Geometric modeling method for soybean seeds
A technology of geometric modeling and grain, applied in the field of mathematical modeling and analysis of soybean grain, can solve problems such as consumption, complex algorithm, long time, etc., and achieve the effect of improving simulation calculation efficiency, high accuracy and strong pertinence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0104] Experimental Example 1: Using the geometric modeling method provided by the present invention to create a three-dimensional five-sphere combination ball model of Suinong No. 42 soybean grains, wherein the average spherical rate of Suinong No. 42 soybean grains is 0.95;
[0105] Step 1. Randomly select 200 Suinong 42 soybean grains with good appearance, measure their three-axis dimensions with a digital display vernier caliper, and obtain the average value of each characteristic dimension;
[0106] Step 2, according to the average value of each feature size in step 1, determine the three-axis size of the corresponding ellipsoid,
[0107] With the geometric center of the corresponding ellipsoid as the coordinate origin, find the coordinates of each vertex of the ellipsoid:
[0108] (0,0,7.44), (0,0,-7.44), (0,7.24,0), (0,-7.24,0), (6.51,0,0), (-6.51,0,0)
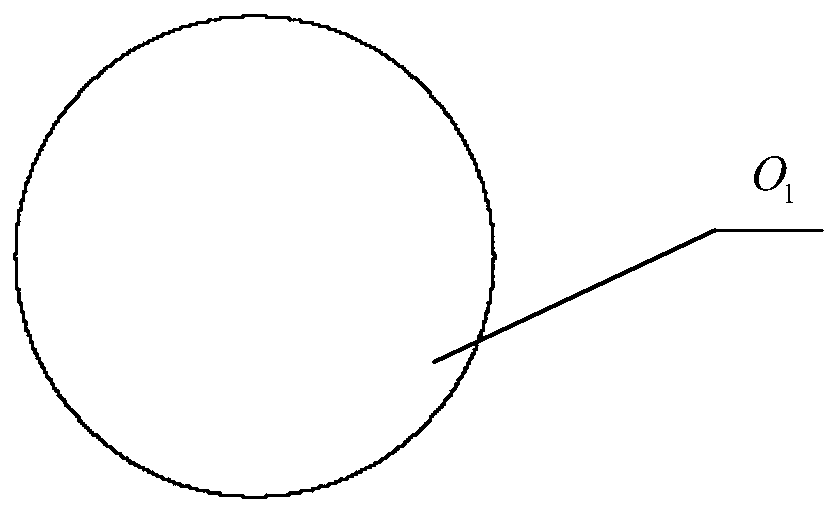
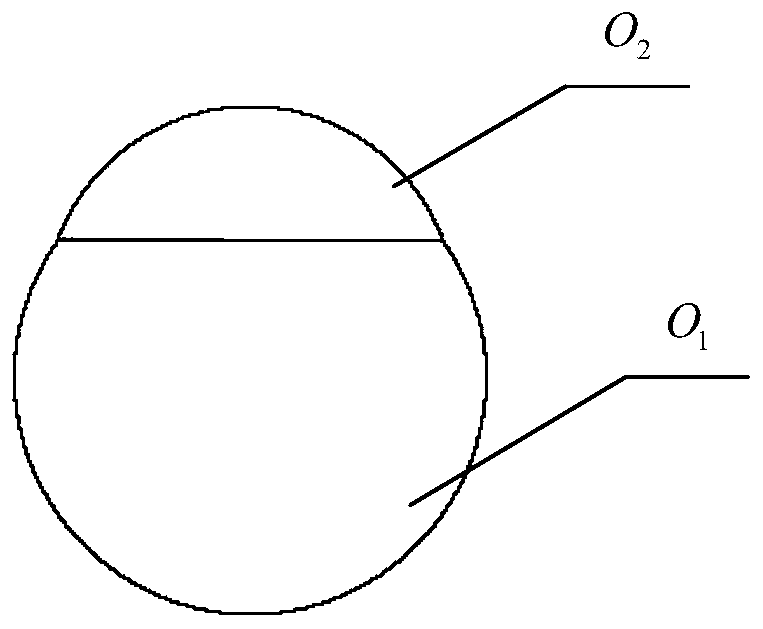
[0109] Taking the coordinate origin (0,0,0) of the soybean grain model as the center, fill the first ball O with a r...
experiment example 2
[0112] Experimental example 2: use the present invention to create a three-dimensional nine-ball combination ball model of Jidou 17 (spherical rate 0.87):
[0113] Step 1, randomly select 200 Jidou 17 soybean grains with good appearance, measure their three-axis dimensions with a digital display vernier caliper, and obtain the average value of each characteristic dimension;
[0114] Step 2 is to determine the three-axis size of the corresponding ellipsoid according to the average value of each characteristic size in step 1, and take the geometric center of the corresponding ellipsoid as the coordinate origin to obtain the coordinates of each vertex of the ellipsoid,
[0115]
[0116] (0,0,6.96), (0,0,-6.96), (0,6.2,0), (0,-6.2,0), (5.1,0,0), (-5.1,0,0)
[0117] Step 3, fill according to the combination of five balls: take the coordinate origin (0,0,0) of the soybean grain model as the center, fill the first ball O with a radius of 2.56 in the soybean grain model 1 ;
[01...
experiment example 3
[0121] Experimental example 3: Using the present invention to create a three-dimensional thirteen-ball combination ball model of Zhongdou 39, the spherical rate is 0.81;
[0122] Step 1, randomly select 200 Zhongdou 39 soybean grains with good appearance, measure their three-axis dimensions with a digital display vernier caliper, and obtain the average value of the characteristic dimensions;
[0123]
[0124] Step 2, according to the average value of each feature size in step 1, determine the three-axis size of the corresponding ellipsoid, take the geometric center of the corresponding ellipsoid as the coordinate origin, and obtain the coordinates of each vertex of the ellipsoid,
[0125] (0,0,7.36), (0,0,-7.36), (0,6,0), (0,-6,0), (4.73,0,0), (-4.73,0,0)
[0126] Step 3, fill according to the combination of five balls: take the coordinate origin (0,0,0) of the soybean grain model as the center, fill the first ball O with a radius of 2.365 in the soybean grain model 1 ;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com