Composition for promoting stem cell activity, comprising histone deacetylase inhibitor and priming factor as active ingredients
An acetylase inhibitor and deacetylase technology, which is applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, cell culture active agents, anhydride/acid/halide active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of failure to completely remove activating factors, Low implantation in the body and other issues, to improve activity and promote cell movement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example
[0069] The following experimental examples are experimental examples that can be commonly applied to various embodiments according to the present invention.
[0070] 1. Culture of MSCs derived from human umbilical cord
[0071] Human umbilical cords (UC) were obtained from healthy and normal full-term newborns according to guidelines recognized by the Theory of Life Review Committee at Asan Hospital, Korea, after obtaining written consent from their parents. Consent was obtained from all mothers prior to obtaining UC. Umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-derived MSCs, UC-MSCs) using low-glucose Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) (HyClone, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania (HyClone, Pittsburgh, PA )), at 5% CO 2 The culture was carried out under the conditions of 37°C and 2mM L-glutamine, 20mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (4-(2-hydroxyethyl )-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid, HEPES) (pH 7.3), minimum-essential medium (minimum-essential medium, MEM), non-essenti...
Embodiment 1
[0095] The influence of 5-Aza in the human UC-MSCs activation based on S1P
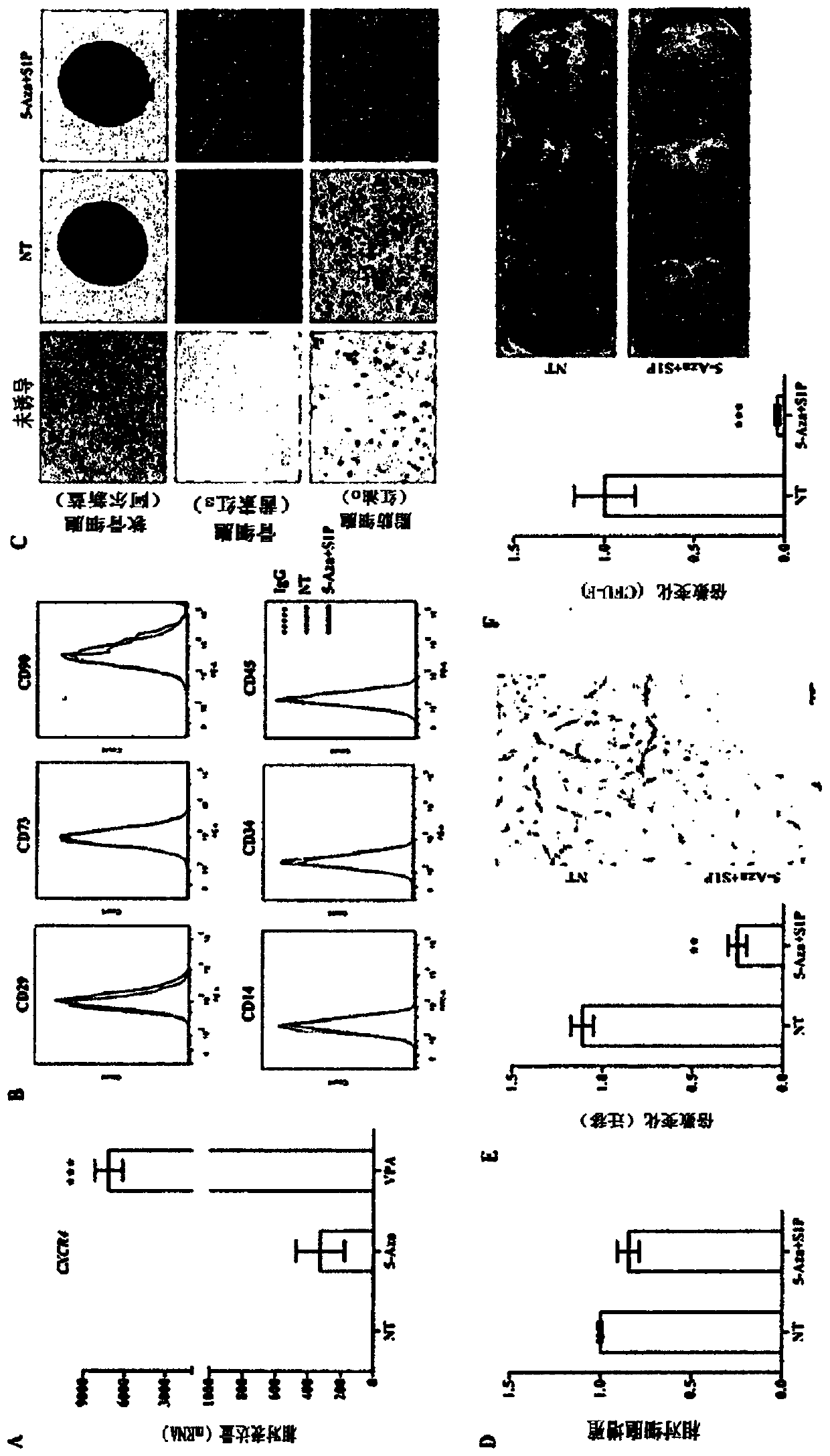
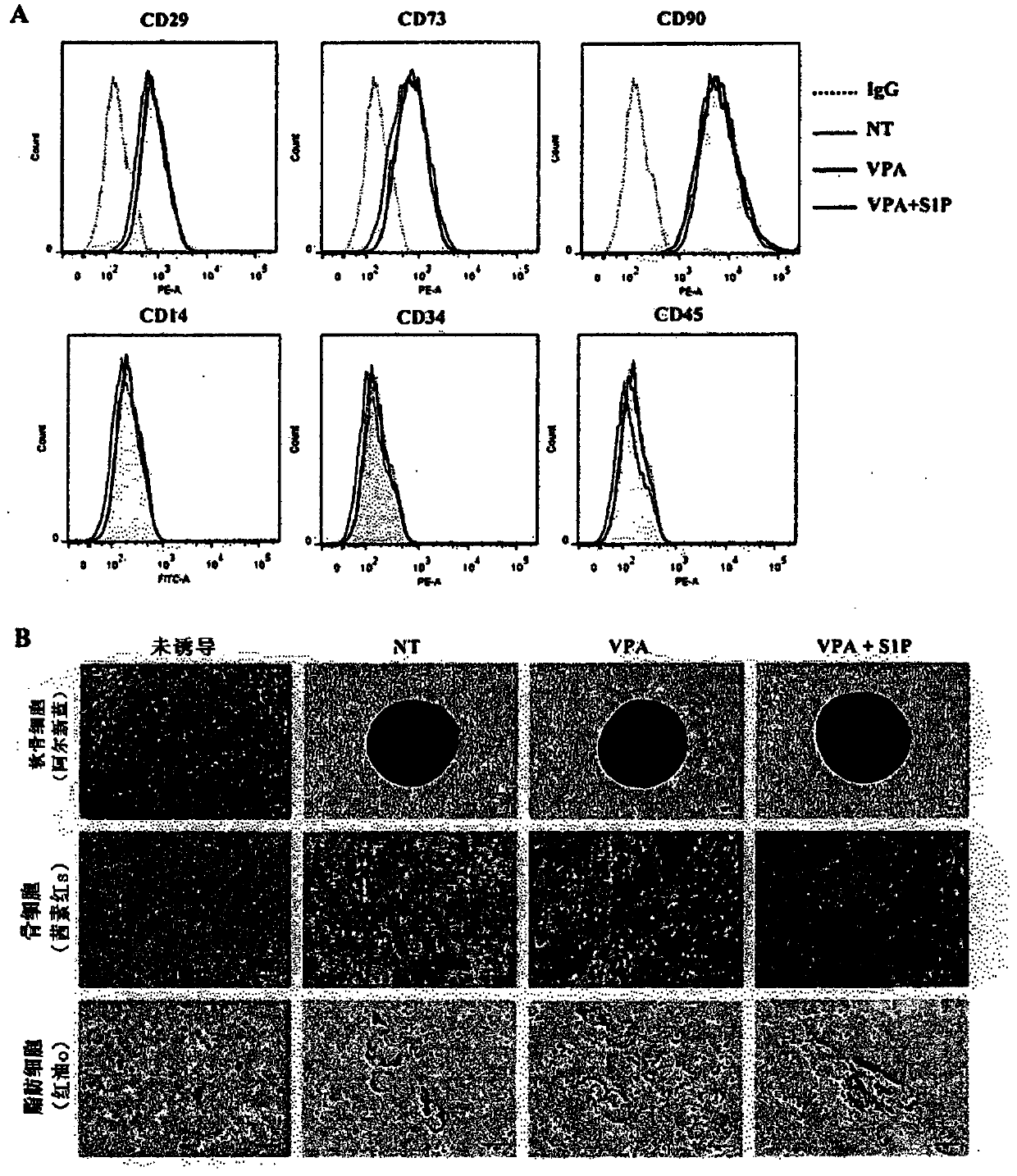
[0096] Low concentration treatment of 5-Aza and VPA ((1 μM and 0.5mM) significantly increased the expression of CXCR4 in UC-MSCs ( figure 1 A). Next, the present inventors confirmed the effects of the above-mentioned epigenetic regulators on the basic characteristics of UC-MSCs. Unlike the activation of S1P at 50 nM, neither 5-Aza nor VPA had much effect on the expression of surface marker proteins (positive for CD29, CD73 and CD90, negative for CD34 and CD45) (see figure 1 B and figure 2 A). Moreover, the activation of S1P treated together with 5-Aza (5-Aza+S1P) or VPA (VPA+S1P) hardly affected the multisystem differentiation ability, for which glycosaminoglycans (glycosaminoglycans; Al New blue (Alcian blue)), mineral deposition (mineral deposition; Alizarine Red S (Alizarine Red S)) and lipid accumulation (lipidaccumulation; Oil red O staining (Oil red O staining)) increased degree, which w...
Embodiment 2
[0098] When treated with low concentration of S1P, it can strengthen the VPA activated by UC-MSCs
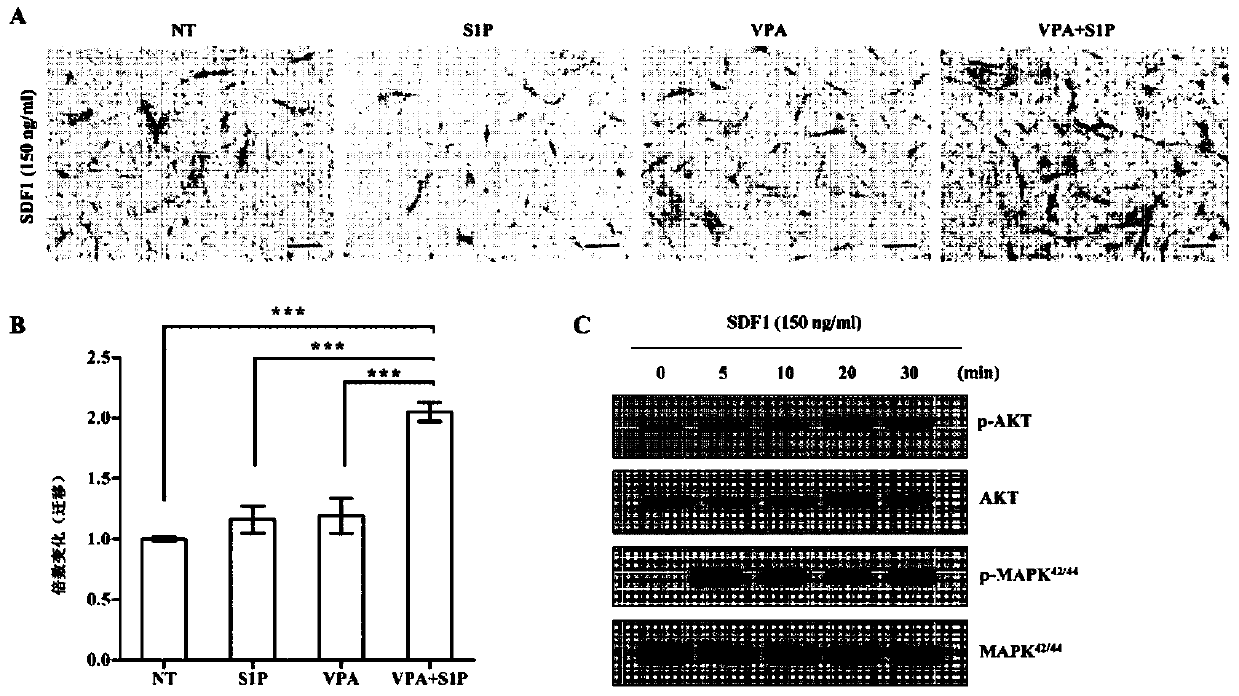
[0099]Next, the inventors examined the effect of VPA on the activation of UC-MSCs when treated with low concentrations of S1P. To this end, the inventors applied 50 nM of S1P, which is 4 times smaller than the optimal amount (200 nM) used for activation of adipose and UCB derived MSCs. Different from VPA alone treatment and S1P alone treatment, the activation of UC-MSCs under VPA+S1P treatment increased the chemotactic activity to SDF-1, which increased 2-3 times compared with unactivated cells ( image 3 A and image 3 B). The enhanced response to SDF-1 based on VPA+S1P activation was completely different from that of 5-Aza+S1P activation. Next, the present inventors confirmed the status of signaling pathways involved in the movement of HSPCs. Consistent with the chemotaxis analysis results, UC-MSCs exposed to VPA+S1P increased MAPK p42 / 44 and AKT protein phosphorylation,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com