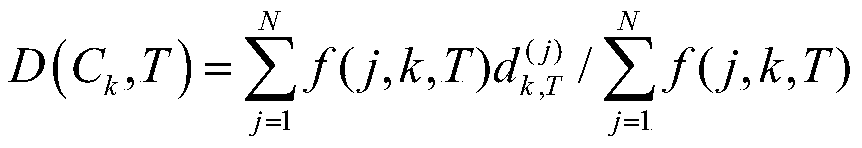Differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method
A differential evolution, protein technology, applied to the analysis of two-dimensional or three-dimensional molecular structures, instruments, computational models, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
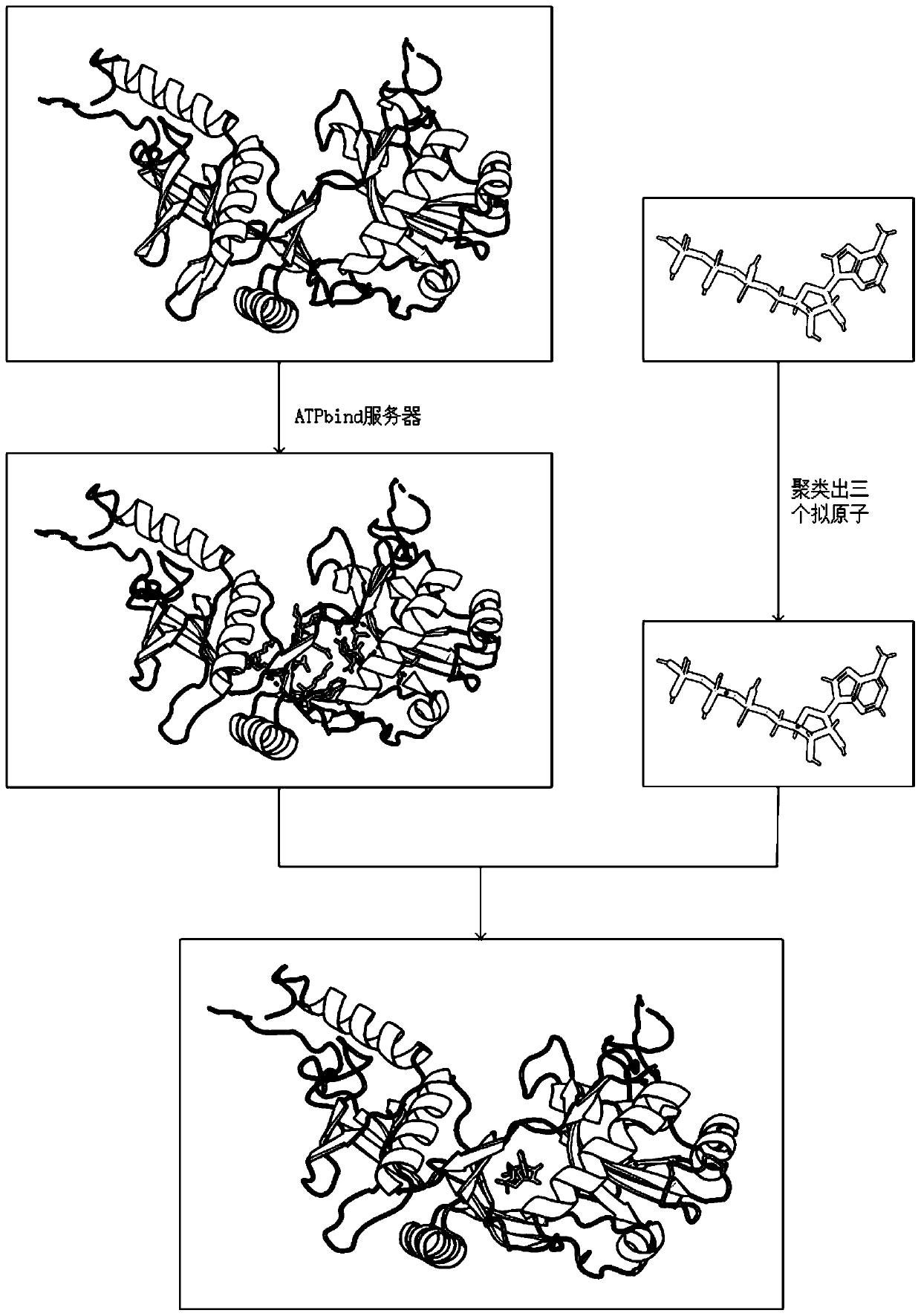
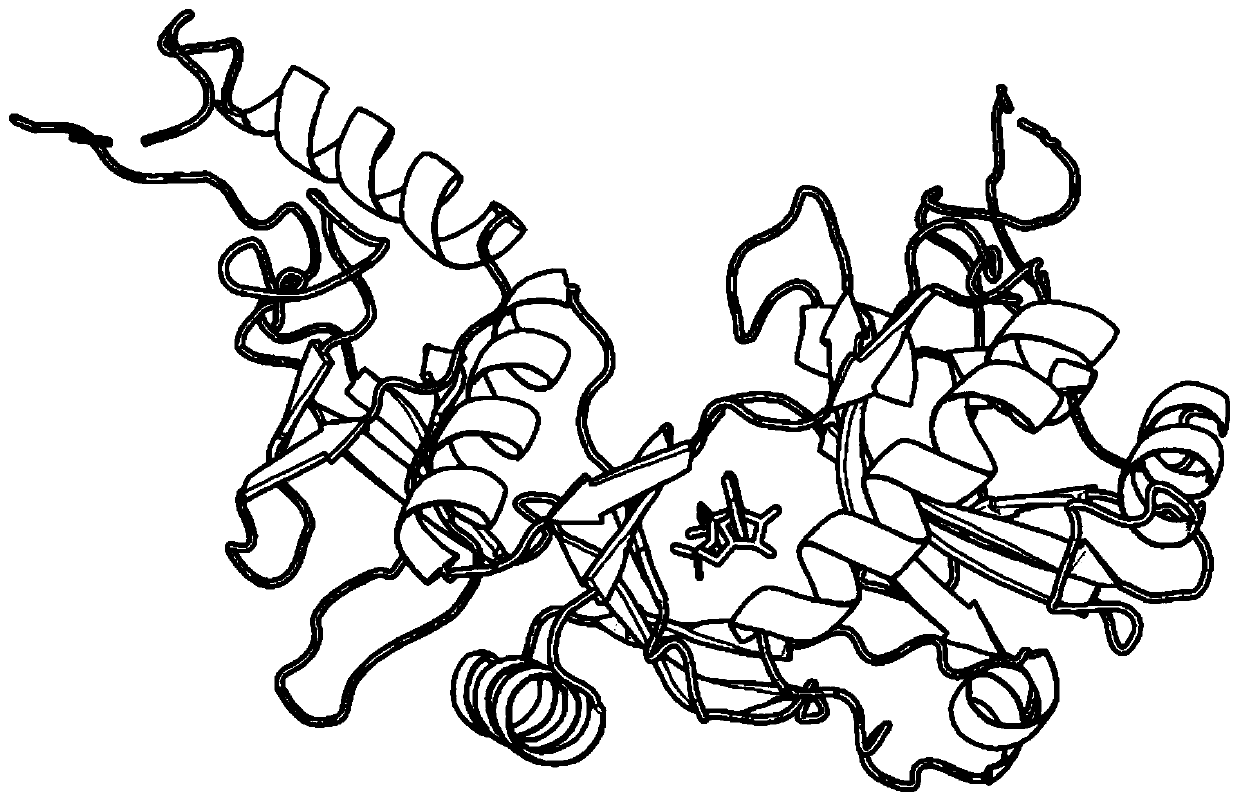
[0045] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , a method for docking proteins and ATP based on differential evolution, comprising the following steps:
[0046] 1) Input the structural information of protein and ATP, denoted as R and A respectively;
[0047] 2) For the input structure information R, use the ATPbind server (https: / / zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu / ATPbind / ) to predict the residue site information of protein-ATP binding, and obtain the protein-ATP binding residue site information The given n residues are denoted as r 1 ,r 2 ,...,r n ;
[0048] 3) According to r 1 ,r 2 ,...,r n The central carbon atom C α Coordinate information clusters a center point C R , according to the coordinate information of each atom in A, a center point C is clustered A , moving ATP such that C A and C R The coordinates of these two points coincide;
[0049] 4) According to th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com