Cross-domain image classification method based on coupling knowledge migration
A classification method and image technology, applied in the field of cross-domain image classification based on coupled knowledge transfer, can solve the problems of long calculation time and insufficient classification accuracy, and achieve the effect of accurate classification and reduction of differences.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
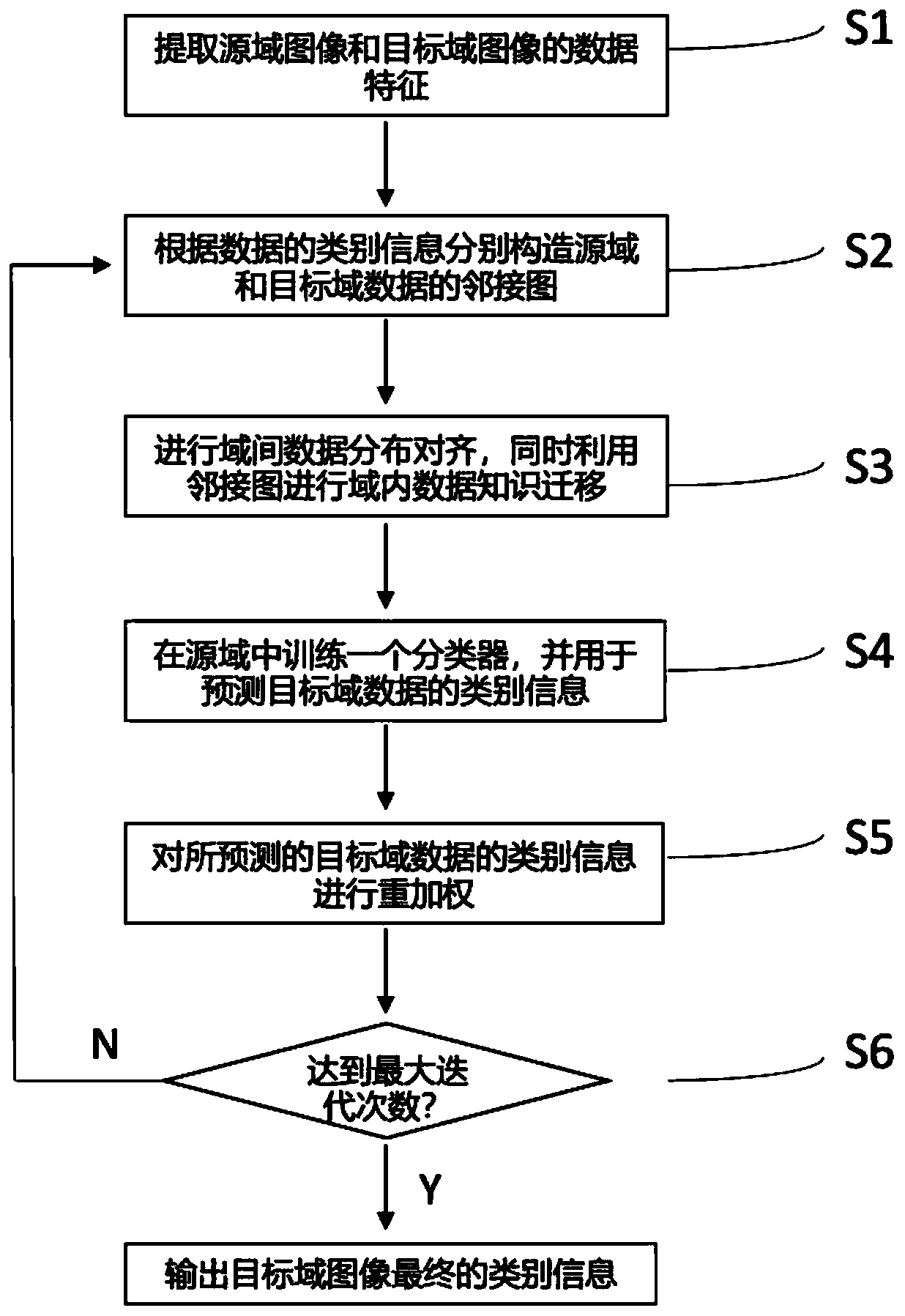
[0063] A cross-domain image classification method based on coupled knowledge transfer, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0064] S1. Obtain the source domain image and the target domain image and perform feature extraction, respectively obtain the source domain feature matrix as the source domain data, and obtain the target domain feature matrix as the target domain data:
[0065] S1.1. Input n s labeled source domain images and n t unlabeled target domain images; where n s , n t is a positive integer;
[0066] S1.2. Feature extraction is performed on the source domain image and the target domain image respectively, and the feature vectors of the source domain image and the target domain image are respectively extracted by any of the pre-trained VGG16, GoogLeNe, and ResNet50 neural networks, and the The feature vectors obtained by extracting the source domain image are arranged in columns to obtain the source domain data feature matrix where m is t...
Embodiment 2
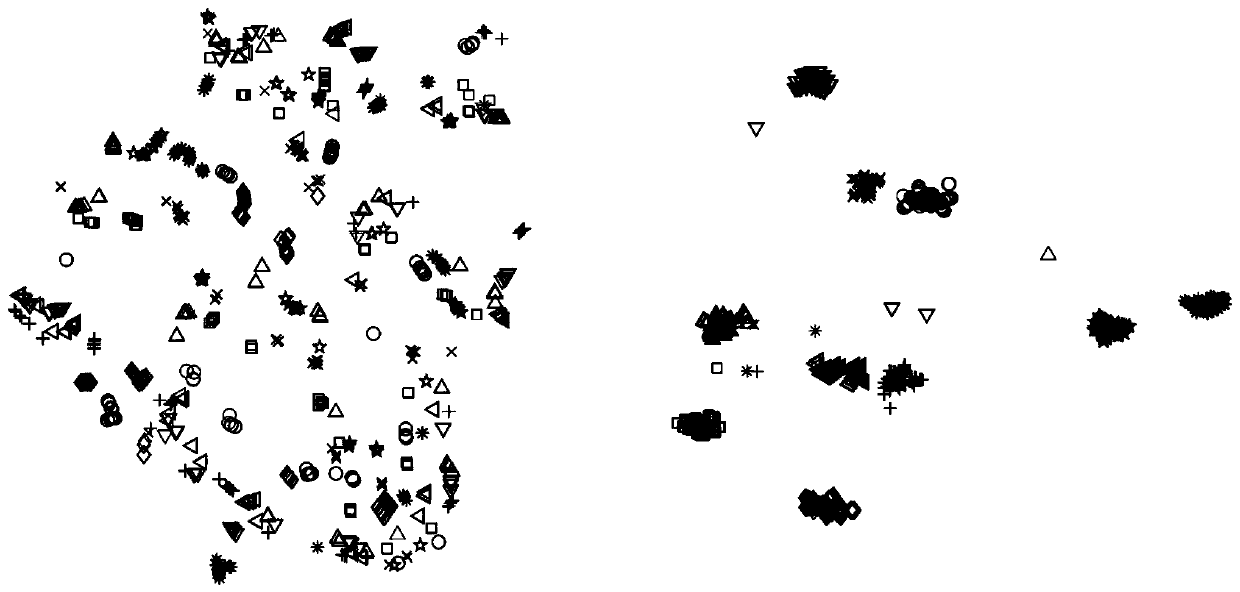
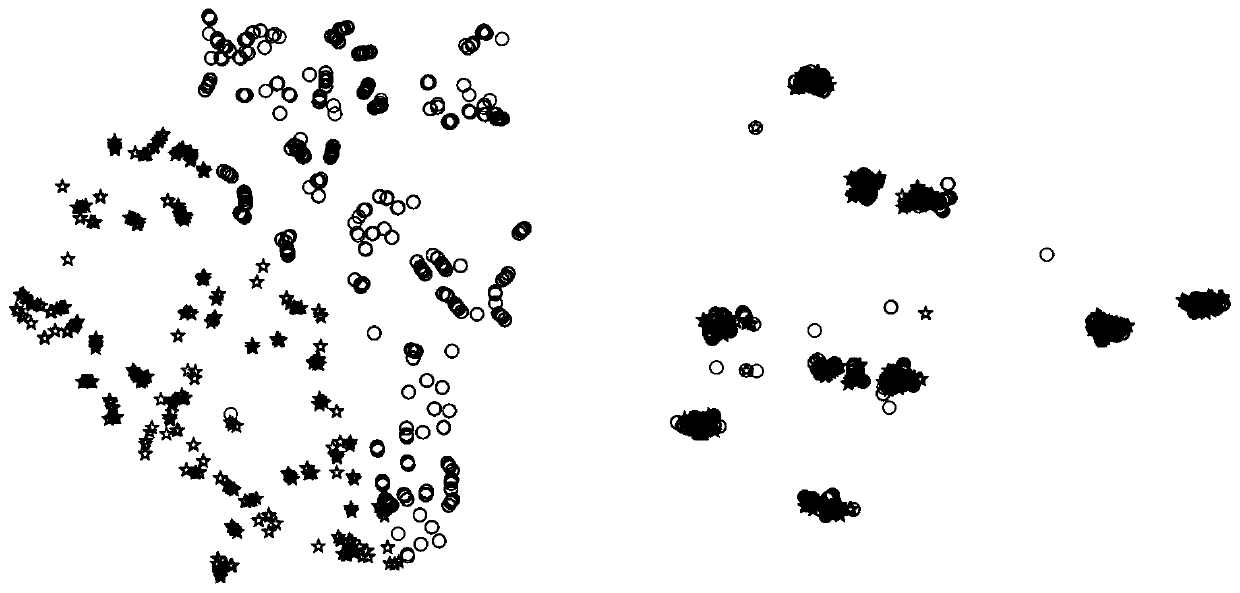
[0096] In Example 2, 980 face images composed of 10 people's face images randomly selected from the CMU PIE data set were selected, and each image was cropped to a resolution of 32×32. Further, a total of 490 images of the C05 subset are used as the source domain dataset, and a total of 490 images of the C27 subset are used as the target domain dataset to be classified.
[0097] S1. Acquire the source domain image in the source domain data set and the target domain image in the target domain data set, grayscale the source domain image and the target domain image respectively, and arrange the grayscale values of the source domain image into The feature vector and the gray value of the target domain image are arranged into a feature vector. In this embodiment 2, the gray value of each image is arranged into a feature vector, that is, each image is represented as a 1024-dimensional column vector, Correspondingly, the feature matrix of the source domain data can be obtained by a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com