Power assembly for electric automobile
An electric vehicle and powertrain technology, applied in the field of vehicles, can solve problems such as inability to meet driving dynamics requirements, inability to meet traction requirements, improper structure, etc., and achieve the effects of large vibration, reduced processing difficulty, and avoided efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
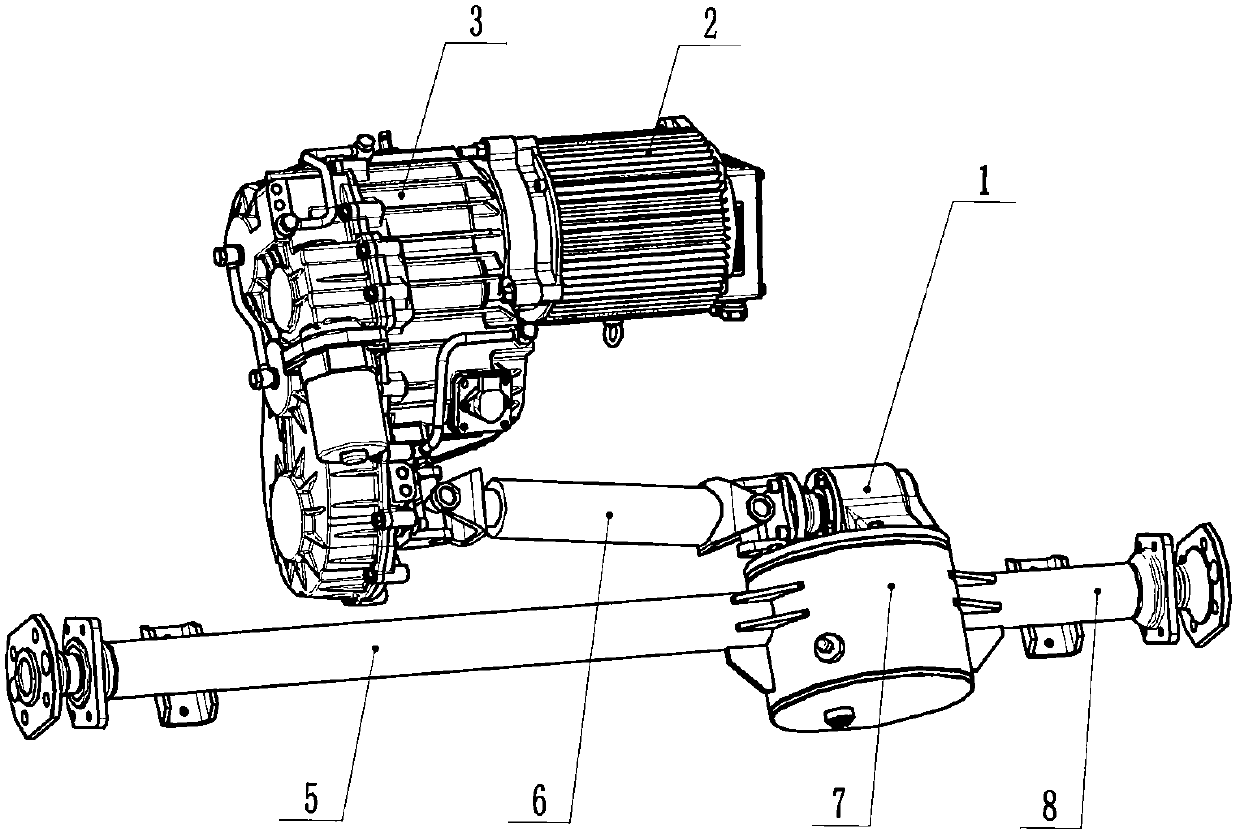
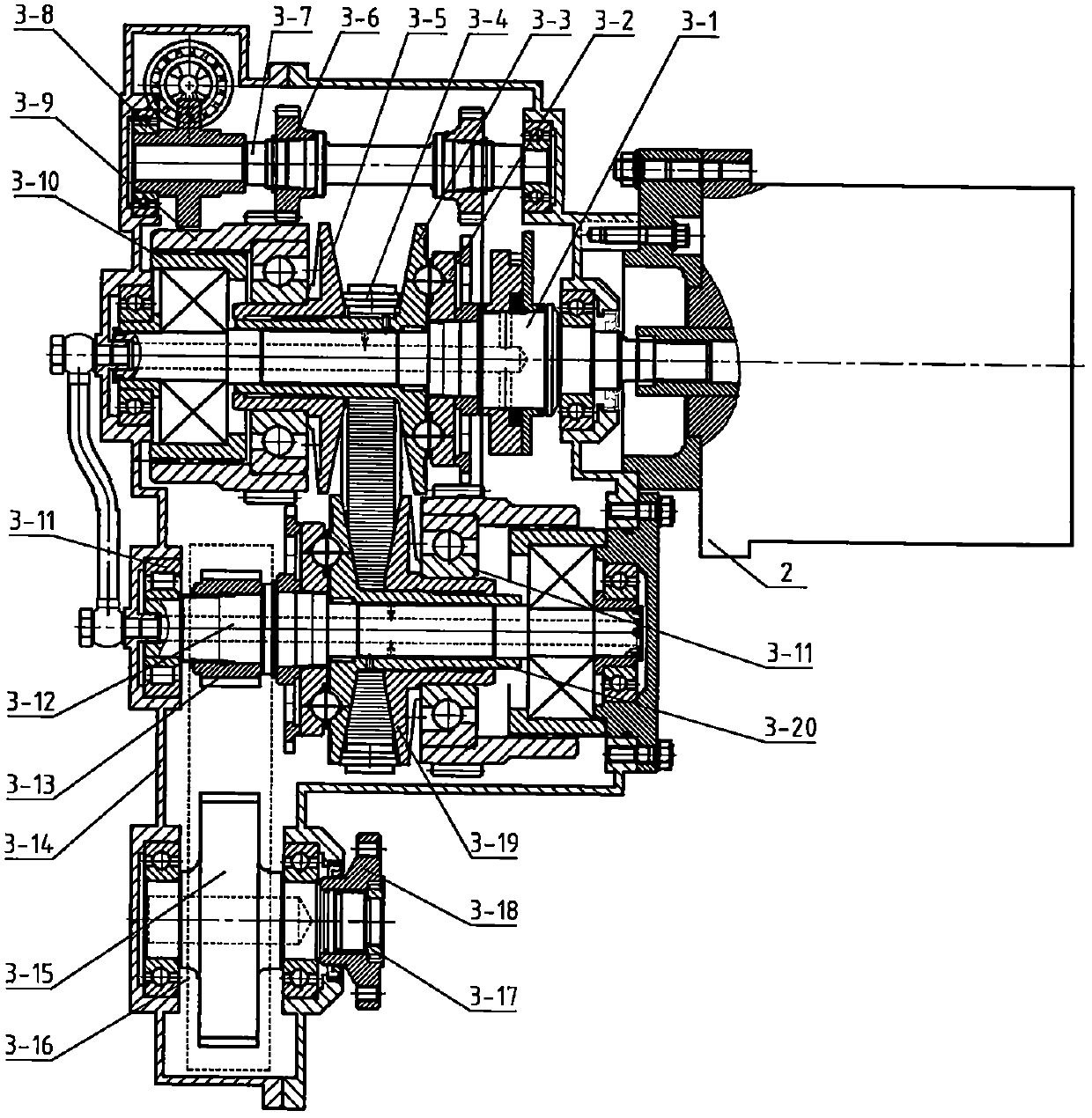
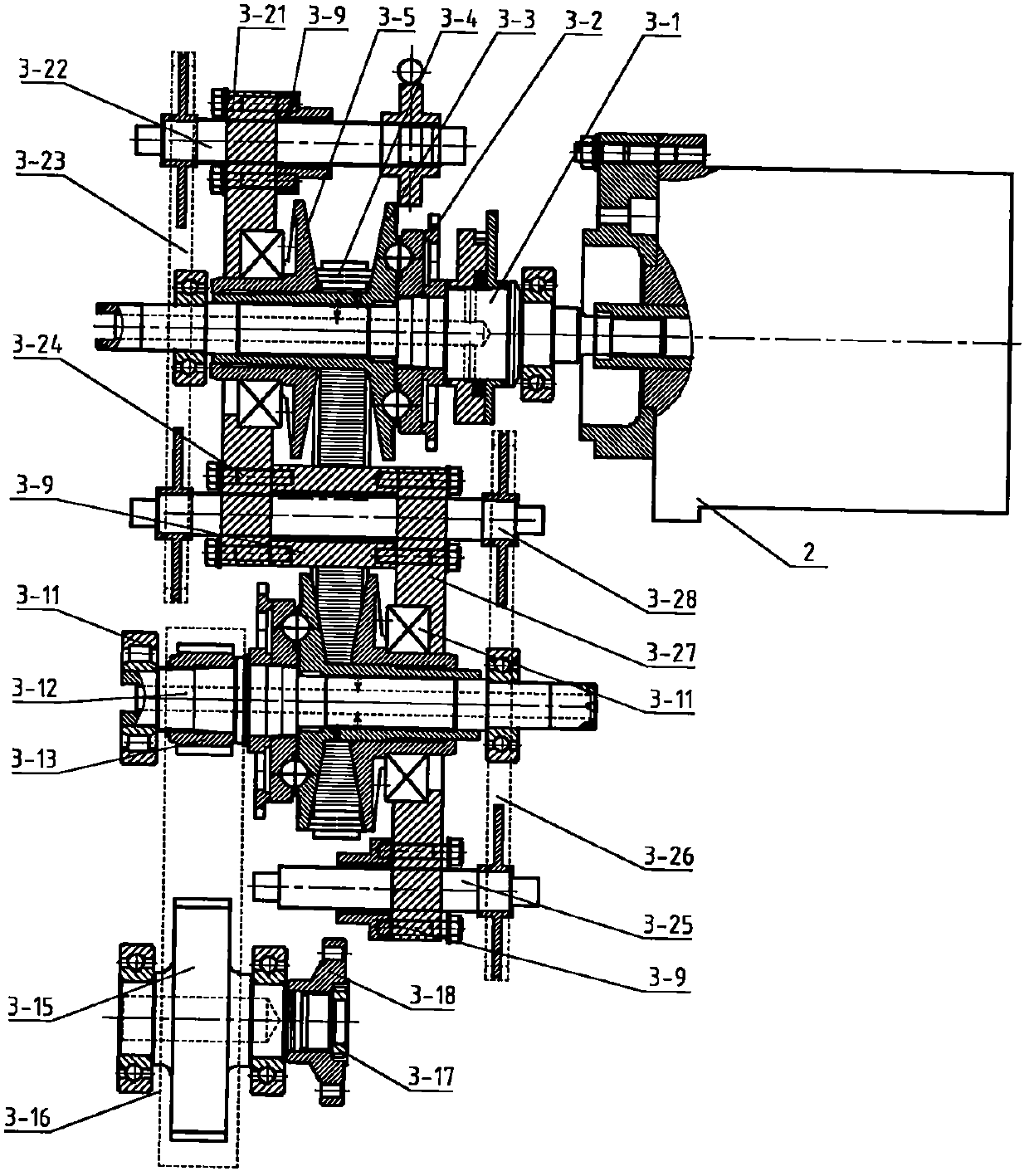
[0048] Such as Figure 1-2 As shown, a power assembly for an electric vehicle includes a drive motor, a continuously variable transmission, a universal joint transmission shaft and a rear axle with a differential. The universal joint drive shaft is placed in front of the rear axle. The motor is fixedly connected to the continuously variable transmission, and the power output end of the motor is directly or indirectly connected to the power input end of the continuously variable transmission. One end of the shaft is connected, and the other end of the universal joint transmission shaft is connected with the differential through the transmission gear set. The differential is set on the rear axle, and the differential on the rear axle is offset relative to the wheels on both sides; The offset setting of the transmission relative to the wheels on both sides; the angle range between the output shaft of the continuously variable transmission and the center line of the drive shaft o...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Such as figure 1 , 3 As shown, a power assembly for an electric vehicle includes a drive motor, a continuously variable transmission, a universal joint transmission shaft and a rear axle with a differential. The universal joint drive shaft is placed in front of the rear axle. The motor is fixedly connected to the continuously variable transmission, and the power output end of the motor is directly or indirectly connected to the power input end of the continuously variable transmission. One end of the shaft is connected, and the other end of the universal joint transmission shaft is connected with the differential through the transmission gear set. The differential is set on the rear axle, and the differential on the rear axle is offset relative to the wheels on both sides; the output of the continuously variable transmission The angle between the shaft and the centerline of the universal joint transmission shaft is less than 8° and greater than -8°, and the angle betw...
Embodiment 3
[0075] A power assembly for an electric vehicle includes a driving motor, a continuously variable transmission, a universal joint transmission shaft and a rear axle with a differential. The drive shaft is placed ahead of the rear axle. The motor is fixedly connected to the continuously variable transmission, and the power output end of the motor is directly or indirectly connected to the power input end of the continuously variable transmission. One end of the shaft is connected, and the other end of the universal joint transmission shaft is connected with the differential through the transmission gear set. The differential is set on the rear axle, and the differential on the rear axle is offset relative to the wheels on both sides; the output of the continuously variable transmission The angle between the shaft and the centerline of the universal joint transmission shaft is less than 10° and greater than -10°, and the angle between the output shaft of the continuously variabl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com