Movement control method of omni-directional heavy-load mobile robot
A mobile robot and robot movement technology, applied in the field of mobile robots, can solve problems such as complex control systems, limited logistics paths, and small carrying capacity, and achieve the effects of mobile robots being flexible, improving use efficiency, and improving control accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A motion control method for an omnidirectional heavy-duty mobile robot, the mobile robot includes a control system, at least two steering wheels, and at least two steering wheels; the control system is electrically connected to the steering wheels and the steering wheels, and the control system controls the Describe steering wheel rotation and steering. And at the same time control the steering of the steering wheel to realize the control of the motion of the mobile robot.
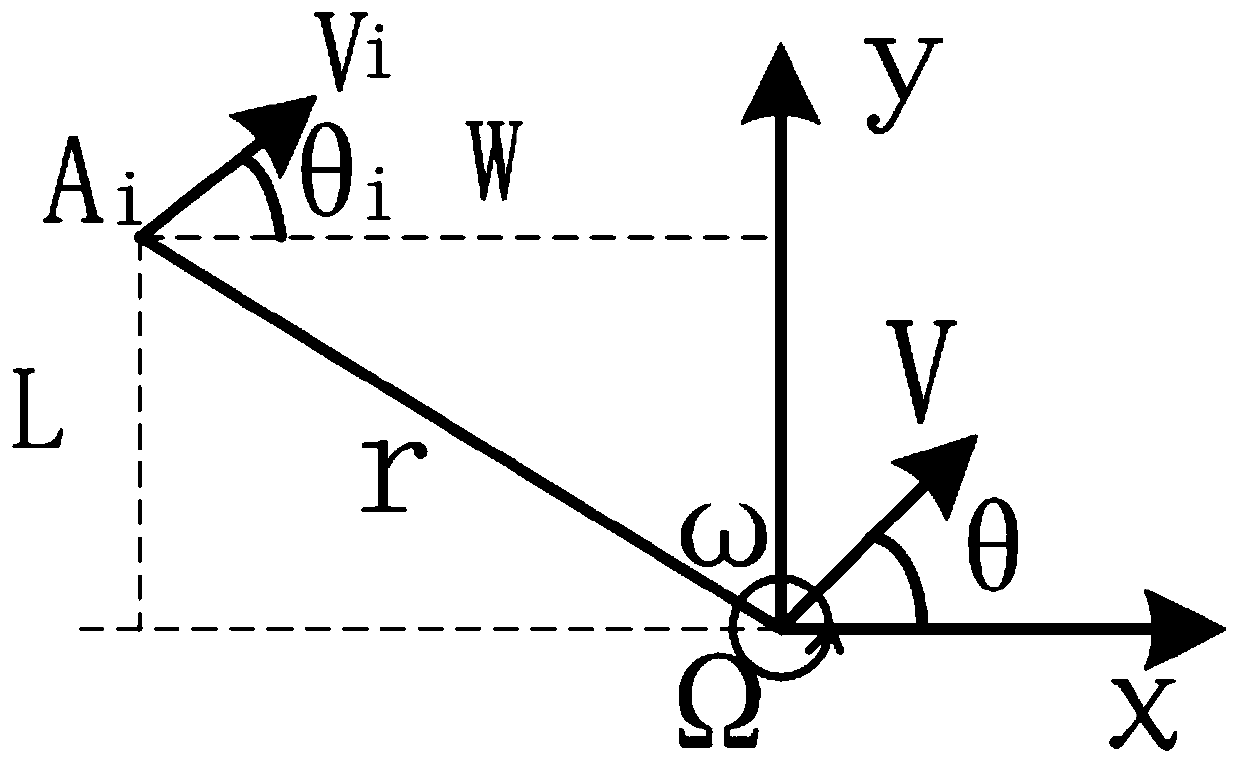
[0039] The specific control system controls the rotation and steering of the steering wheel and the calculation of controlling the steering of the steering wheel refers to the appended figure 1 As shown, a coordinate system is set on the motion level plane of the mobile robot. The motion center of the mobile robot is a point Ω in the coordinate system. The planned motion center of the mobile robot moves at a velocity V and an angular velocity ω. A certain wheel is at the coordinate point A in the s...
example A
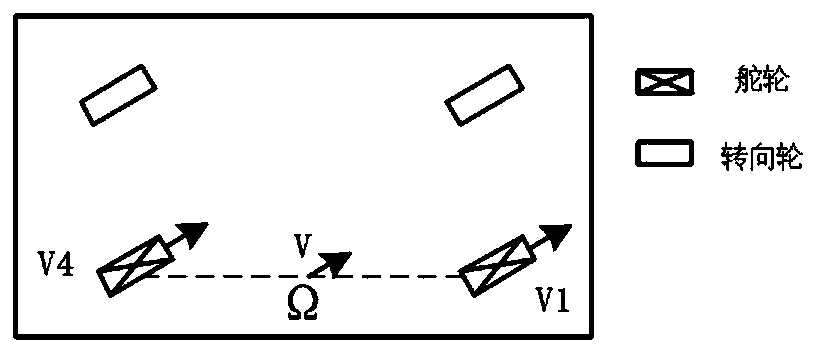
[0052] Take a mobile robot with a wheel train structure composed of two steering wheels and two steering wheels as an example. The two steering wheels are the main control unit, and the two steering wheels assist in controlling the direction. Specifically, the two steering wheels are located on the same side and the opposite side The steering wheel is set, and the omnidirectional motion control method of the mobile robot in this way will be further described below.
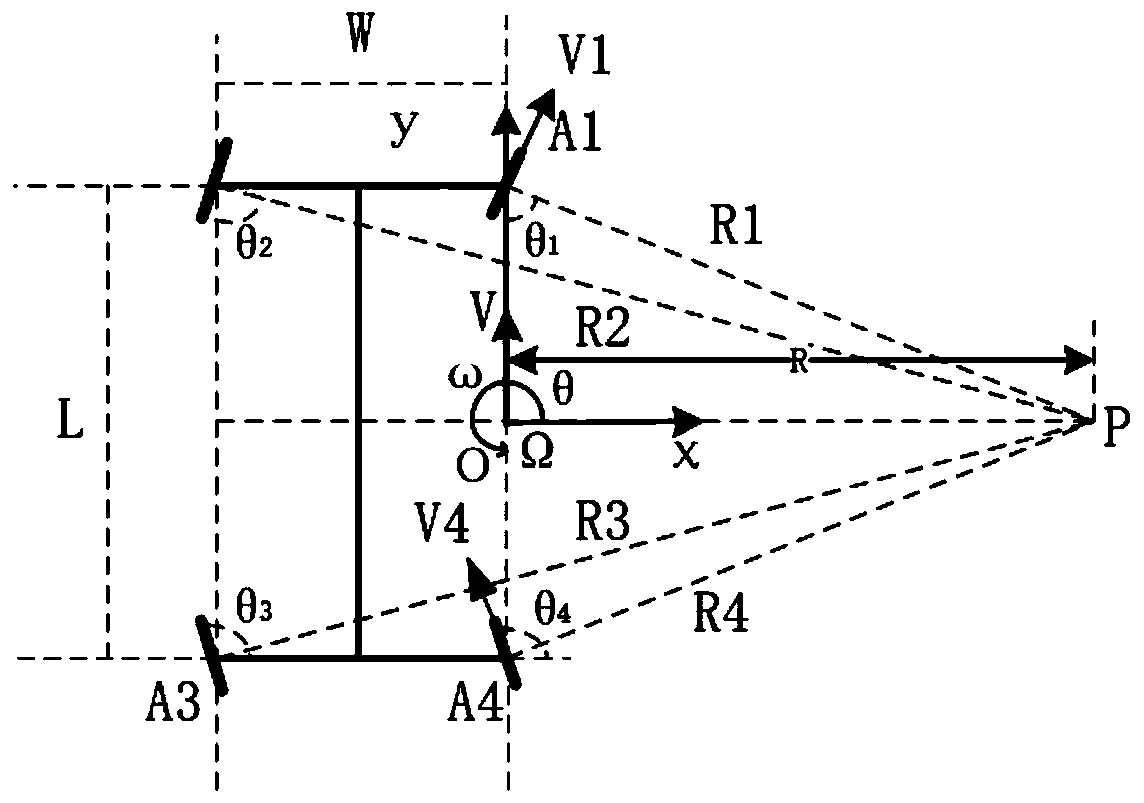
[0053] Refer to attached figure 2 As shown, the motion center Ω of the mobile robot is taken as the origin of the coordinate system, A1 and A4 are the steering wheels, A2 and A3 are the steering wheels, and the midpoint Ω between the two steering wheels A1 and A4 is used as the motion center of the mobile robot. The center of motion of the robot is planned to move at a speed of V, the angular velocity is ω, and the point P is used as the center of rotation of the mobile robot to perform steering motion, where the...
example B
[0072] Take a mobile robot with a wheel train structure composed of two steering wheels and two steering wheels as an example, in which the two steering wheels are the main control unit, and the two steering wheels assist in controlling the direction. Specifically, the double steering wheels are arranged diagonally, and the steering wheels are also Arranged in a diagonal line, the omnidirectional motion control method of the mobile robot in this way will be further described below.
[0073] Refer to attached Figure 6 As shown, the motion center Ω of the mobile robot is taken as the origin of the coordinate system, A1 and A3 are the steering wheels, A2 and A4 are the steering wheels, and the midpoint Ω between the two steering wheels A1 and A3 is used as the motion center of the mobile robot. The center of motion of the robot is planned to move at a speed of V, the angular velocity is ω, and the point P is used as the center of rotation of the mobile robot to perform steering ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com