Autonomous positioning method of end effector of under-constraint cable-driven parallel robot
An end effector and autonomous positioning technology, which is applied in the direction of instruments, manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, etc., to achieve the effects of expanding the application range, realizing vibration suppression control, and improving measurement accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
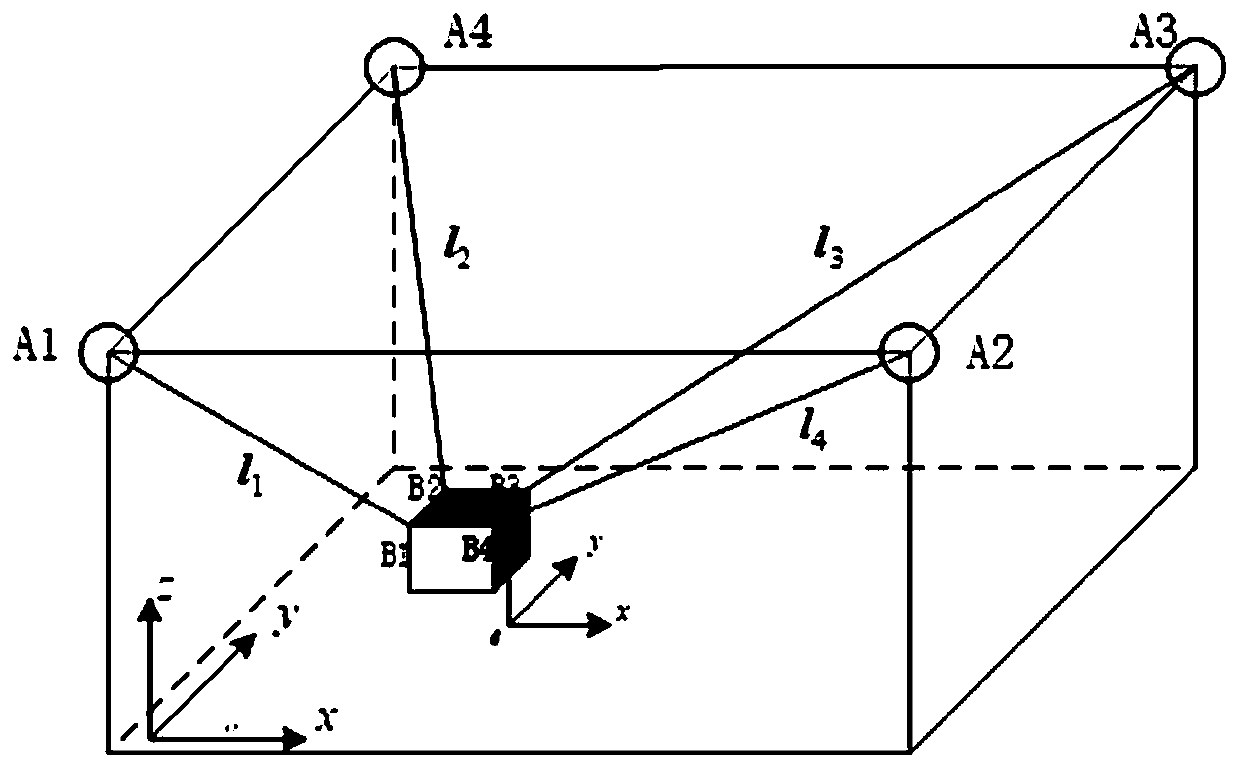
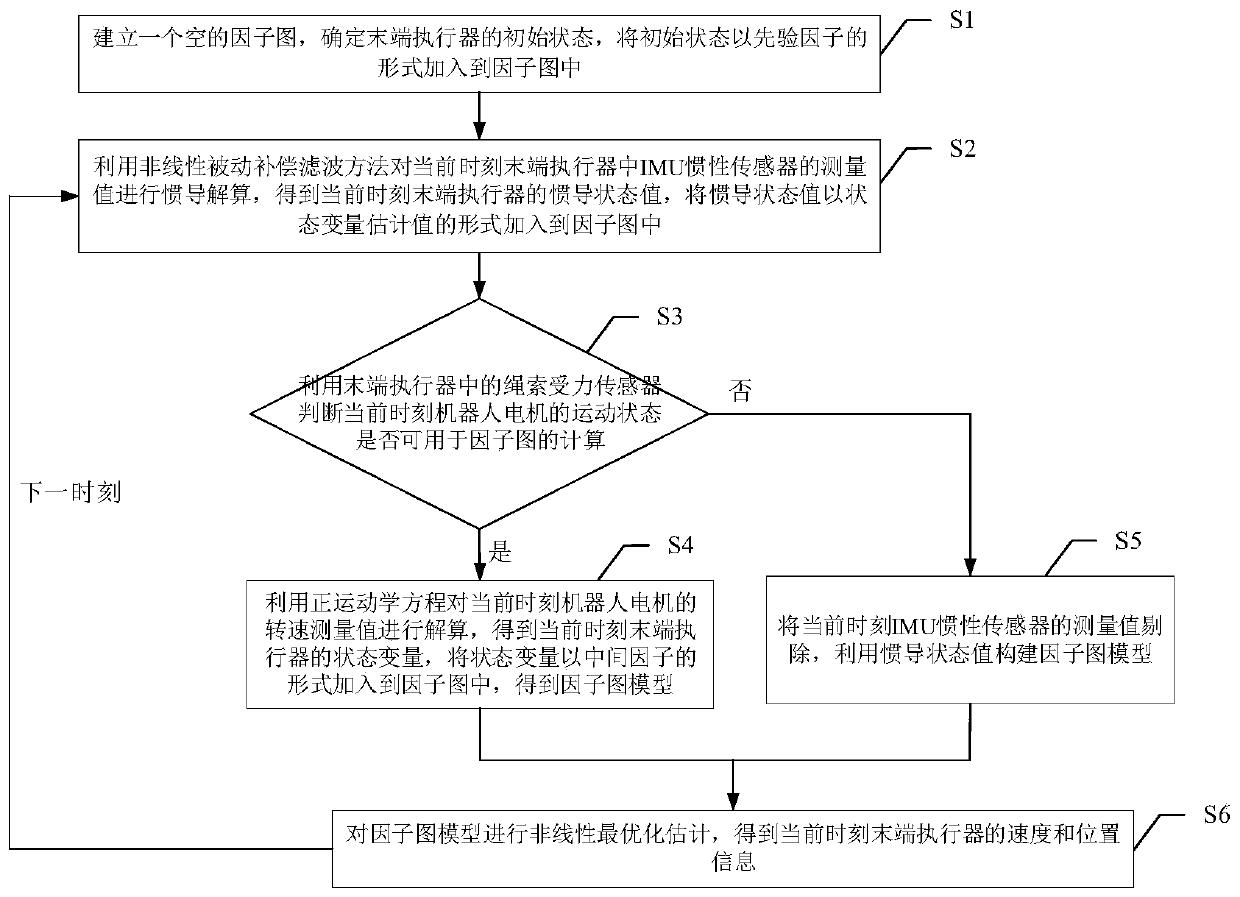
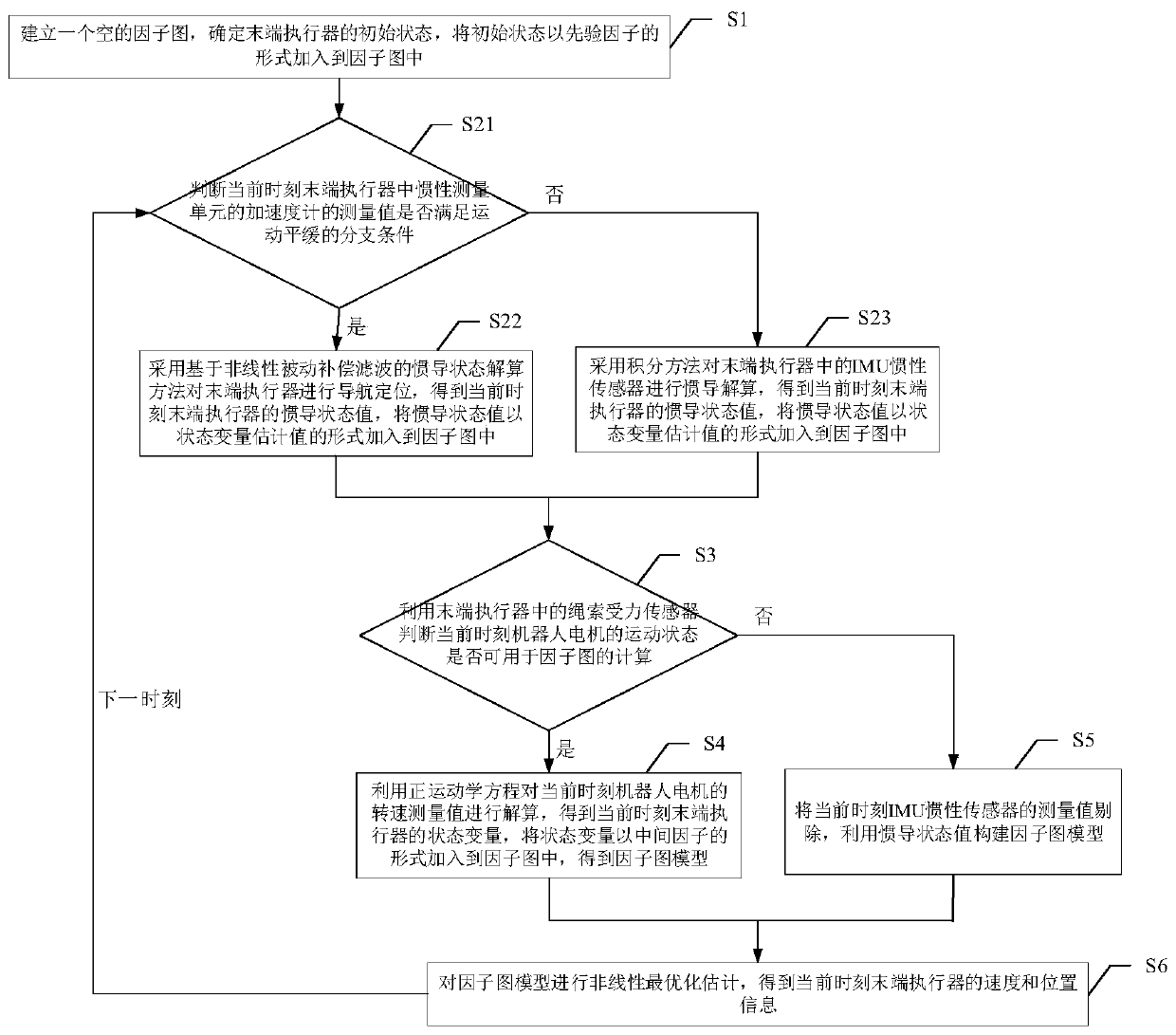
[0056] 1. Principle and Construction Method of Factor Graph Algorithm
[0057] Let x denote the state variable of the end effector, x i Indicates that the end effector at t i state of the moment. The set of all state variables defining the end effector is X k , X k Expressed as:
[0058]
[0059] Since there are other sensors, the definition from the initial moment to t k The set of all state variables of all end effectors and sensors obtained at any time is V k . will t i The measurement value obtained at time is defined as z i , will be from the initial moment to t k All measurements obtained at time instants are defined as Z k ,Z k Expressed as:
[0060]
[0061] On the basis of the above definition, when the known measured value is Z k The posterior probability joint probability distribution function of the reliability of sensor state variables can be defined as p(V k |Z k ). According to the prior information of the system, the state variables of dif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com