Magnesium Addition Technology for Free Cutting Steel Containing Magnesium
A technology of free-cutting steel and process method, which is applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy to achieve the effects of good inclusion shape, stable wire feeding process and excellent cutting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
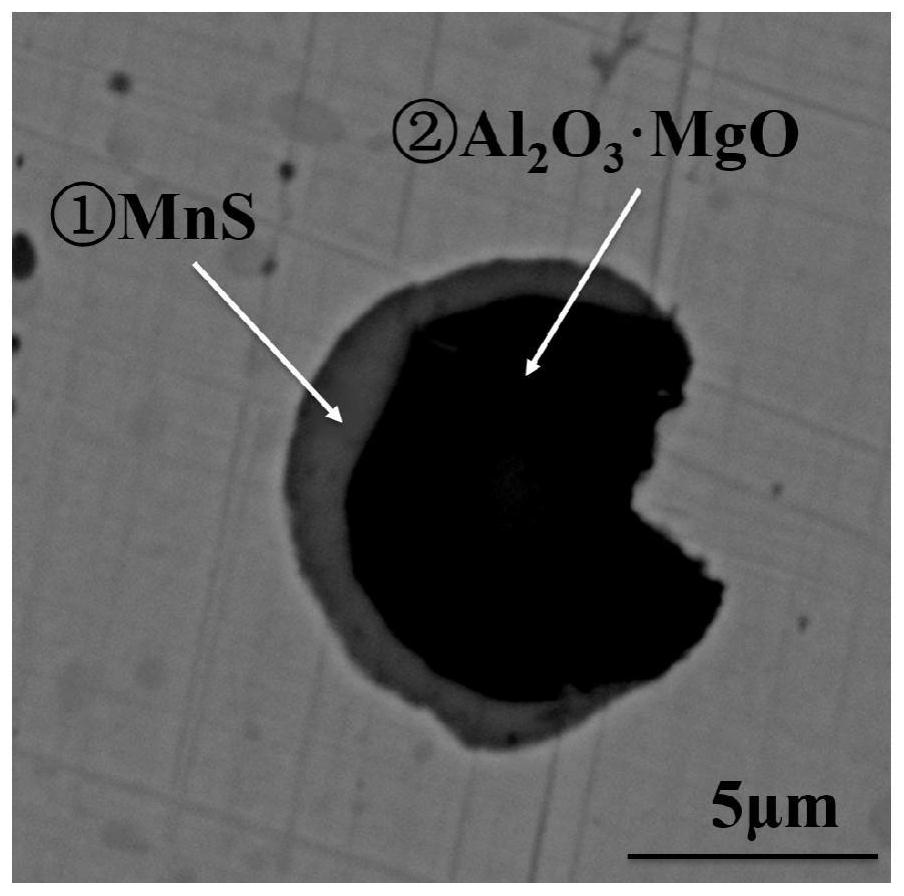
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] In this example, a magnesium addition process method for free-cutting steel containing magnesium, the production process of free-cutting stainless steel containing magnesium is electric furnace → AOD → LF → wire feeding → continuous casting → rolling, and the molten steel measured at the end of refining The composition is C: 0.13%, Si: 0.36%, Mn: 1.10%, P: 0.02%, S: 0.28%, Cr: 12.75%, Ni: 13.22%, the balance is iron and unavoidable trace elements, molten steel The composition meets the requirements of the free-cutting steel grade. At the end of molten steel refining, after the adjustment of other components except magnesium is completed, the process of adding magnesium-containing cored wire to the wire is carried out to prepare the target magnesium-containing free-cutting steel. Its feeding line adding process method comprises the following steps:
[0056] a. Control the production conditions before feeding the line, mainly to control the molten steel slag layer, temper...
Embodiment 2
[0074] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0075] In this example, a magnesium addition process method for free-cutting steel containing magnesium, the production process of free-cutting stainless steel containing magnesium is electric furnace → AOD → LF → wire feeding → continuous casting → rolling, and the molten steel measured at the end of refining The composition is C: 0.13%, Si: 0.36%, Mn: 1.10%, P: 0.02%, S: 0.28%, Cr: 17.65%, Ni: 12.84%, the balance is iron and unavoidable trace elements, molten steel The composition meets the requirements of the free-cutting steel grade. At the end of molten steel refining, after the adjustment of other components except magnesium is completed, the process of adding magnesium-containing cored wire to the wire is carried out to prepare the target magnesium-containing free-cutting steel. Its feeding line adding process method comprises the following steps:
[0076] a. Control the production cond...
Embodiment 3
[0094] This embodiment is basically the same as the previous embodiment, and the special features are:
[0095] In this example, a magnesium addition process method for free-cutting steel containing magnesium, the production process of free-cutting stainless steel containing magnesium is electric furnace → AOD → LF → wire feeding → continuous casting → rolling, and the molten steel measured at the end of refining The composition is: C: 0.15%, Si: 1.00%, Mn: 1.20%, P: 0.09%, S: 0.35%, Cr: 19.0%, Ni: 14.0%, the balance is iron and unavoidable trace elements, steel The composition of the liquid meets the requirements of the free-cutting steel grade. At the end of molten steel refining, after the adjustment of other components except magnesium is completed, the process of adding magnesium-containing cored wire to the wire is carried out to prepare the target free-cutting steel containing magnesium. , its feeding line adding process method comprises the steps:
[0096] a. Control ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com