Preparation method for composite zero-valent iron dechlorination agent from flos sophorae and application of composite zero-valent iron dechlorination agent
A zero-valent iron and Sophora japonica technology is applied in the field of environmental remediation, which can solve problems such as affecting the use effect, easy failure in storage and transportation, and reducing reactivity, and achieves the effects of uniform load, good dispersion, and increased specific surface area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: Preparation of composite zero-valent iron dechlorination agent
[0029] Weigh 0.5g of 200 mesh dry silkworm excrement biochar and add it to 30mL of 13g / L microcrystalline cellulose solution, then add 0.23g of citric acid, ultrasonically disperse for 30min, and shake at 25°C for 4h. After the shaking is completed, place it in a 50mL high-pressure sealed reaction kettle, react at a constant temperature of 220°C for 12h, cool naturally to room temperature, wash and centrifuge the material with absolute ethanol, and dry it in an oven at 75°C for 12h before use; oxidize a small amount of hydrogen Dissolve calcium and borax into 150ml of acetone and deionized water mixture, stir evenly, then add 10g of Sophora japonica rice into it, heat, boil for 20-30min, filter the residue while it is hot, and concentrate the remaining liquid by rotary steaming at 55°C When the volume is reduced to 1 / 3, the Sophora japonica rice dissolution solution is obtained; weigh 4g FeSO...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Degradation experiment of chlorinated organic matter (1,2-dichlorobenzene) in aqueous solution
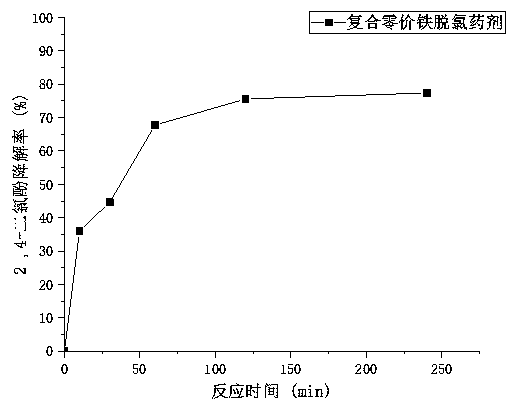
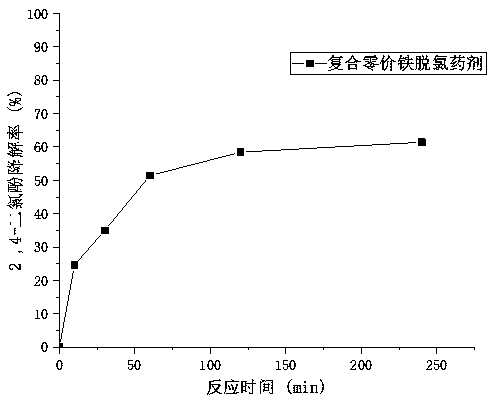
[0031] Weigh 0.5g of the composite zero-valent iron dechlorination agent prepared in the above-mentioned implementation case 1, add it to 40mL of 2,4-dichlorophenol simulated wastewater with an initial concentration of 10mg / L, seal it and put it in a constant temperature (25°C) The reductive dechlorination reaction was carried out in a water-bath oscillator, and samples were regularly sampled and analyzed after 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hours of reaction respectively. The experiment was set up as a blank test and a parallel test. The calculated degradation rate-time curve is shown in figure 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Degradation experiment of chlorinated organic matter (o-chlorophenol) in aqueous solution
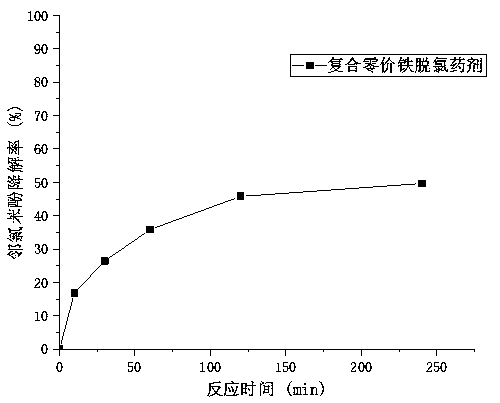
[0033] Weigh 1 g of the composite zero-valent iron dechlorination agent prepared in the above-mentioned implementation case 1, add it to 40 mL of o-chlorophenol simulated wastewater with an initial concentration of 50 mg / L, seal it and place it in a constant temperature (25°C) water bath shaker for For the reductive dechlorination reaction, samples were taken and analyzed at regular intervals after 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hours of reaction, respectively, and blank tests and parallel tests were set up in the experiments. The calculated degradation rate-time curve is shown in figure 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com