Optimization method based on non-convex non-smooth second-order regular term and sparse fidelity term
An optimization method, a non-smooth technology, applied in the field of geometric modeling, which can solve problems such as time-consuming, fuzzy model geometric features, and performance depending on the training data set.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0063] In order to have a clearer understanding of the technical features, purposes and effects of the present invention, the specific implementation manners of the present invention will now be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
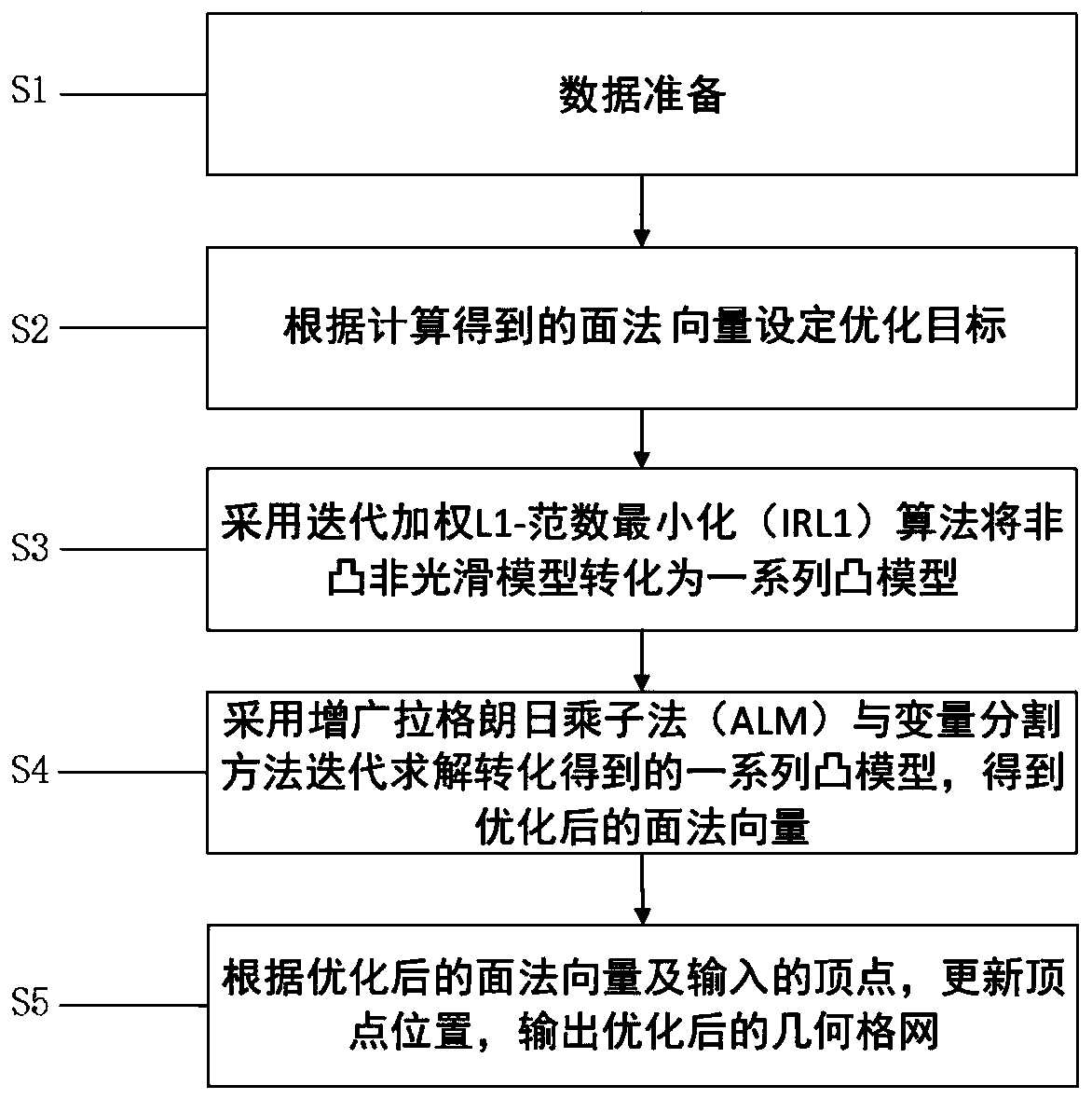
[0064] refer to figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flow chart of the optimization method based on the non-convex and non-smooth second-order regular term and the sparse fidelity term of the present invention. The optimization method based on the non-convex and non-smooth second-order regular term and the sparse fidelity term of the present invention is used to optimize the quality of the three-dimensional grid, including the following steps:
[0065] S1. Data preparation, specifically including the following sub-steps:
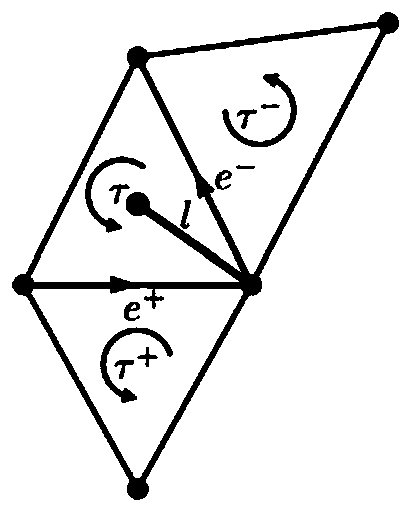
[0066] S11. Obtain the vertices, edges and faces of the three-dimensional geometric grid model, respectively use {v i : i=1,2,...,V},{e j : j = 1, 2, ..., E}, {τ k : k=1, 2, ..., T} represents, wherein V,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com