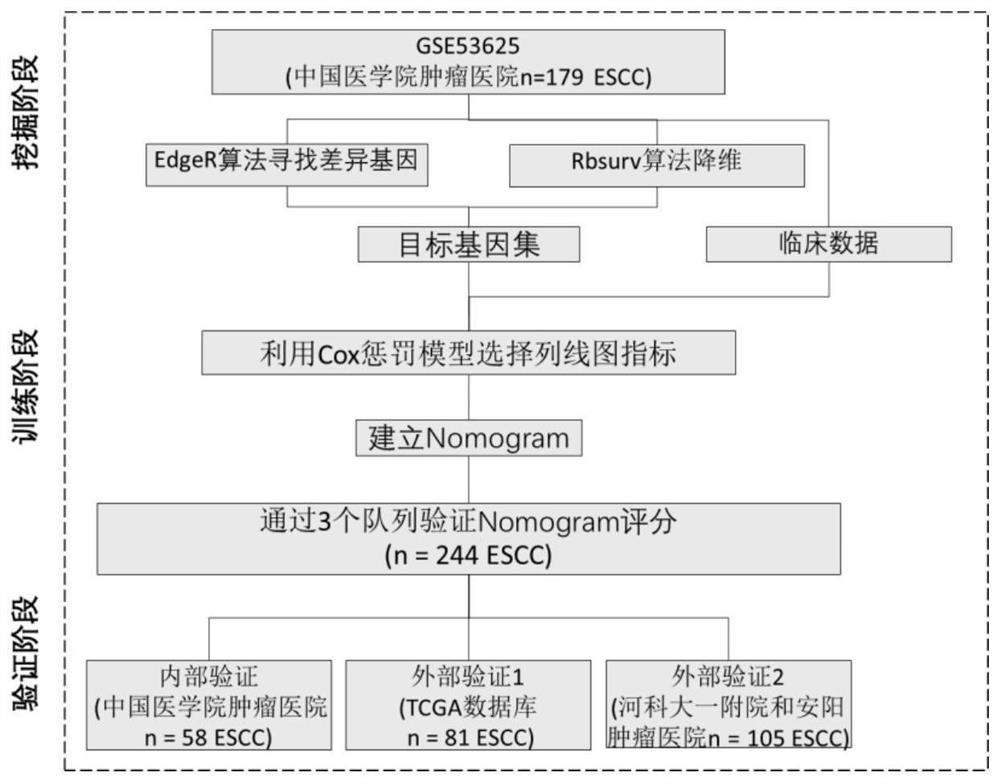
A prognostic early warning system for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its application
A technology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and early warning system, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve limitations and other problems, and achieve the effect of accurate prognosis and staging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1 Mining of gene markers in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
[0058] 1. Experimental method
[0059] 1.1 EdgeR algorithm to find differential genes
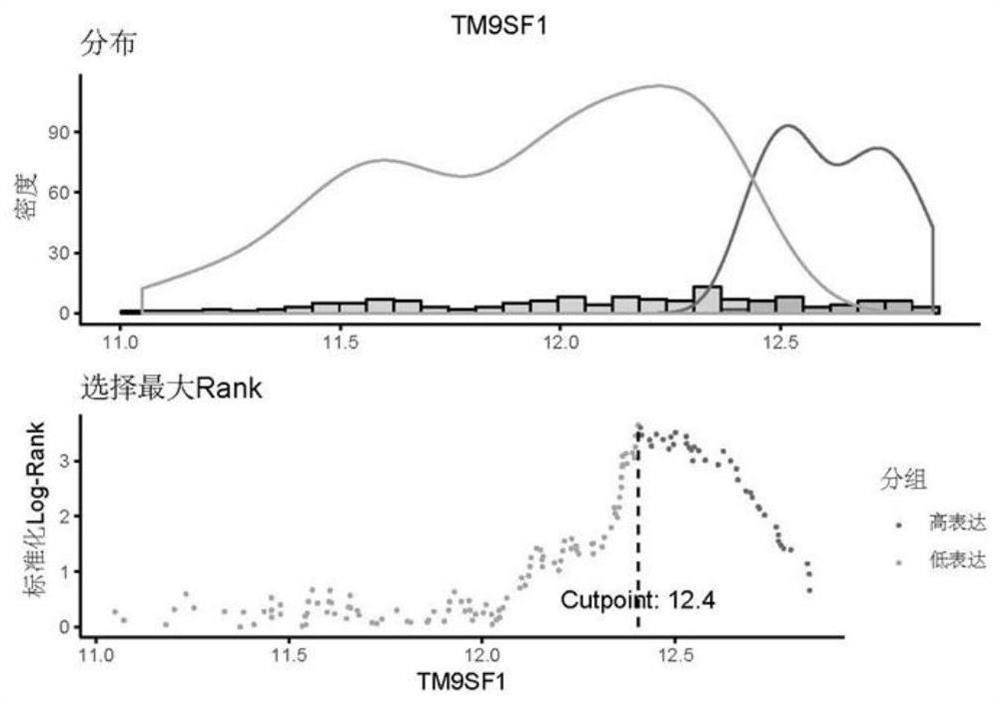
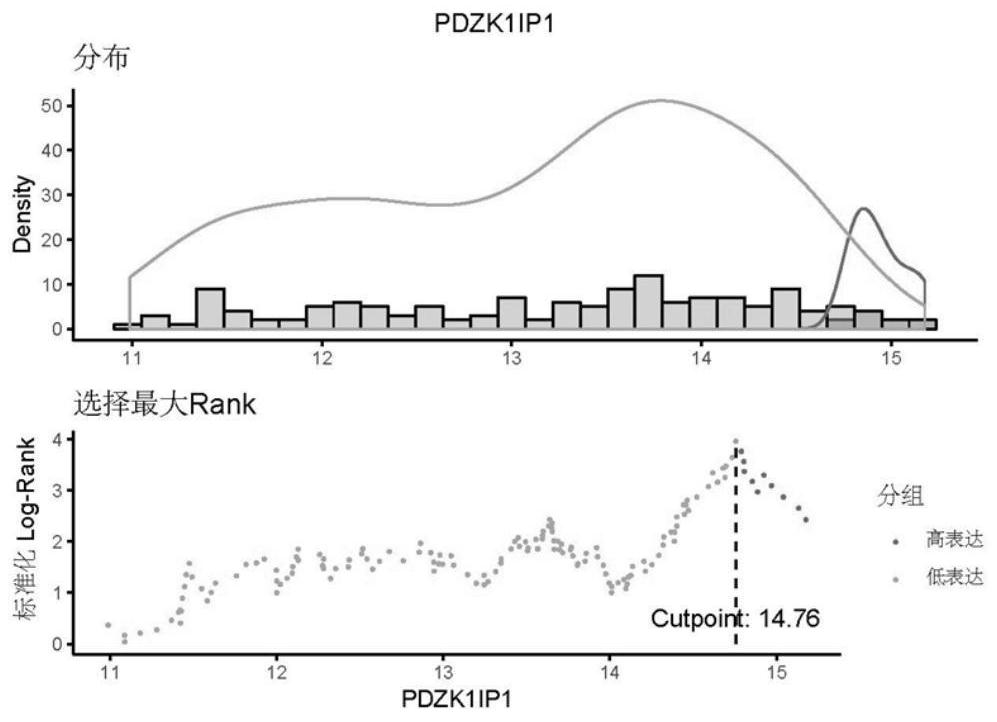
[0060] First, annotate the GSE53625 raw data (chip data) to obtain the gene ID and gene expression matrix (complete gene expression value), then use the edgeR package of R software to screen differential genes, and finally use the surv_cutpoint() function of the survminer package Determine the cutoff value of the gene ( figure 2 and image 3 ), the expression value higher than the cutoff value is high expression, and the expression value lower than the cutoff value is low expression. The specific screening steps for differential genes are as follows:
[0061] (1) Build a DGEList object
[0062] According to the gene expression matrix and sample grouping information, construct the DGEList object, the specific command is:
[0063] dgelist<-DGEList(counts=targets, group=group)
[0064] (2) Filter low-expres...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Example 2 Single factor analysis of clinicopathological characteristics
[0102] 1. Experimental method
[0103] We initially identified clinical features previously shown to be associated with survival and considered these as candidate features: age, sex, smoking, alcohol consumption, tumor invasion, tumor grade, T stage, N stage, TNM stage, arrhythmia, pneumonia, Anastomotic leakage, adjuvant therapy. For each factor, Cox single factor analysis was used to analyze the training samples and internal test samples, and the p-values were all less than 0.05 were selected. Due to the certain repeatability of the N stage and the TNM stage, the N stage was eliminated. In this way, only age and TNM stage are left as the clinicopathological characteristic factors.
[0104] 2. Result analysis
[0105] 2.1 Clinicopathological features of patients
[0106] The characteristics of the patients in the training sample and the internal test sample are shown in Table 4.
[0107] 2...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3 Construction and Verification of Nomogram
[0113] 1. Experimental method
[0114] 1.1 Cox multivariate analysis
[0115] Example 1 The transcriptome sequencing data of 179 ESCC patients of GSE53625 were processed by edgeR and rbsure algorithm, and then the differential genes were calculated and then subjected to dimensionality reduction processing of associated survival data, Cox univariate and multivariate analysis, and the prognosis was obtained Directly related gene sets; poor prognosis clinicopathological characteristics obtained by Cox univariate analysis of clinical characteristic factors in Example 2.
[0116] In this example, on the basis of Example 1 and Example 2, the above factors were added to the established Nomogram model, and Cox multivariate analysis was performed on the gene set and clinicopathological characteristics, and further verification showed that age (p=0.031), age (p=0.031), TNM stage (p=0.004), PDZK1IP1 expression value (p=0.001)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com