Time headway-based road vehicle lane change model calibration method, time headway-based road vehicle lane change decision making method and device
A technology of headway distance and calibration method, applied in the field of traffic flow, can solve the problems of complex structure of lane changing model, difficult to solve, difficult to meet research needs, etc., achieving good simulation effect, low complexity, and convenient simulation research and application. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
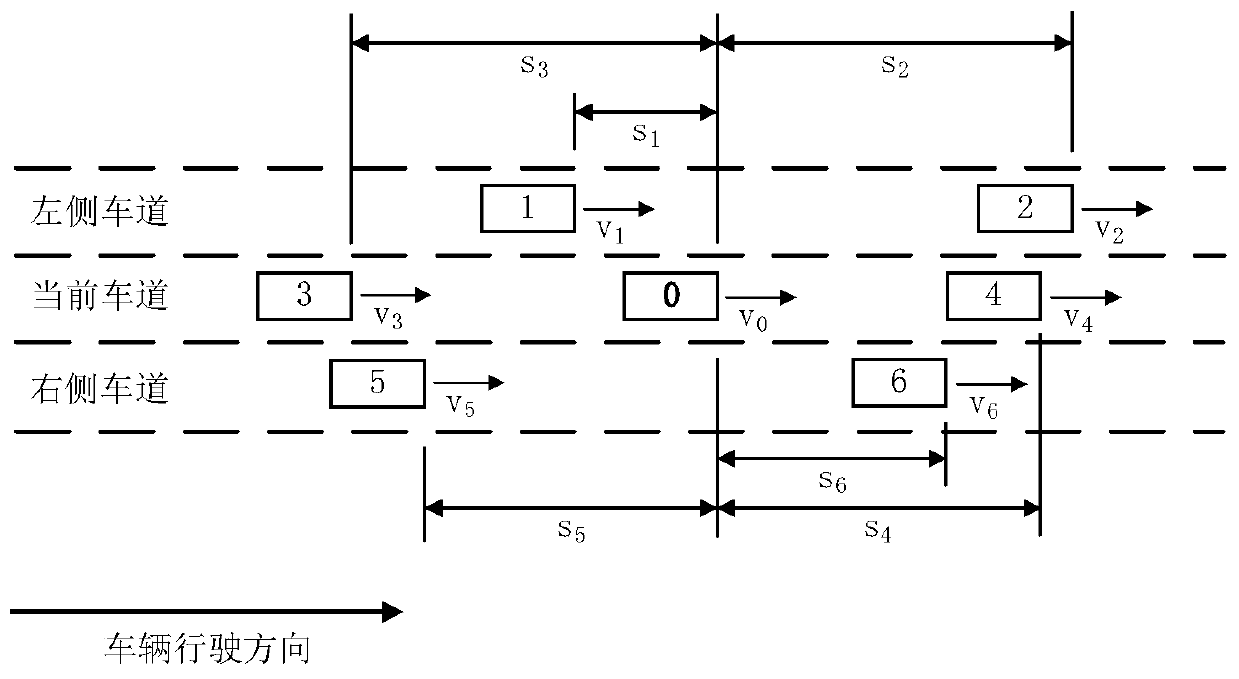
[0034] Example 1: If the observation area is an ordinary road section, such as figure 2 As shown, the vehicle is driving to the right, and car 0 is the target vehicle. Car 4 and Car 3 are the front car and rear car in the current lane respectively; Car 2 and Car 1 are the front car and rear car in the left lane respectively; Car 6 and Car 5 are the front car and rear car in the right lane. Then the measured data includes the target vehicle speed v 0 , the surrounding vehicle speed v i (i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), the headway distance s between the target vehicle and surrounding vehicles i (i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6).
Embodiment 2
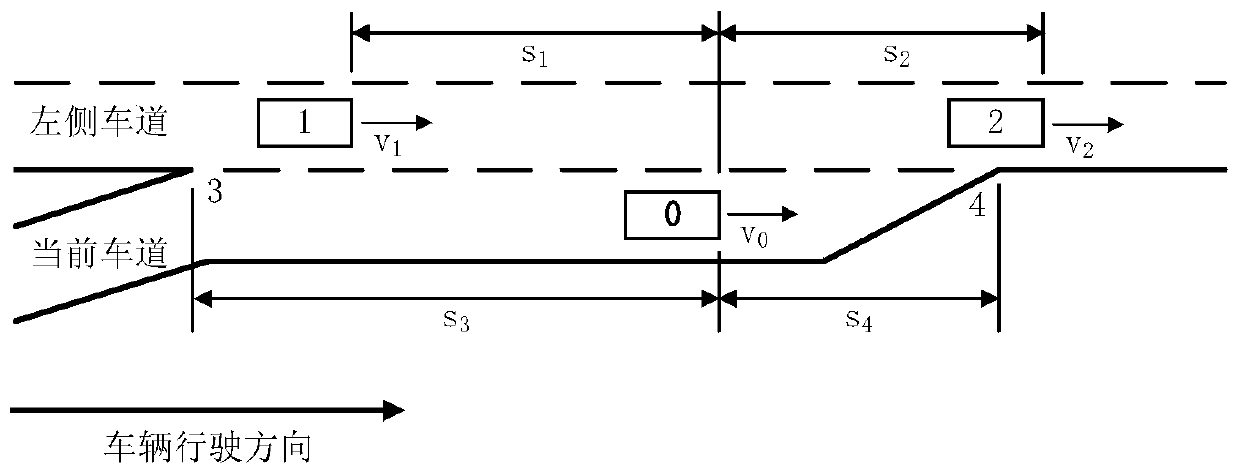
[0035] Example 2: If the observation area is the entrance ramp area, such as image 3 As shown, vehicle 0 is the target vehicle. If there is no vehicle in front of the current lane, the end point of the on-ramp (the vehicle must complete the lane change before this position) is taken as the static obstacle in front, which is recorded as point 4; Road) as the rear static obstacle, recorded as point 3; car 2 and car 1 are the front car and rear car in the left lane respectively; there is no right lane. Then the measured data includes the target vehicle speed v 0 , the speed of surrounding vehicles or obstacles v i (i=1, 2, 3, 4), the headway distance s between the target vehicle and surrounding vehicles or obstacles i (i=1, 2, 3, 4).
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: If the observation area is the off-ramp area, such as Figure 4As shown, vehicle 0 is the target vehicle. Car 4 and Car 3 are the front car and the rear car in the current lane respectively; Car 2 and Car 1 are the front car and the rear car in the left lane respectively; there is no car in front of the right lane, and the end of the exit ramp is taken as the static obstacle ahead, which is recorded as Point 4: There is no car behind the right lane, and the starting point of the exit ramp is taken as the rear static obstacle, which is recorded as point 3. Then the measured data includes the target vehicle speed v 0 , the speed of surrounding vehicles or obstacles v i (i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), the headway distance s between the target vehicle and surrounding vehicles or obstacles i (i=1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com