Method for detecting genomic structure variation based on nanopore sequencing
A technology for nanopore sequencing and structural variation, which is applied in the field of bioinformatics and can solve problems such as low accuracy and precision, and difficulty in structural variation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1 The method for detecting structural variation based on nanopore sequencing is applied to the detection of structural variation in rice individual resequencing
[0051] Rice individual resequencing structural variation detection, including the following steps:
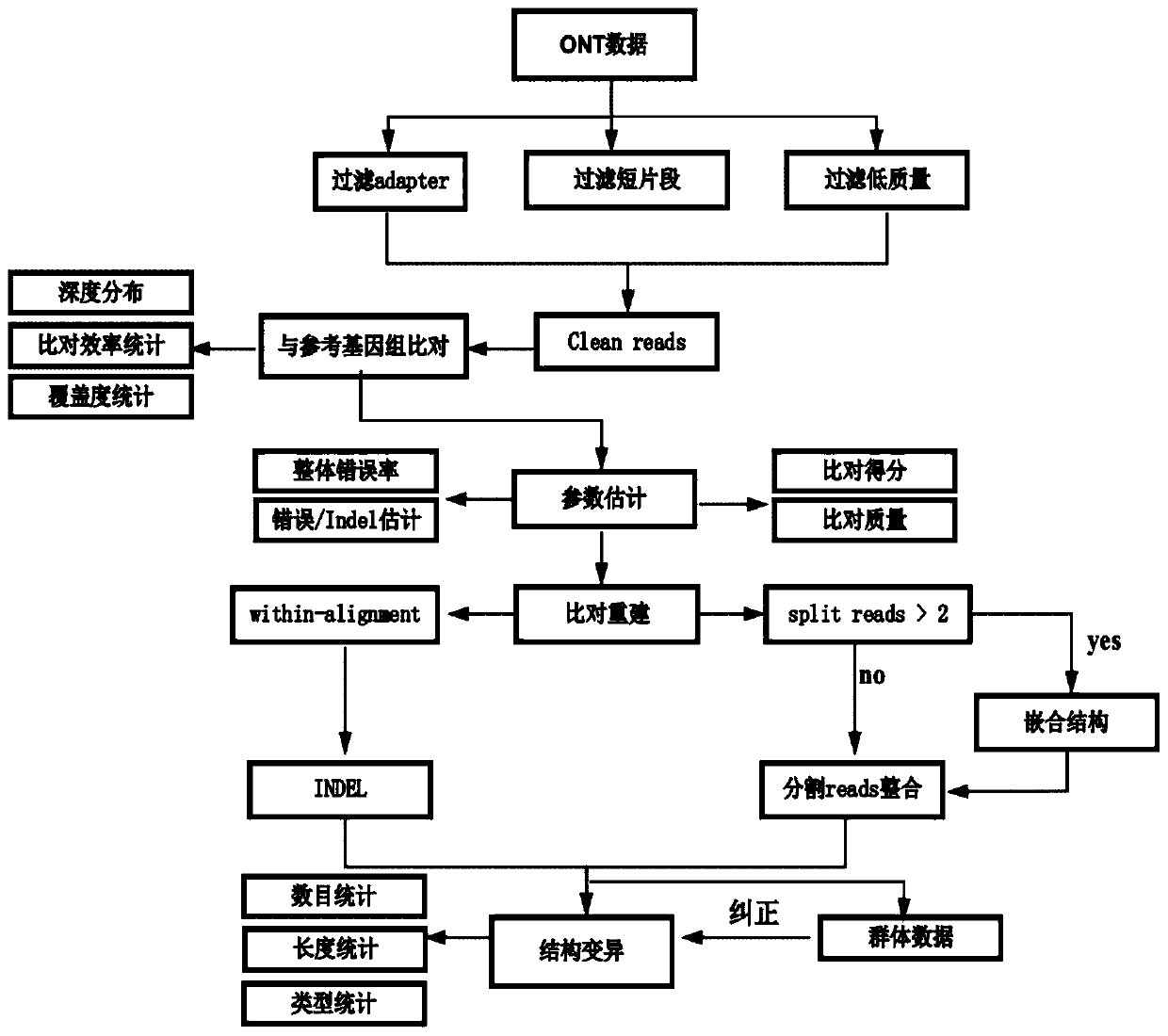
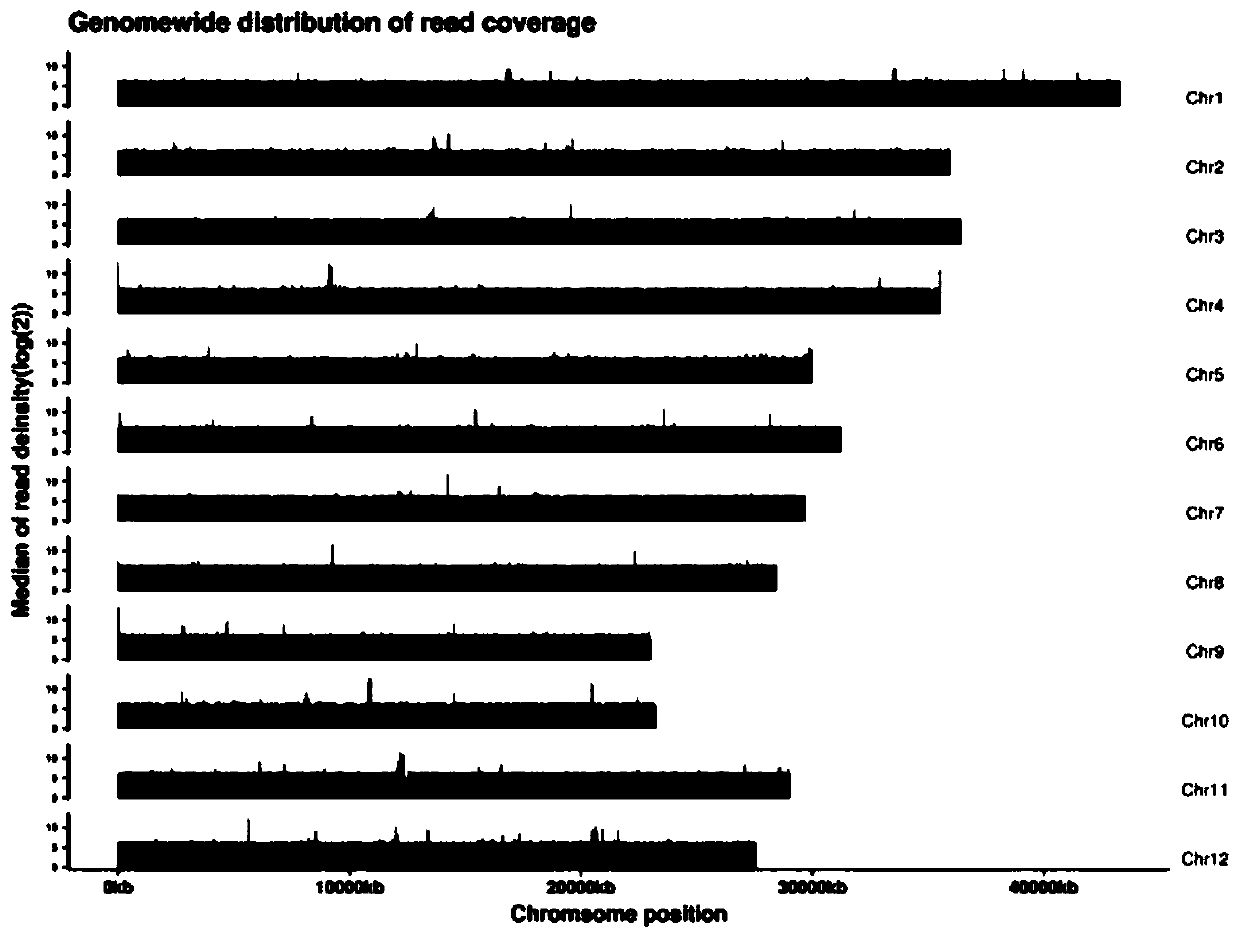
[0052] 1. Perform quality control on the off-machine data of nanopore sequencing, mainly including filtering adapter sequences, reads quality value lower than 7 and reads length shorter than 500bp. Based on the filtered data statistics clean data, the results are as follows:
[0053] Table 1 Clean data statistics
[0054] #DataType SeqNum SumBase N50Len N90Len MeanLen Max Len MeanQual clean data 2001147 1300993204 21490 4007 10081 211522 9.33
[0055] Note: Data type: data type; SeqNum: sequence number; SumBase: total base number; N50Len: data N50 length; N90Len: data N90 length; MeanLen: average length of reads; MaxLen: longest Reads length; MeanQual: average R...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2 The method of detecting structural variation based on nanopore sequencing is applied to rice resequencing transgenic events and insertion fragment search
[0066] Rice resequencing transgenic events and insertion fragment search, including the following steps:
[0067] 1. Perform quality control on the off-machine data of nanopore sequencing, mainly including filtering adapter sequences, reads quality value lower than 7 and reads length shorter than 500bp. Based on the filtered data statistics clean data, the results are as follows:
[0068] Table 4 Clean data statistics
[0069] #DataType SeqNum SumBase N50Len N90Len MeanLen Max Len MeanQual clean data 2826773 2057904109 28822 14733 22062 207257 8.32
[0070] Note: Data type: data type; SeqNum: sequence number; SumBase: total base number; N50Len: data N50 length; N90Len: data N90 length; MeanLen: average length of reads; MaxLen: longest Reads length; MeanQual: average...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com