Flow cell stack
A technology of liquid flow batteries and electric stacks, applied in fuel cells, regenerative fuel cells, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of weakening local thermal effects, increasing electrolyte utilization, and uneven flow velocity distribution, so as to reduce local heat release and improve Battery performance, the effect of suppressing local overheating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
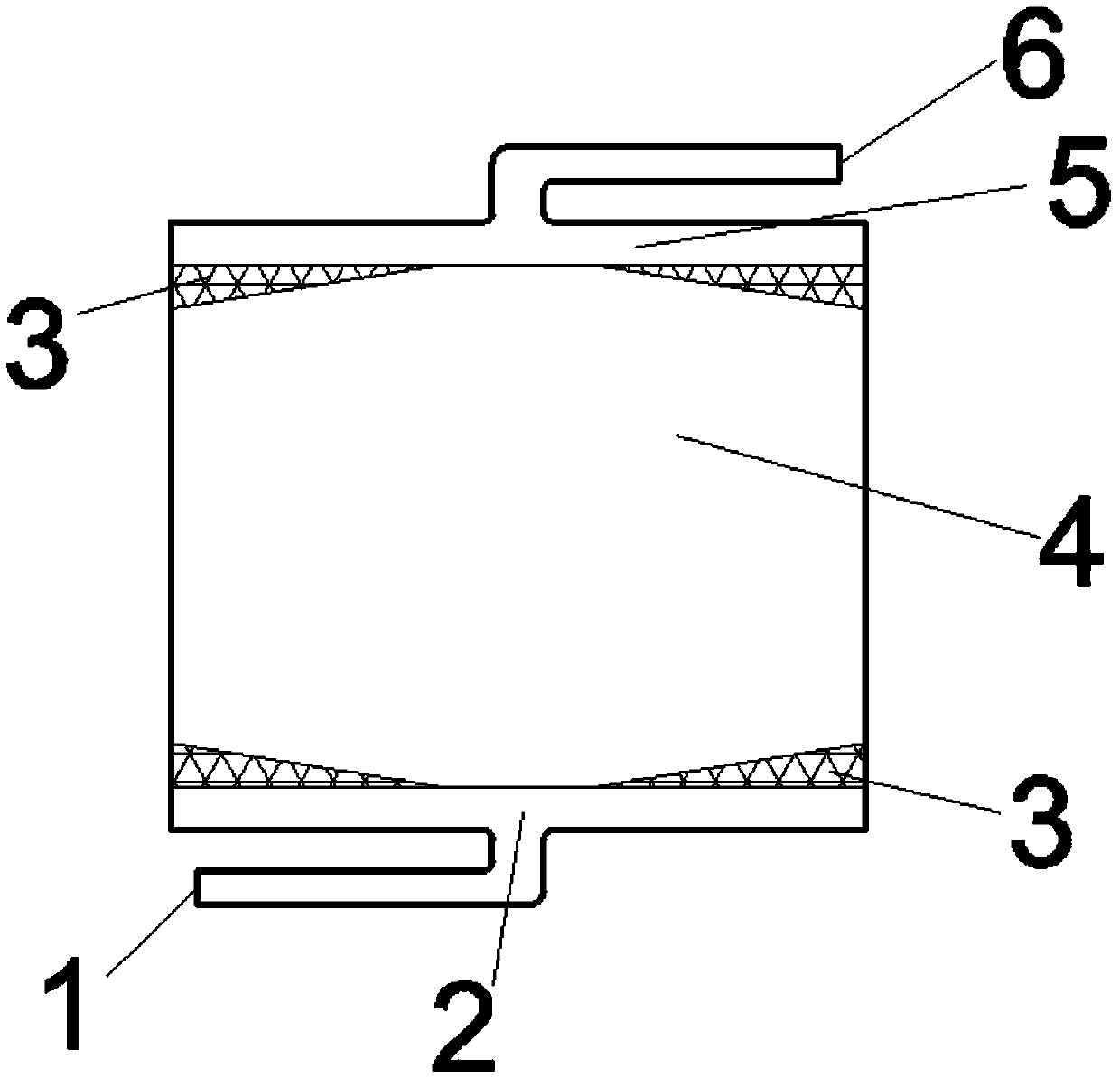
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, a flow battery assembly structure. The outside of the area shown in the figure is the liquid flow frame, and the figure is the main area through which the electrolyte flows, including the inlet diversion area 2 , the buffer cavity 3 , the porous electrode 4 and the outlet diversion area 5 . The main electrolyte inlet 1 is arranged on the inlet guide area, the main electrolyte outlet 6 is arranged on the outlet guide area, and the buffer cavity is located between the porous electrode 4 and the liquid flow frame. The porous electrode is an octagon with a maximum width of 30mm in the horizontal direction and a maximum width of 25mm in the vertical direction. The length of the top and bottom sides is 8mm, and the width of the sides attached to the electrode frame on the left and right sides is 17mm. Felt; four cavities are arranged around the porous electrode, which are triangular in shape. The horizontal width of the inlet guide area and the ou...
Embodiment 2
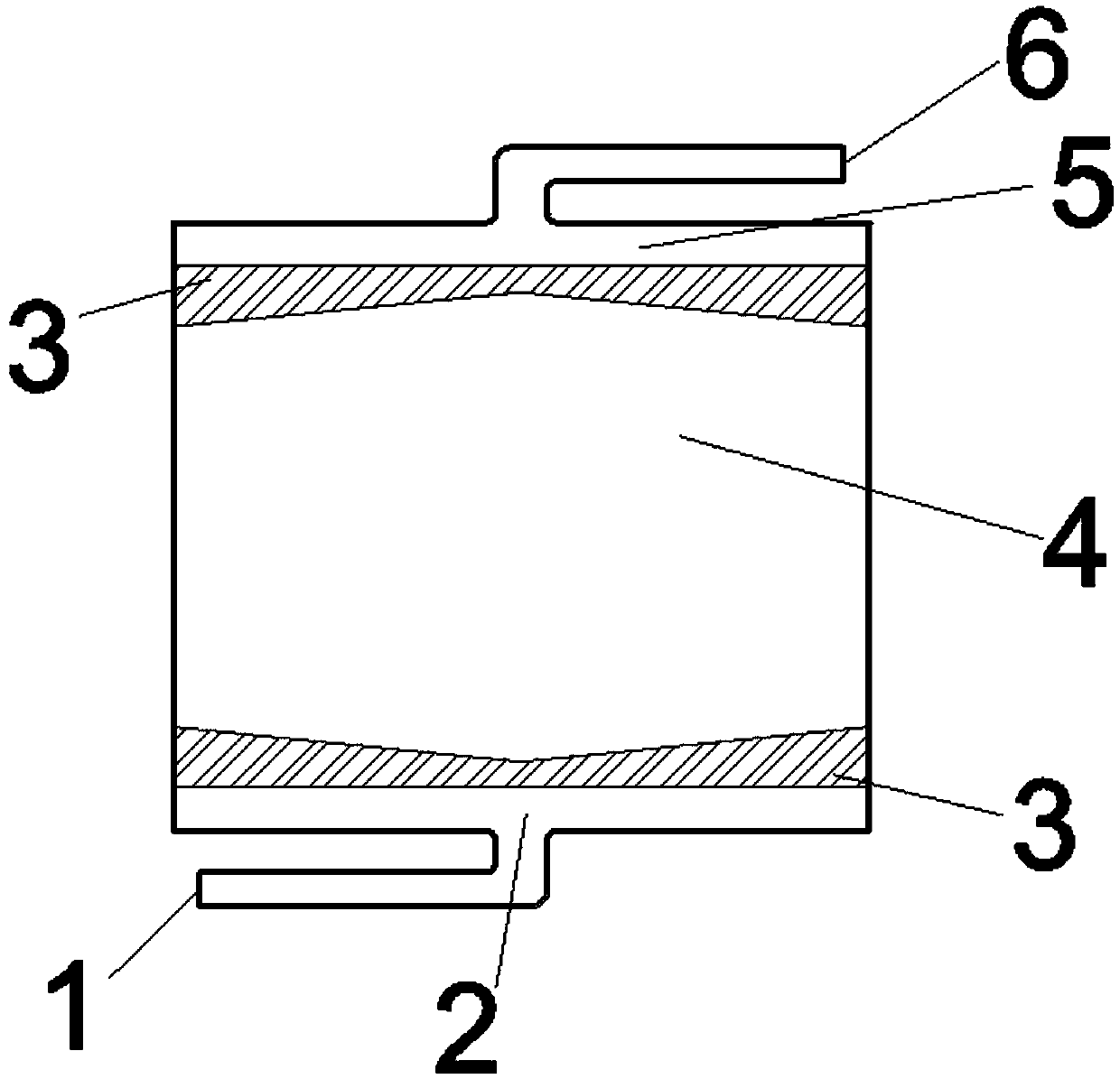
[0022] Such as figure 2 As shown, a flow battery assembly structure. The outside of the area shown in the figure is the liquid flow frame, and the figure is the main area through which the electrolyte flows, including the inlet diversion area 2 , the buffer cavity 3 , the porous electrode 4 and the outlet diversion area 5 . The main electrolyte inlet 1 is arranged on the inlet guide area, the main electrolyte outlet 6 is arranged on the outlet guide area, and the buffer cavity is located between the porous electrode 4 and the liquid flow frame. The porous electrode is a hexagon with a maximum width of 30mm in the horizontal direction and a maximum width of 17mm in the vertical direction. A cavity is provided, which is in the shape of a concave pentagon, with a maximum vertical width of 5mm and a minimum width of 4mm. The horizontal width of the inlet guide area and the outlet guide area is equal to the width of the porous electrode, which is 30 mm.
Embodiment 3
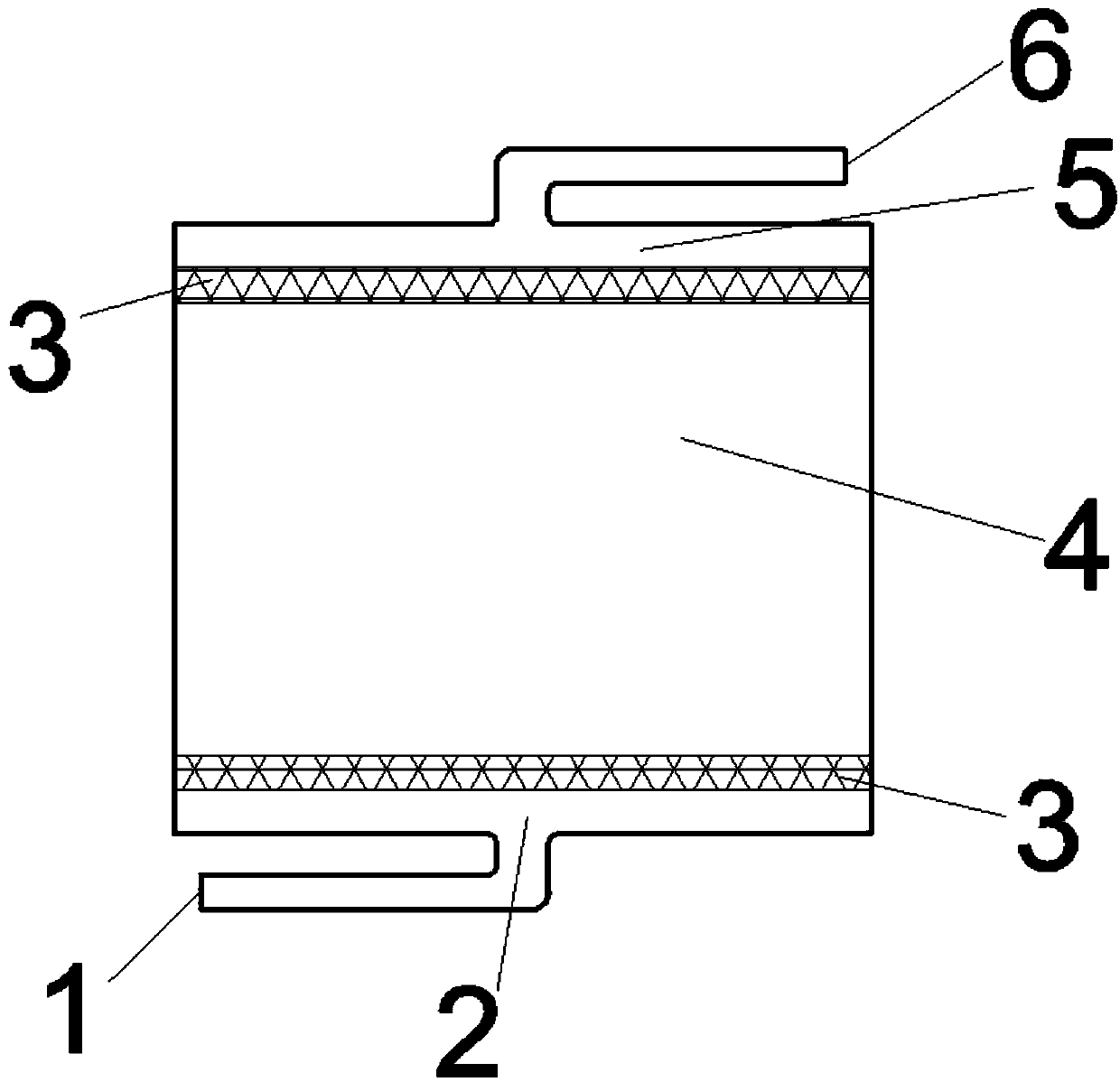
[0024] Such as image 3 As shown, a flow battery assembly structure. The outside of the area shown in the figure is the liquid flow frame, and the figure is the main area through which the electrolyte flows, including the inlet diversion area 2 , the buffer cavity 3 , the porous electrode 4 and the outlet diversion area 5 . The main electrolyte inlet 1 is arranged on the inlet guide area, the main electrolyte outlet 6 is arranged on the outlet guide area, and the buffer cavity is located between the porous electrode 4 and the liquid flow frame. The porous electrode is a rectangle with a length of 30 mm in the horizontal direction and a width of 20 mm in the vertical direction, made of carbon felt; the inlet and outlet sides of the porous electrode are each provided with a cavity, which is rectangular in shape, 30 mm long in the horizontal direction and 5 mm wide in the vertical direction. The horizontal width of the inlet guide area and the outlet guide area is equal to the w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com