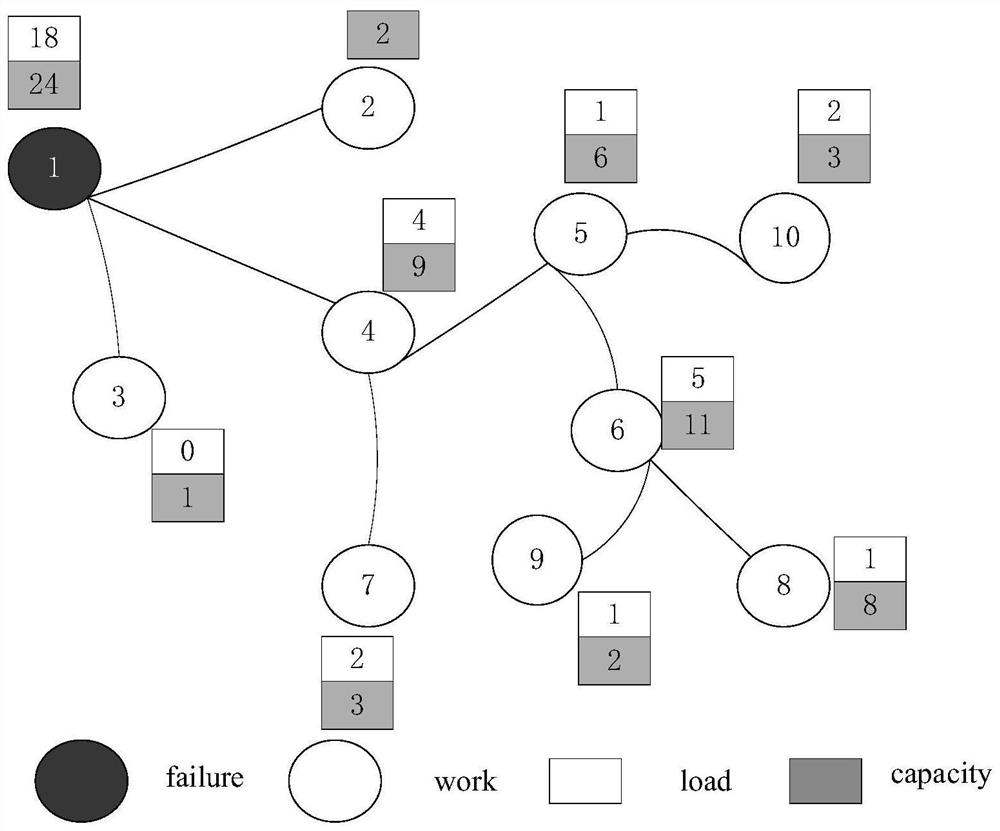
[0034] An improved load redistribution method based on the maximum remaining capacity of nodes, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0035] Step 1: Construct the network topology graph G=(V, E), where the node set V={v 0 ,v 2 ,...,v N}, v N is the node in the node set V, N is the number of nodes and N is a positive integer, E is the edge set, and initializes the complex network, where the initial capacity of the complex network is C 0 (v j )(j=0,1,2,…,N), the initial load is L 0 (v j )(j=0,1,2,...,N);
[0036] Step 2: Assume that the node v with the largest load in the network i (i=0) fails, the load to be distributed is L 0 (v i ).
[0037] Step 3: Select the allocation node, set node v i There are m neighbor nodes, load distribution first selects the node v with the largest remaining capacity among its neighbo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com