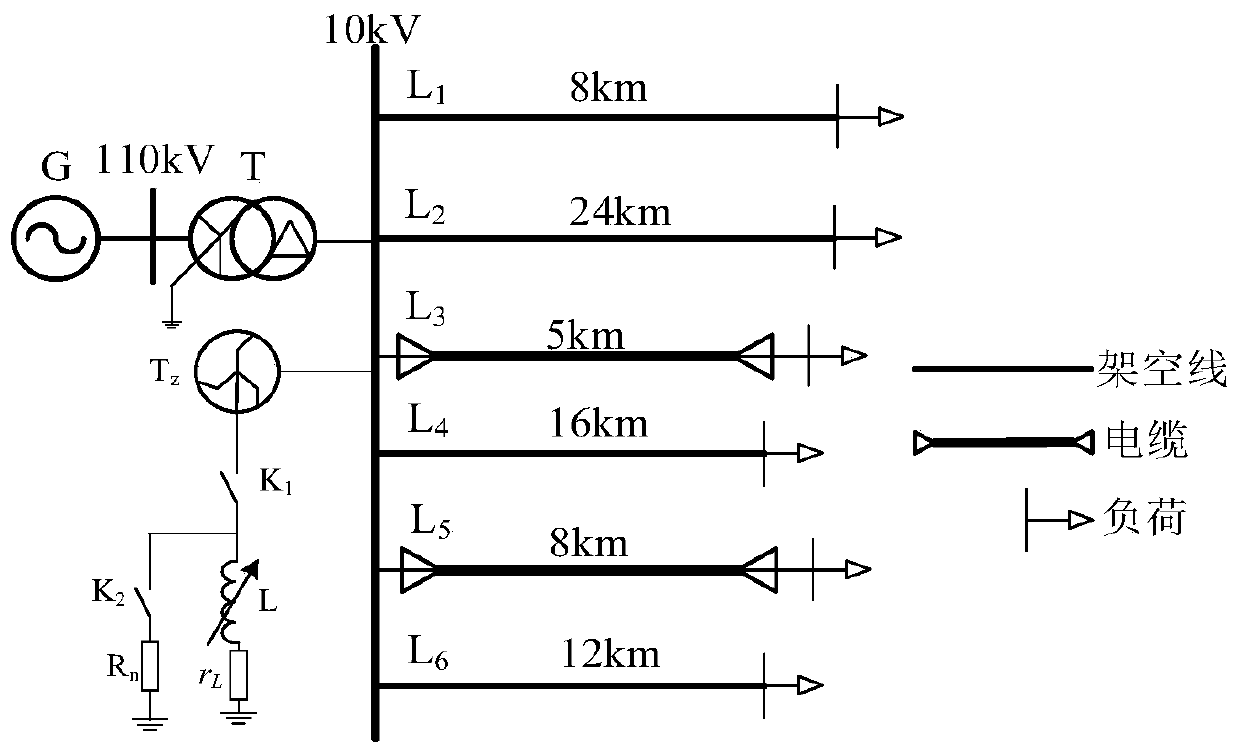
Power distribution network single-phase earth fault development trend discrimination method based on zero-sequence volt-ampere curve area
A single-phase ground fault and volt-ampere curve technology, applied in the fault location, detecting faults according to conductor types, measuring electricity and other directions, can solve problems such as affecting the reliability of power supply, surge in trip rate, adverse personnel and equipment safety, etc., to achieve judgment. The results are reliable and the effect of simplifying the judgment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
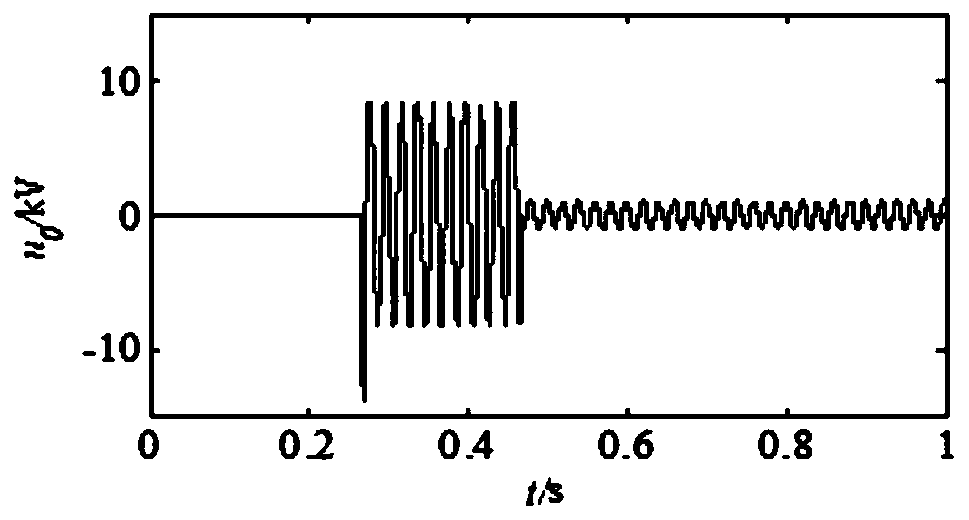
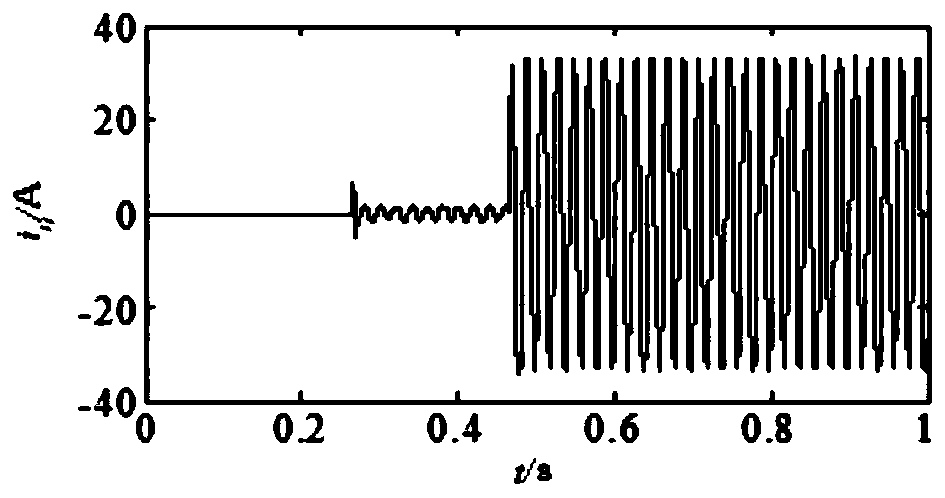
[0034] (1) Assuming that a permanent fault with constant transition resistance occurs on the line L2 at a distance of 7 kilometers from the bus, its zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current are as follows: figure 2 , image 3 shown.
[0035] (2) Intercept the zero-sequence volt-ampere curve from 20ms to 120ms after the fault, such as Figure 4 As shown, the area of each curve and its one-time fitting are as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0036] (3) The area of each surface is 37.8068, 37.8022, 37.8017, 37.8018, 37.8021, and the slope of the straight line fitting is -0.00068, which is greater than -0.01, so it is predicted to be a permanent failure;
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Assuming that a transient fault occurs on the line L4 at a distance of 10 kilometers from the bus, its zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current are as follows: Image 6 , Figure 7 shown.
[0039] (2) Intercept the zero-sequence volt-ampere curve from 20ms to 120ms after the fault, such as Figure 8 As shown, the area of each curve and its one-time fitting are as follows Figure 9 shown.
[0040] (3) The area of each surface is 34.3355, 29.7728, 21.7906, 12.1546, 5.0260, and the slope of the straight line fitting is -0.3812, which is less than -0.01, so it is predicted to be an instantaneous fault;
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Assuming that a permanent fault occurs on the line L5 at a distance of 3 kilometers from the busbar, the transition resistance becomes smaller, and its zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current are as follows: Figure 10 , Figure 11 shown.
[0043] (2) Intercept the zero-sequence volt-ampere curve from 20ms to 120ms after the fault, such as Figure 12 As shown, the area of each curve and its one-time fitting are as follows Figure 13 shown.
[0044] (3) The area of each surface is 18.5833, 29.0997, 44.4465, 65.7231, 93.0446, and the slope of the straight line fitting is 0.9277, which is greater than -0.01, so it is predicted to be a permanent failure;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com