A lysate for extracting nucleic acid by magnetic bead method and method for extracting nucleic acid using the lysate
A technology for extracting nucleic acid and lysate, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of nucleic acid loss, nucleic acid leakage pollution, low extraction efficiency, etc., and achieve the effects of avoiding pollution, good repeatability, and reducing nucleic acid loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
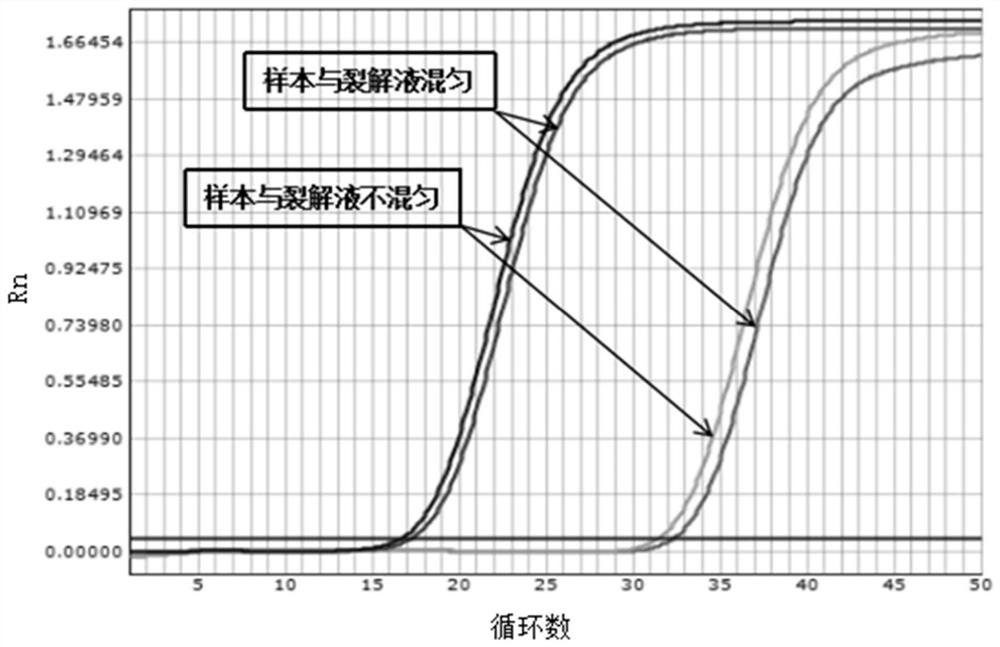
[0064] Embodiment 1: Comparison of whether sample and lysate are mixed to detect HBV DNA
[0065] Using the above lysate and rinse solution, the clinical diagnosis is clear and the quantitative value of HBV DNA after testing is 1.5×10 6 The hepatitis B patient serum of IU / mL and 30IU / mL carries out the operation of following steps:
[0066] (1) Dispensing of PCR lysate: Dispense the prepared lysate containing magnetic beads into dedicated PCR tubes at a rate of 100 μL per tube.
[0067] (2) Adding samples: Take 100 μL of serum and add it to the above-mentioned PCR tube containing the lysate containing magnetic beads. The sample and the lysate are not evenly mixed, and stand at room temperature for 5 minutes.
[0068] (3) Absorb and discard the liquid: Place the above PCR tubes on the eight-row magnetic stand, let it stand for 2 minutes, and use a negative pressure pump to suck up the liquid on the opposite side of the magnetic beads, and be careful not to suck off the magneti...
Embodiment 2
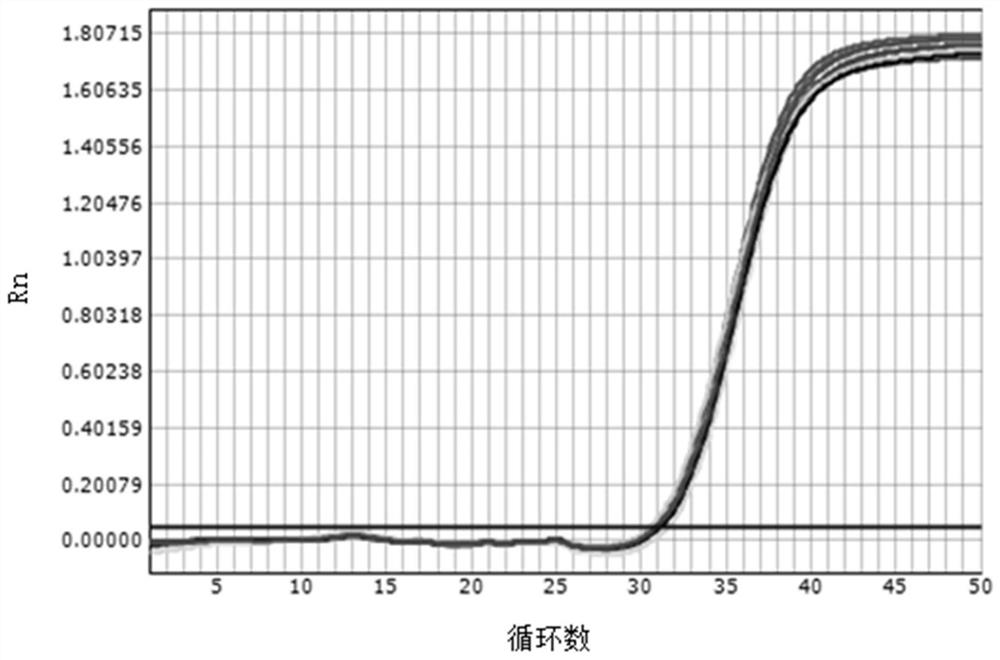
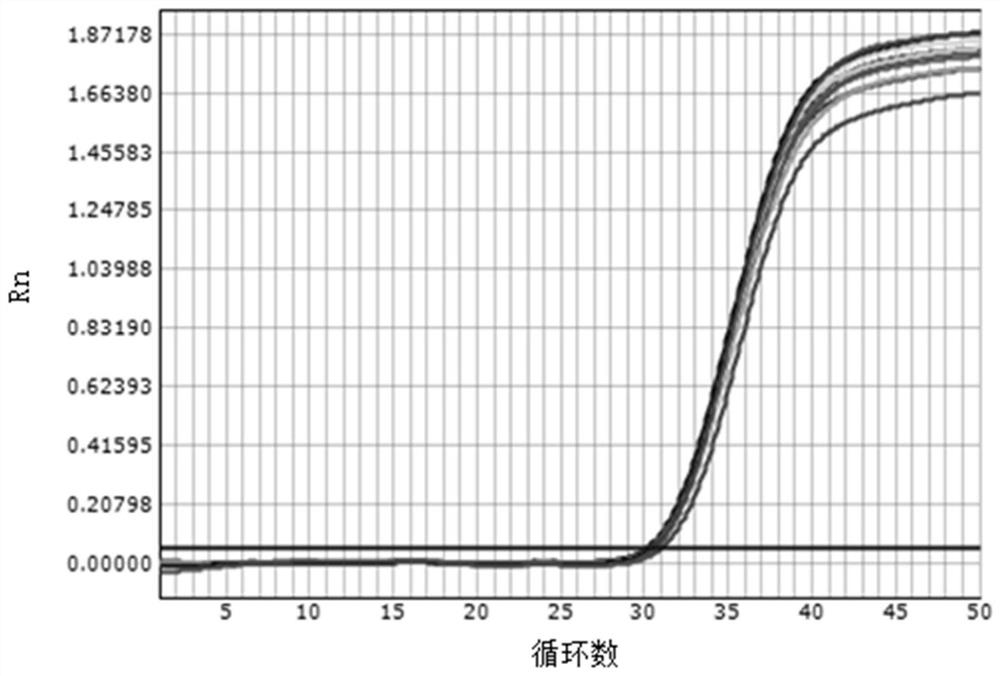
[0080] Example 2: Comparison of whether the sample and the lysate are mixed evenly to detect the repeatability of 80IU / mL HBV DNA
[0081] In order to verify the impact of whether the sample and lysate are mixed uniformly on the repeatability of low-value samples, the non-mixed method of the present invention is compared with the mixed method.
[0082] Using the same method as in Example 1, the serum of hepatitis B patients with a clear clinical diagnosis and a quantitative HBV DNA value of 80 IU / mL was tested repeatedly in 10 wells.
[0083] The result is as figure 2 , image 3 As shown, the experimental results show that when the sample to be tested is added to the lysate, the repeatability of 80IU / mL amplified by the non-mixing method is significantly higher than that of the 80IU / mL amplified by the mixing method.
Embodiment 3
[0084] Embodiment 3: Comparison of whether to blow off magnetic beads to detect HBV DNA during rinsing
[0085] In order to verify the effect of blowing off the magnetic beads during rinsing on the efficiency of nucleic acid extraction, use the above lysate and rinsing solution to determine the clinical diagnosis and the tested HBV DNA quantitative value is 1.5×10 8 IU / mL and 1.5×10 4IU / mL serum from patients with hepatitis B was tested. Scheme 1) blowing off the magnetic beads during rinsing, scheme 2) not blowing off the magnetic beads during rinsing, and other steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0086] Experimental results such as Figure 4 As shown, the results show that according to the example scheme 2) the inventive method of not blowing off the magnetic beads during rinsing, for 1.5 × 10 8 IU / mL and 1.5×10 4 When the IU / mL hepatitis B patient serum sample is tested, not only can it be quantified effectively, but also its PCR efficiency is higher than the PCR effi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com