Method for reducing water eutrophication by chlorella culture
A technology for eutrophication and chlorella in water body, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of complex phytoplankton community structure, etc. The effect of promoting chlorophyll and bacterial protein accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
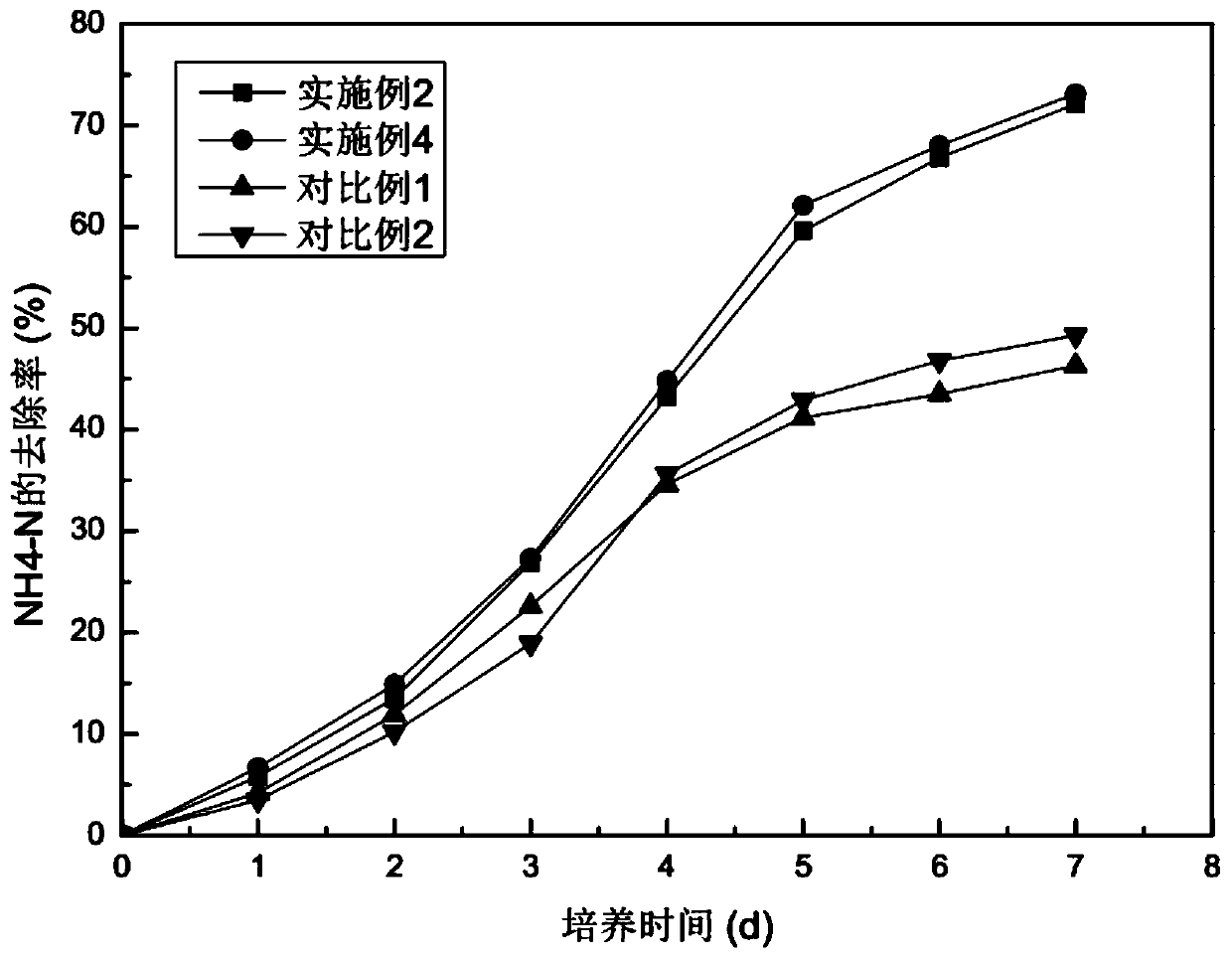
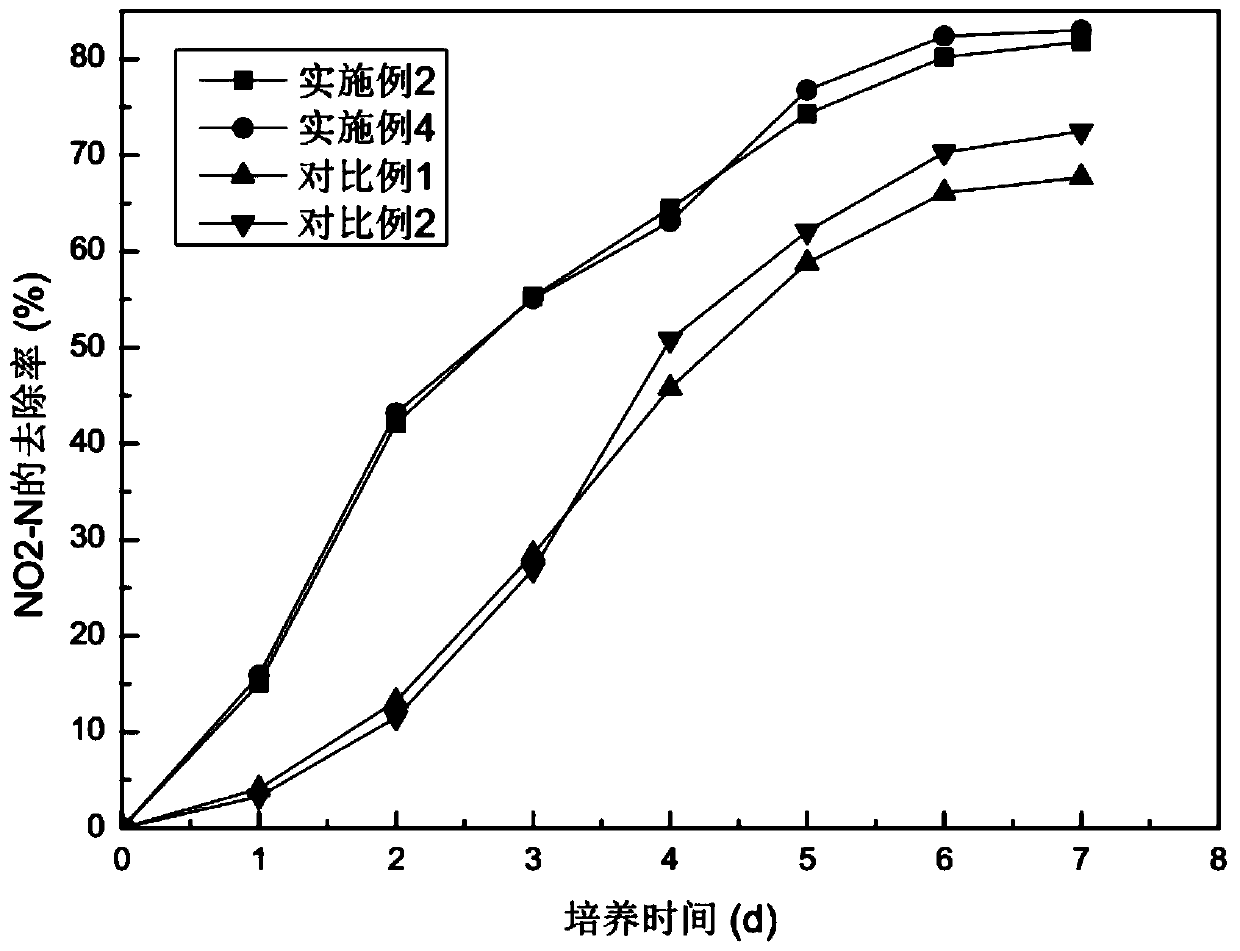
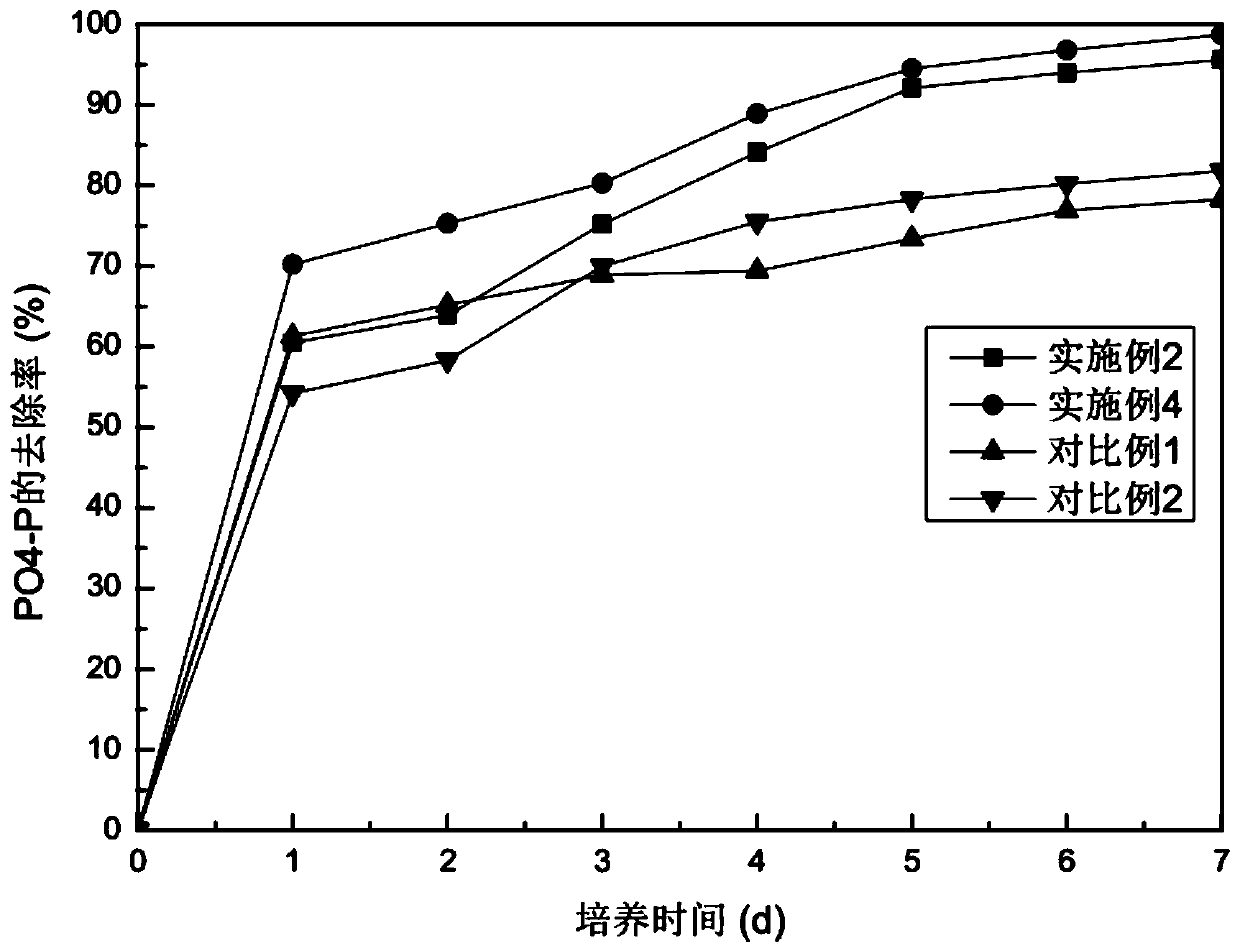
[0033] A method for domesticating chlorella, exposing the chlorella to intense pulsed light radiation during the domestication process. The method for acclimating Chlorella is as follows: inoculate algae cells in nutrient-rich water according to 5% of the working volume, and cultivate them for 3 days at a temperature of 20°C, a light intensity of 2000Lux, and a light-dark ratio of 12h:12h after being irradiated by intense pulsed light. After five batches of heterotrophic domestication, the heterotrophic domesticated algae are separated and purified to obtain the domesticated chlorella. Chlorella has good nitrogen and phosphorus removal ability and pollution resistance, high growth rate, and can be used as the dominant algal species for nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
[0034] Wherein, the wavelength of the intense pulsed optical radiation is 570nm, the pulse duration is 3ms, and the pulse delay is 20ms. The photothermolysis and photochemical effects of intense pulsed light r...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A method for domesticating Chlorella is as follows: inoculate algae cells in nutrient-rich water according to 10% of the working volume, and irradiate with intense pulsed light with a wavelength of 600nm, a pulse duration of 3.5ms, and a pulse delay of 30ms The temperature was 27°C, the light intensity was 2600 Lux, and the light-dark ratio was 12h:12h and cultured for 3.5 days. After 6 batches of heterotrophic domestication, the heterotrophic domesticated algae were separated and purified to obtain the domesticated Chlorella.
[0043] A method for reducing eutrophication in water bodies by using chlorella culture, using the domesticated chlorella obtained by the method for domesticating chlorella. Methods to reduce eutrophication in water bodies include,
[0044] 1) The nutrient-rich water body is pretreated by adding a flocculant, the dosage of the flocculant is 0.85g / L, and the flocculant is medical stone flocculant;
[0045] 2) Put the domesticated chlorella into t...
Embodiment 3
[0048] A method for domesticating Chlorella is as follows: inoculate algae cells in nutrient-rich water body according to 15% of the working volume, irradiate with intense pulsed light with a wavelength of 640nm, a pulse duration of 4ms, and a pulse delay of 40ms. The temperature was 30°C, the light intensity was 3000 Lux, and the light-to-dark ratio was 12h:12h and cultured for 4 days. After 8 batches of heterotrophic domestication, the heterotrophic domesticated algae were separated and purified to obtain the domesticated Chlorella.
[0049] A method for reducing eutrophication in water bodies by using chlorella culture, using the domesticated chlorella obtained by the method for domesticating chlorella. Methods to reduce eutrophication in water bodies include,
[0050] 1) The nutrient-rich water body is pretreated by adding a flocculant, the dosage of the flocculant is 1.0g / L, and the flocculant is medical stone flocculant;
[0051] 2) Put the domesticated chlorella into t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com