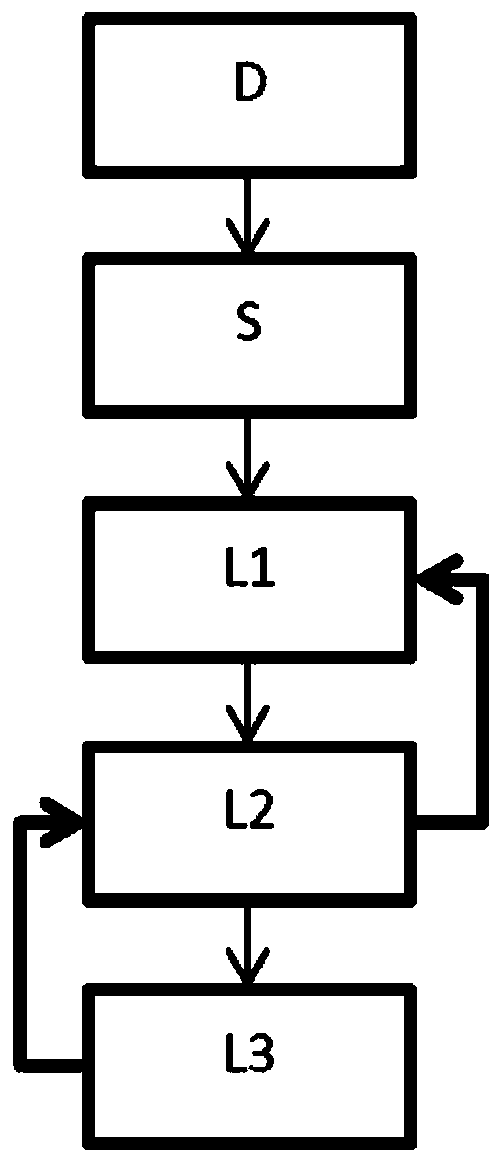
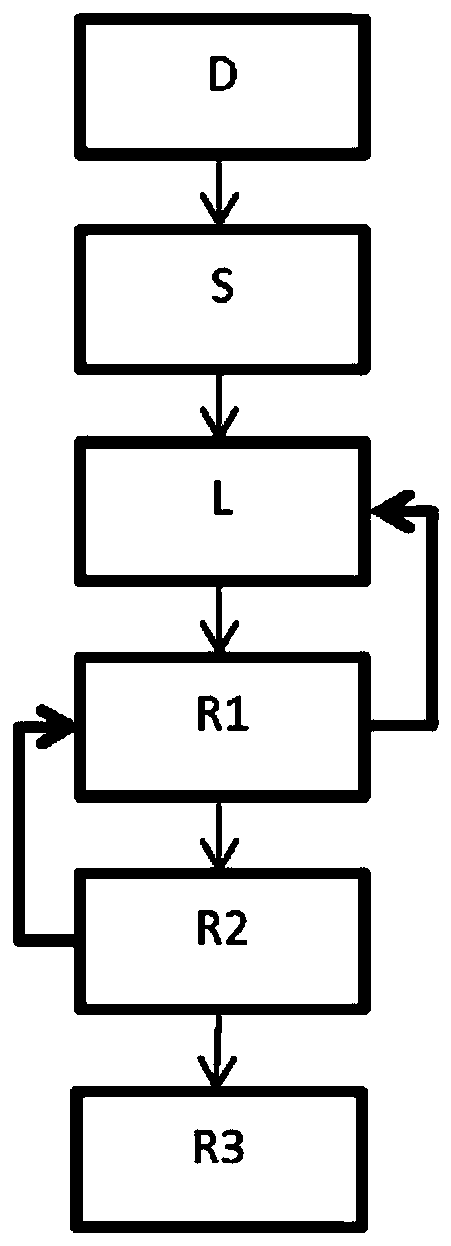
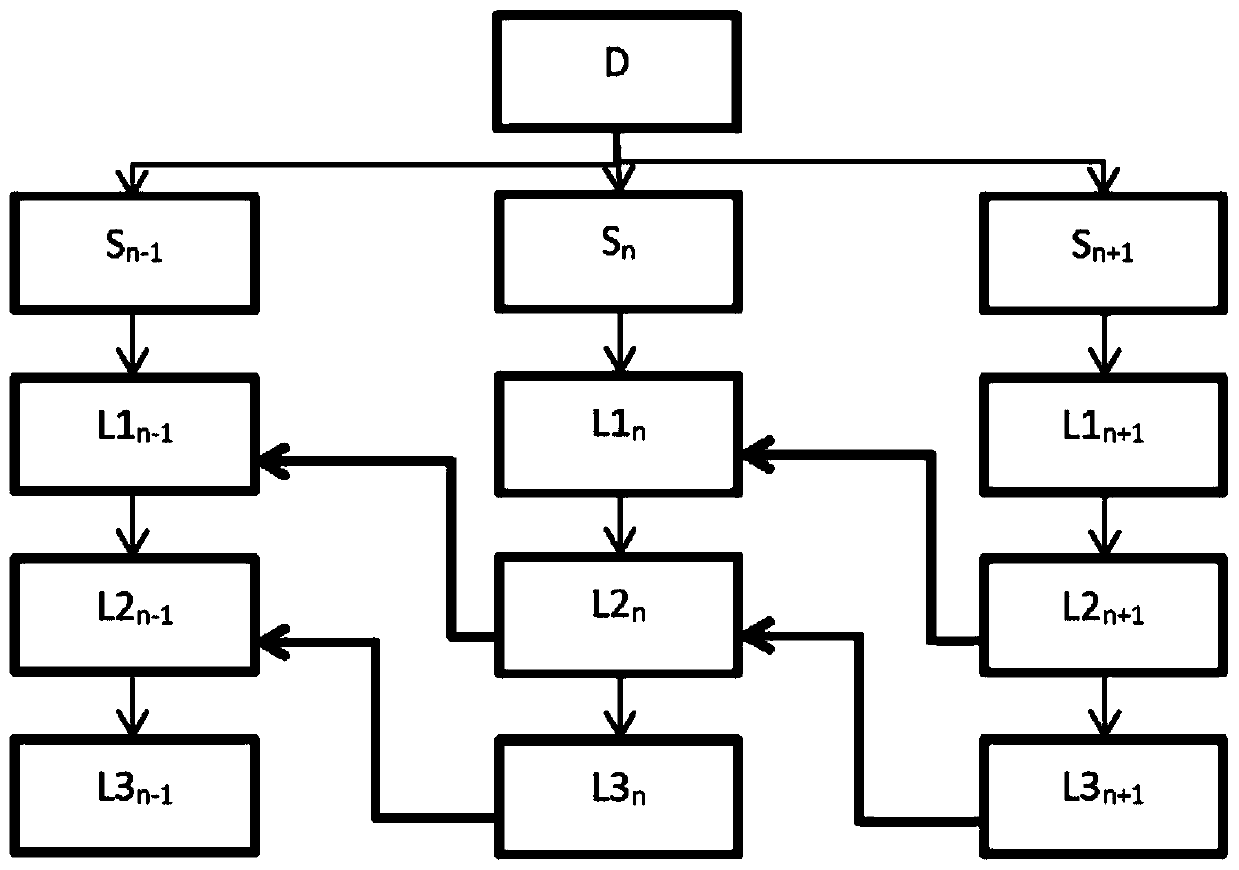
Purification method using a low granulometry resin
A resin and resin regeneration technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, purification using ion exchange materials, separation methods, etc., can solve the problem of high regenerant and achieve the effect of reducing productivity and permeability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] In this example, a loading of 100 BV (or resin bed volume equivalent) consisting of syrup with 60% dry matter and 545 ICUMSA unit color was used. The resin used was a strong anionic resin in the chloride form (FPA90RF Cl from The Dow Chemical Company).
[0164] In test N°1, a raw resin with a porosity between 500 and 800 μm was contacted with syrup in a 400 mL beaker, thermostated at 60° C. and stirred with a magnetic stirring bar.
[0165] In test N° 2, the resin was preground to a particle size of 100 to 500 μm. The contacting with the syrup was carried out in the same manner as in Test N°1.
[0166] In test N°3, the resin was preground to a particle size of 80 to 100 μm. The contacting with the syrup was carried out in the same manner as in Test N°1.
[0167] In test N°4, the resin was preground to a particle size of 35 to 80 μm. The contacting with the syrup was carried out in the same manner as in Test N°1.
[0168] The evolution of syrup color was measured by...
Embodiment 2
[0171] In this example, a load of 300 BV, larger than in Example 1, consisting of syrup with 60% dry matter and 545 ICUMSA units of color was used. The resin used was FPA90RF Cl resin as in Example 1.
[0172] In test N°1, a raw resin with a porosity between 500 and 800 μm was contacted with syrup in a 400 mL beaker, thermostated at 60° C. and stirred with a magnetic stirring bar.
[0173] In test N°2, the resin was preground to a particle size of 80 to 100 μm. The contacting with the syrup was carried out in the same manner as in Test N°1.
[0174] In test N°3, the resin was preground to a particle size of 35 to 80 μm. The contacting with the syrup was carried out in the same manner as in Test N°1.
[0175] The evolution of syrup color was measured by taking samples over time. result in Figure 10 Given in , as indicated by the box text, each curve corresponds to one of the above trials.
[0176] According to these results, approximately 50% decolorization of a 300 BV l...
Embodiment 3
[0180] In this example, experiments were performed on a chromatographic column.
[0181] Using a column with a diameter of 1 cm and a height of 4 cm, the resin volume is 3.14 mL. The adsorption step (test N°1) was carried out by passing a volume of 180 BV of colored syrup through a bed of resin. The resin used was that of Example 1, ground to a particle size of 80 to 100 μm.
[0182] Measure the color of the decolorized syrup at the outlet of the column. result in Figure 11 Given in , the curve N°1 of the solid line represents the instantaneous decolorization rate, and the curve N°1 of the dashed line represents the average decolorization rate.
[0183] After the adsorption step, a washing step is performed by passing 2Bv volumes of water; then a regeneration step is performed by passing 1.8BV volumes of regeneration solution (10% NaCl + 1% NaOH); then 5BV demineralized water Rinse step. Each step lasts 40 to 90 minutes.
[0184] Another adsorption (test N° 2) was carri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com